Interaction between growth arrest-DNA damage protein 34 and Src kinase Lyn negatively regulates genotoxic apoptosis
- PMID: 11517336
- PMCID: PMC56934
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.191130798
Interaction between growth arrest-DNA damage protein 34 and Src kinase Lyn negatively regulates genotoxic apoptosis
Abstract
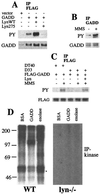
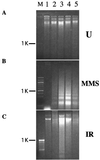
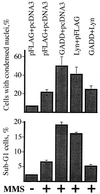
Genotoxic stresses activate intracellular signaling molecules, which lead to growth arrest, DNA repair, and/or apoptosis. Among these molecules are the growth arrest and DNA damage protein 34 (GADD34) and the Src-related protein tyrosine kinase Lyn. Here, we report that these two proteins physically and functionally interact to regulate DNA damage-induced apoptosis. Multiple isolates of GADD34 and the related murine protein MyD116 were identified as binding partners of Lyn in a yeast two-hybrid screen. The specific interaction was confirmed by in vitro association of GADD34 with glutathione S-transferase fusion proteins containing the Src Homology 3 (SH3) domain of Lyn, as well as coimmunoprecipitation of GADD34 and Lyn from mammalian cells. GADD34 was tyrosine-phosphorylated in vivo in a Lyn-dependent manner. Lyn efficiently phosphorylated affinity-purified GADD34 in vitro. Lyn negatively regulated the proapoptotic function of GADD34 in a kinase-dependent manner. Expression of wild-type, but not kinase-inactive, Lyn weakened promotion of apoptosis by GADD34 following treatment with methyl-methanesulfonate or ionizing radiation in HEK293 and HeLa cells. In contrast, pretreatment of cells with the Src-specific tyrosine kinase inhibitor PP1 strengthened promotion of apoptosis by GADD34. We propose that Lyn regulates the proapoptotic function of GADD34 by binding and phosphorylating it.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interaction between DNA-damage protein GADD34 and a new member of the Hsp40 family of heat shock proteins that is induced by a DNA-damaging reagent.Biochem J. 2000 Dec 15;352 Pt 3(Pt 3):795-800. Biochem J. 2000. PMID: 11104688 Free PMC article.
-
Gadd34 functional domains involved in growth suppression and apoptosis.Oncogene. 2003 Jun 19;22(25):3827-32. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206567. Oncogene. 2003. PMID: 12813455
-
Growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible protein GADD34 assembles a novel signaling complex containing protein phosphatase 1 and inhibitor 1.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Oct;21(20):6841-50. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.20.6841-6850.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11564868 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of a murine gene encoding an acidic-basic dipeptide repeat that interacts with GADD34.J Cell Biochem. 2000 Apr;77(4):596-603. J Cell Biochem. 2000. PMID: 10771515
-
Myeloid differentiation (MyD)/growth arrest DNA damage (GADD) genes in tumor suppression, immunity and inflammation.Leukemia. 2002 Apr;16(4):527-41. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2402477. Leukemia. 2002. PMID: 11960329 Review.
Cited by
-
Cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of Br-containing oxaphosphole on Allium cepa L. root tip cells and mouse bone marrow cells.Genet Mol Biol. 2009 Apr;32(2):389-93. doi: 10.1590/S1415-47572009000200028. Epub 2009 Jun 1. Genet Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 21637696 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation at tyrosine 262 promotes GADD34 protein turnover.J Biol Chem. 2013 Nov 15;288(46):33146-55. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.504407. Epub 2013 Oct 3. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24092754 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying altered gene expression in neuroblastoma cells preceding apoptosis.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2008 Mar;134(3):411-9. doi: 10.1007/s00432-007-0303-0. Epub 2007 Sep 5. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2008. PMID: 17786477
-
Alteration of DNA damage signaling pathway profile in radiation-treated glioblastoma stem-like cells.Oncol Lett. 2015 Sep;10(3):1769-1774. doi: 10.3892/ol.2015.3411. Epub 2015 Jun 22. Oncol Lett. 2015. PMID: 26622748 Free PMC article.
-
mda-7 (IL-24) Mediates selective apoptosis in human melanoma cells by inducing the coordinated overexpression of the GADD family of genes by means of p38 MAPK.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Jul 23;99(15):10054-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.152327199. Epub 2002 Jul 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 12114539 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

