E2F mediates induction of the Sp1-controlled promoter of the human DNA polymerase epsilon B-subunit gene POLE2
- PMID: 11433027
- PMCID: PMC55767
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/29.13.2810
E2F mediates induction of the Sp1-controlled promoter of the human DNA polymerase epsilon B-subunit gene POLE2
Abstract
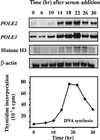
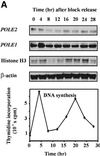
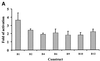
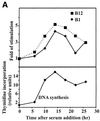
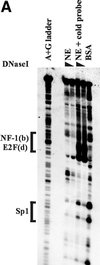
The B-subunits of replicative DNA polymerases from Archaea to humans belong to the same protein family, suggesting that they share a common fundamental function. We report here the gene structure for the B-subunit of human DNA polymerase epsilon (POLE2), whose expression and transcriptional regulation is typical for replication proteins with some unique features. The 75 bp core promoter region, located within exon 1, contains an Sp1 element that is a critical determinant of promoter activity as shown by the luciferase reporter, electrophoretic mobility shift and DNase I footprinting assays. Two overlapping E2F elements adjacent to the Sp1 element are essential for full promoter activity and serum response. Binding sites for E2F1 and NF-1 reside immediately downstream from the core promoter region. Our results suggest that human POLE2 is regulated by two E2F-pocket protein complexes, one associated with Sp1 and the other with NF-1. So far, only one replicative DNA polymerase B-subunit gene promoter, POLA2 encoding the B-subunit of DNA polymerase alpha, has been characterized. Mitogenic activation of the POLE2 promoter by an E2F-mediated mechanism resembles that of POLA2, but the regulation of basal promoter activity is different between these two genes.
Figures











Similar articles
-
Transcription factors of the Sp1 family: interaction with E2F and regulation of the murine thymidine kinase promoter.J Mol Biol. 1999 Nov 12;293(5):1005-15. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1999.3213. J Mol Biol. 1999. PMID: 10547281
-
Activity of the human cytochrome c1 promoter is modulated by E2F.Biochem J. 2000 Oct 1;351(Pt 1):251-6. doi: 10.1042/0264-6021:3510251. Biochem J. 2000. PMID: 10998368 Free PMC article.
-
E2F-1 represses transcription of the human telomerase reverse transcriptase gene.Nucleic Acids Res. 2001 Jul 1;29(13):2789-94. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.13.2789. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001. PMID: 11433024 Free PMC article.
-
Context-dependent transcriptional regulation.J Biol Chem. 1999 Oct 15;274(42):29583-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.42.29583. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10514422 Review. No abstract available.
-
Characterisation of the promoter region of the human DNA-repair gene Rad51.Eur J Gynaecol Oncol. 2005;26(6):589-98. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol. 2005. PMID: 16398215 Review.
Cited by
-
Canine parvovirus induces G1/S cell cycle arrest that involves EGFR Tyr1086 phosphorylation.Virulence. 2020 Dec;11(1):1203-1214. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2020.1814091. Virulence. 2020. PMID: 32877289 Free PMC article.
-
A single cell cycle genes homology region (CHR) controls cell cycle-dependent transcription of the cdc25C phosphatase gene and is able to cooperate with E2F or Sp1/3 sites.Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 May 1;30(9):1967-76. doi: 10.1093/nar/30.9.1967. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002. PMID: 11972334 Free PMC article.
-
Basal transcriptional regulation of human damage-specific DNA-binding protein genes DDB1 and DDB2 by Sp1, E2F, N-myc and NF1 elements.Nucleic Acids Res. 2003 Jan 15;31(2):562-9. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg152. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003. PMID: 12527763 Free PMC article.
-
A distance difference matrix approach to identifying transcription factors that regulate differential gene expression.Genome Biol. 2007;8(5):R83. doi: 10.1186/gb-2007-8-5-r83. Genome Biol. 2007. PMID: 17504544 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide in silico identification of transcriptional regulators controlling the cell cycle in human cells.Genome Res. 2003 May;13(5):773-80. doi: 10.1101/gr.947203. Genome Res. 2003. PMID: 12727897 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burgers P.M. (1998) Eukaryotic DNA polymerases in DNA replication and DNA repair. Chromosoma, 107, 218–227. - PubMed
-
- Hübscher U., Nasheuer,H.-P. and Syväoja,J.E. (2000) Eukaryotic DNA polymerases, a growing family. Trends Biochem. Sci., 25, 143–147. - PubMed
-
- Wang T.S.-F. (1996) Cellular DNA polymerases. In Depamphilis,M.L. (ed.), DNA Replication in Eukaryotic Cells. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY, pp. 461–493.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

