Delivery of the Cre recombinase by a self-deleting lentiviral vector: efficient gene targeting in vivo
- PMID: 11553794
- PMCID: PMC58750
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.201415498
Delivery of the Cre recombinase by a self-deleting lentiviral vector: efficient gene targeting in vivo
Abstract
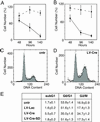
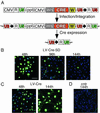
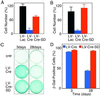
The Cre recombinase (Cre) from bacteriophage P1 is an important tool for genetic engineering in mammalian cells. We constructed lentiviral vectors that efficiently deliver Cre in vitro and in vivo. Surprisingly, we found a significant reduction in proliferation and an accumulation in the G(2)/M phase of Cre-expressing cells. To minimize the toxic effect of Cre, we designed a lentiviral vector that integrates into the host genome, expresses Cre in the target cell, and is subsequently deleted from the genome in a Cre-dependent manner. Thus, the activity of Cre terminates its own expression (self-deleting). We showed efficient modification of target genes in vitro and in the brain after transduction with the self-deleting vectors. In contrast to sustained Cre expression, transient expression of Cre from the self-deleting vector induced significantly less cytotoxicity. Such a self-deleting Cre vector is a promising tool for the induction of conditional gene modifications with minimal Cre toxicity in vivo.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Efficient in vitro and in vivo excision of floxed sequences with a high-capacity adenoviral vector expressing Cre recombinase.Genesis. 2002 Jul;33(3):119-24. doi: 10.1002/gene.10099. Genesis. 2002. PMID: 12124944
-
Genetic engineering of herpes simplex virus and vector genomes carrying loxP sites in cells expressing Cre recombinase.Virology. 2000 Feb 1;267(1):102-10. doi: 10.1006/viro.1999.0108. Virology. 2000. PMID: 10648187
-
Placenta-specific gene activation and inactivation using integrase-defective lentiviral vectors with the Cre/LoxP system.Genesis. 2009 Dec;47(12):793-8. doi: 10.1002/dvg.20563. Genesis. 2009. PMID: 19830817
-
[Modification of gene targeting method for functional analysis of the target gene in vivo].Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 1997 Feb;24(4):460-5. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 1997. PMID: 9063484 Review. Japanese.
-
Cre recombinase: the universal reagent for genome tailoring.Genesis. 2000 Feb;26(2):99-109. Genesis. 2000. PMID: 10686599 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Identification of astrocyte-expressed factors that modulate neural stem/progenitor cell differentiation.Stem Cells Dev. 2006 Jun;15(3):407-21. doi: 10.1089/scd.2006.15.407. Stem Cells Dev. 2006. PMID: 16846377 Free PMC article.
-
A Cre-lox approach for transient transgene expression in neural precursor cells and long-term tracking of their progeny in vitro and in vivo.BMC Dev Biol. 2007 May 15;7:45. doi: 10.1186/1471-213X-7-45. BMC Dev Biol. 2007. PMID: 17504531 Free PMC article.
-
Site-specific gene insertion mediated by a Cre-loxP-carrying lentiviral vector.Mol Ther. 2010 Oct;18(10):1814-21. doi: 10.1038/mt.2010.150. Epub 2010 Jul 13. Mol Ther. 2010. PMID: 20628360 Free PMC article.
-
An Animal Model for Chronic Meningeal Inflammation and Inflammatory Demyelination of the Cerebral Cortex.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 9;24(18):13893. doi: 10.3390/ijms241813893. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762198 Free PMC article.
-
Cre-Recombinase Induces Apoptosis and Cell Death in Enterocyte Organoids.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jul 26;11(8):1452. doi: 10.3390/antiox11081452. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35892654 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

