A bacterial type III secretion system inhibits actin polymerization to prevent pore formation in host cell membranes
- PMID: 11574469
- PMCID: PMC125656
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.19.5373
A bacterial type III secretion system inhibits actin polymerization to prevent pore formation in host cell membranes
Abstract
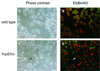
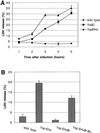
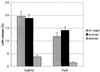
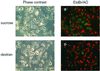
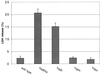
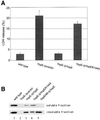
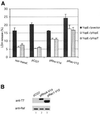
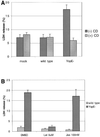
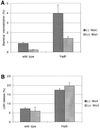
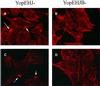
The bacterial pathogen Yersinia pseudotuberculosis uses type III secretion machinery to translocate Yop effector proteins through host cell plasma membranes. A current model suggests that a type III translocation channel is inserted into the plasma membrane, and if Yops are not present to fill the channel, the channel will form a pore. We examined the possibility that Yops act within the host cell to prevent pore formation. Yop- mutants of Y.pseudotuberculosis were assayed for pore-forming activity in HeLa cells. A YopE- mutant exhibited high levels of pore-forming activity. The GTPase-downregulating function of YopE was required to prevent pore formation. YopE+ bacteria had increased pore-forming activity when HeLa cells expressed activated Rho GTPases. Pore formation by YopE- bacteria required actin polymerization. F-actin was concentrated at sites of contact between HeLa cells and YopE- bacteria. The data suggest that localized actin polymerization, triggered by the type III machinery, results in pore formation in cells infected with YopE- bacteria. Thus, translocated YopE inhibits actin polymerization to prevent membane damage to cells infected with wild-type bacteria.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Yersinia controls type III effector delivery into host cells by modulating Rho activity.PLoS Pathog. 2008 Jan;4(1):e3. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0040003. PLoS Pathog. 2008. PMID: 18193942 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Yersinia Yop-effector delivery by translocated YopE.Int J Med Microbiol. 2008 Apr;298(3-4):183-92. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2007.04.007. Epub 2007 Jun 26. Int J Med Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 17597003
-
TyeA of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis is involved in regulation of Yop expression and is required for polarized translocation of Yop effectors.Cell Microbiol. 2003 Mar;5(3):187-202. doi: 10.1046/j.1462-5822.2003.00267.x. Cell Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12614462
-
Modulation of Rho GTPases and the actin cytoskeleton by Yersinia outer proteins (Yops).Int J Med Microbiol. 2001 Sep;291(4):269-76. doi: 10.1078/1438-4221-00130. Int J Med Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11680787 Review.
-
Modulation of Rho GTPases and the actin cytoskeleton by YopT of Yersinia.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2005;291:167-75. doi: 10.1007/3-540-27511-8_9. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15981463 Review.
Cited by
-
Visualization of translocons in Yersinia type III protein secretion machines during host cell infection.PLoS Pathog. 2018 Dec 26;14(12):e1007527. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007527. eCollection 2018 Dec. PLoS Pathog. 2018. PMID: 30586431 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced secretion of YopJ by Yersinia limits in vivo cell death but enhances bacterial virulence.PLoS Pathog. 2008 May 16;4(5):e1000067. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000067. PLoS Pathog. 2008. PMID: 18483548 Free PMC article.
-
Patterns of pathogenesis: discrimination of pathogenic and nonpathogenic microbes by the innate immune system.Cell Host Microbe. 2009 Jul 23;6(1):10-21. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2009.06.007. Cell Host Microbe. 2009. PMID: 19616762 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell-type-specific hypertranslocation of effectors by the Pseudomonas aeruginosa type III secretion system.Mol Microbiol. 2021 Feb;115(2):305-319. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14617. Epub 2020 Nov 5. Mol Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33012037 Free PMC article.
-
Random mutagenesis identifies a C-terminal region of YopD important for Yersinia type III secretion function.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 25;10(3):e0120471. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120471. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25807250 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Black D.S. and Bliska,J.B. (2000) The RhoGAP activity of the Yersinia pseudotuberculosis cytotoxin YopE is required for antiphagocytic function and virulence. Mol. Microbiol., 37, 515–527. - PubMed
-
- Bliska J.B. (2000) Yop effectors of Yersinia spp. and actin rearrangements. Trends Microbiol., 8, 205–208. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

