A genomewide screen for autism: strong evidence for linkage to chromosomes 2q, 7q, and 16p
- PMID: 11481586
- PMCID: PMC1235486
- DOI: 10.1086/323264
A genomewide screen for autism: strong evidence for linkage to chromosomes 2q, 7q, and 16p
Abstract
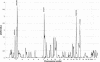
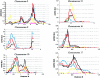
Autism is characterized by impairments in reciprocal communication and social interaction and by repetitive and stereotyped patterns of activities and interests. Evidence for a strong underlying genetic predisposition comes from twin and family studies, although susceptibility genes have not yet been identified. A whole-genome screen for linkage, using 83 sib pairs with autism, has been completed, and 119 markers have been genotyped in 13 candidate regions in a further 69 sib pairs. The addition of new families and markers provides further support for previous reports of linkages on chromosomes 7q and 16p. Two new regions of linkage have also been identified on chromosomes 2q and 17q. The most significant finding was a multipoint maximum LOD score (MLS) of 3.74 at marker D2S2188 on chromosome 2; this MLS increased to 4.80 when only sib pairs fulfilling strict diagnostic criteria were included. The susceptibility region on chromosome 7 was the next most significant, generating a multipoint MLS of 3.20 at marker D7S477. Chromosome 16 generated a multipoint MLS of 2.93 at D16S3102, whereas chromosome 17 generated a multipoint MLS of 2.34 at HTTINT2. With the addition of new families, there was no increased allele sharing at a number of other loci originally showing some evidence of linkage. These results support the continuing collection of multiplex sib-pair families to identify autism-susceptibility genes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A full genome screen for autism with evidence for linkage to a region on chromosome 7q. International Molecular Genetic Study of Autism Consortium.Hum Mol Genet. 1998 Mar;7(3):571-8. doi: 10.1093/hmg/7.3.571. Hum Mol Genet. 1998. PMID: 9546821
-
Further characterization of the autism susceptibility locus AUTS1 on chromosome 7q.Hum Mol Genet. 2001 Apr 15;10(9):973-82. doi: 10.1093/hmg/10.9.973. Hum Mol Genet. 2001. PMID: 11392322
-
Analysis of autism susceptibility gene loci on chromosomes 1p, 4p, 6q, 7q, 13q, 15q, 16p, 17q, 19q and 22q in Finnish multiplex families.Mol Psychiatry. 2000 May;5(3):320-2. doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4000708. Mol Psychiatry. 2000. PMID: 10889536
-
The genetics of autism.Pediatrics. 2004 May;113(5):e472-86. doi: 10.1542/peds.113.5.e472. Pediatrics. 2004. PMID: 15121991 Review.
-
The molecular genetics of autism.Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2000 Apr;2(2):170-5. doi: 10.1007/s11920-000-0063-x. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2000. PMID: 11122951 Review.
Cited by
-
Autism gene variant causes hyperserotonemia, serotonin receptor hypersensitivity, social impairment and repetitive behavior.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Apr 3;109(14):5469-74. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1112345109. Epub 2012 Mar 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22431635 Free PMC article.
-
Reliability and validity of autism diagnostic interview-revised, Japanese version.J Autism Dev Disord. 2013 Mar;43(3):643-62. doi: 10.1007/s10803-012-1606-9. J Autism Dev Disord. 2013. PMID: 22806002
-
Gene expression profiling of lymphoblastoid cell lines from monozygotic twins discordant in severity of autism reveals differential regulation of neurologically relevant genes.BMC Genomics. 2006 May 18;7:118. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-7-118. BMC Genomics. 2006. PMID: 16709250 Free PMC article.
-
A genetic study of autism in Costa Rica: multiple variables affecting IQ scores observed in a preliminary sample of autistic cases.BMC Psychiatry. 2005 Mar 21;5:15. doi: 10.1186/1471-244X-5-15. BMC Psychiatry. 2005. PMID: 15780135 Free PMC article.
-
Excess of twins among affected sibling pairs with autism: implications for the etiology of autism.Am J Hum Genet. 2001 Nov;69(5):1062-7. doi: 10.1086/324191. Epub 2001 Oct 2. Am J Hum Genet. 2001. PMID: 11590546 Free PMC article.
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Applied Biosystems, http://www.appliedbiosystems.com/
-
- ASPEX program, ftp://lahmed.stanford.edu/pub/aspex
-
- Genome Database, http://www.gdb.org/
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for autism [MIM 209850] and Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome [MIM 180849])
References
-
- Ashley-Koch A, Menold M, Joyer K, Mason S, Poole C, Donnelly S, Wolpert C, Raven S, Abramson R, DeLong G, Cuccaro M, Von Wendt L, McClain C, Wright H, Vance JM, Gilbert JG, Pericak-Vance MA (2000) Examination of epigentic factors and gene-gene interaction influencing genetic susceptibility at chromosome 7 and 15 for autistic disorder. Am J Hum Genet Suppl 67:A46
-
- Ashley-Koch A, Wolpert CM, Menold MM, Zaeem L, Basu S, Donnelly SL, Ravan SA, Powell CM, Qumsiyeh MB, Aylsworth AS, Vance JM, Gilbert JR, Wright HH, Abramson RK, DeLong GR, Cuccaro ML, Pericak-Vance MA (1999) Genetic studies of autistic disorder and chromosome 7. Genomics 61:227–236 - PubMed
-
- Bailey A, Le Couteur A, Gottesman I, Bolton P, Simonoff E, Yuzda E, Rutter M (1995) Autism as a strongly genetic disorder: evidence from a British twin study. Psychol Med 25:63–77 - PubMed
-
- Bailey A, Palferman S, Heavey L, Le Couteur A (1998) Autism: the phenotype in relatives. J Autism Dev Disord 28:369–392 - PubMed
-
- Bass MP, Menold MM, Wolpert CM, Donnelly SL, Ravan SA, Hauser ER, Maddox LO, Powell CM, Qumsiyeh MB, Aylsworth AS, Vance JM, Gilbert JR, Wright HH, Abramson RK, DeLong GR, Cuccaro ML, Pericak-Vance MA (2000) Genetic studies in autistic disorder and chromosome 15. Neurogenetics 2:219–226 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

