An essential role for ARF6-regulated membrane traffic in adherens junction turnover and epithelial cell migration
- PMID: 11532961
- PMCID: PMC125602
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.17.4973
An essential role for ARF6-regulated membrane traffic in adherens junction turnover and epithelial cell migration
Abstract
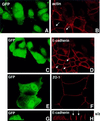
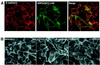
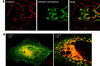
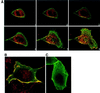
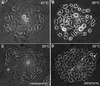
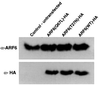
We describe a novel role for the ARF6 GTPase in the regulation of adherens junction (AJ) turnover in MDCK epithelial cells. Expression of a GTPase-defective ARF6 mutant, ARF6(Q67L), led to a loss of AJs and ruffling of the lateral plasma membrane via mechanisms that were mutually exclusive. ARF6-GTP-induced AJ disassembly did not require actin remodeling, but was dependent on the internalization of E-cadherin into the cytoplasm via vesicle transport. ARF6 activation was accompanied by increased migratory potential, and treatment of cells with hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) induced the activation of endogenous ARF6. The effect of ARF6(Q67L) on AJs was specific since ARF6 activation did not perturb tight junction assembly or cell polarity. In contrast, dominant-negative ARF6, ARF6(T27N), localized to AJs and its expression blocked cell migration and HGF-induced internalization of cadherin-based junctional components into the cytoplasm. Finally, we show that ARF6 exerts its role downstream of v-Src activation during the disassembly of AJs. These findings document an essential role for ARF6- regulated membrane traffic in AJ disassembly and epithelial cell migration.
Figures

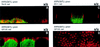
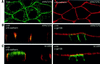

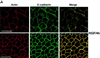


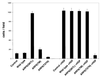
Similar articles
-
ARF6-GTP recruits Nm23-H1 to facilitate dynamin-mediated endocytosis during adherens junctions disassembly.Nat Cell Biol. 2002 Dec;4(12):929-36. doi: 10.1038/ncb881. Nat Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12447393
-
Clathrin dependent endocytosis of E-cadherin is regulated by the Arf6GAP isoform SMAP1.Exp Cell Res. 2008 Apr 15;314(7):1415-28. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2007.11.006. Epub 2007 Nov 17. Exp Cell Res. 2008. PMID: 18331728
-
Sertoli-germ cell adherens junction dynamics in the testis are regulated by RhoB GTPase via the ROCK/LIMK signaling pathway.Biol Reprod. 2003 Jun;68(6):2189-206. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.102.011379. Epub 2003 Jan 22. Biol Reprod. 2003. PMID: 12606349
-
Disassembling adherens junctions: breaking up is hard to do.Trends Cell Biol. 2005 Jan;15(1):19-26. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2004.11.002. Trends Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15653074 Review.
-
Adherens junctions and cadherins in Drosophila development.Subcell Biochem. 2012;60:251-77. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-4186-7_11. Subcell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22674075 Review.
Cited by
-
AMPK promotes Arf6 activation in a kinase-independent manner upon glucose starvation.J Cell Sci. 2022 Sep 15;135(18):jcs259609. doi: 10.1242/jcs.259609. Epub 2022 Sep 14. J Cell Sci. 2022. PMID: 36017701 Free PMC article.
-
Invasive cells in animals and plants: searching for LECA machineries in later eukaryotic life.Biol Direct. 2013 Apr 4;8:8. doi: 10.1186/1745-6150-8-8. Biol Direct. 2013. PMID: 23557484 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FRMD4A regulates epithelial polarity by connecting Arf6 activation with the PAR complex.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Jan 12;107(2):748-53. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0908423107. Epub 2009 Dec 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20080746 Free PMC article.
-
Crk associates with a multimolecular Paxillin/GIT2/beta-PIX complex and promotes Rac-dependent relocalization of Paxillin to focal contacts.Mol Biol Cell. 2003 Jul;14(7):2818-31. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e02-08-0497. Epub 2003 Apr 4. Mol Biol Cell. 2003. PMID: 12857867 Free PMC article.
-
Unregulated ARF6 activation in epithelial cysts generates hyperactive signaling endosomes and disrupts morphogenesis.Mol Biol Cell. 2010 Jul 1;21(13):2355-66. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e09-09-0824. Epub 2010 May 12. Mol Biol Cell. 2010. PMID: 20462959 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Behrens J., Vakaet,L., Friis,R., Winterhager,E., Van Roy,F., Mareel,M.M. and Birchmeier,W. (1993) Loss of epithelial differentiation and gain of invasiveness correlates with tyrosine phosphorylation of the E-cadherin/β-catenin complex in cells transformed with a temperature-sensitive v-SRC gene. J. Cell Biol., 120, 757–766. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Birchmeier C. and Birchmeier,W. (1993) Molecular aspects of mesenchymal–epithelial interactions. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol., 9, 511–540. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

