The cell cycle-regulatory CDC25A phosphatase inhibits apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1
- PMID: 11416155
- PMCID: PMC87174
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.21.14.4818-4828.2001
The cell cycle-regulatory CDC25A phosphatase inhibits apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1
Abstract
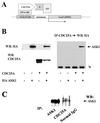
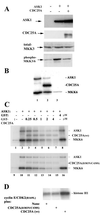
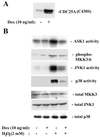
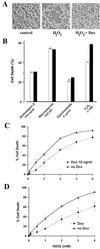
CDC25A phosphatase promotes cell cycle progression by activating G(1) cyclin-dependent kinases and has been postulated to be an oncogene because of its ability to cooperate with RAS to transform rodent fibroblasts. In this study, we have identified apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1) as a CDC25A-interacting protein by yeast two-hybrid screening. ASK1 activates the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and c-Jun NH(2)-terminal protein kinase-stress-activated protein kinase (JNK/SAPK) pathways upon various cellular stresses. Coimmunoprecipitation studies demonstrated that CDC25A physically associates with ASK1 in mammalian cells, and immunocytochemistry with confocal laser-scanning microscopy showed that these two proteins colocalize in the cytoplasm. The carboxyl terminus of CDC25A binds to a domain of ASK1 adjacent to its kinase domain and inhibits the kinase activity of ASK1, independent of and without effect on the phosphatase activity of CDC25A. This inhibitory action of CDC25A on ASK1 activity involves diminished homo-oligomerization of ASK1. Increased cellular expression of wild-type or phosphatase-inactive CDC25A from inducible transgenes suppresses oxidant-dependent activation of ASK1, p38, and JNK1 and reduces specific sensitivity to cell death triggered by oxidative stress, but not other apoptotic stimuli. Thus, increased expression of CDC25A, frequently observed in human cancers, could contribute to reduced cellular responsiveness to oxidative stress under mitogenic or oncogenic conditions, while it promotes cell cycle progression. These observations propose a mechanism of oncogenic transformation by the dual function of CDC25A on cell cycle progression and stress responses.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Negative feedback regulation of ASK1 by protein phosphatase 5 (PP5) in response to oxidative stress.EMBO J. 2001 Nov 1;20(21):6028-36. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.21.6028. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11689443 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological roles of ASK1-mediated signal transduction in oxidative stress- and endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis: advanced findings from ASK1 knockout mice.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2002 Jun;4(3):415-25. doi: 10.1089/15230860260196218. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2002. PMID: 12215209 Review.
-
Protein phosphatase with EF-hand domains 2 (PPEF2) is a potent negative regulator of apoptosis signal regulating kinase-1 (ASK1).Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010 Nov;42(11):1816-22. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2010.07.014. Epub 2010 Jul 30. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20674765
-
The Kelch repeat protein KLHDC10 regulates oxidative stress-induced ASK1 activation by suppressing PP5.Mol Cell. 2012 Dec 14;48(5):692-704. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.09.018. Epub 2012 Oct 25. Mol Cell. 2012. PMID: 23102700
-
The ASK1-MAP kinase cascades in mammalian stress response.J Biochem. 2004 Sep;136(3):261-5. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvh134. J Biochem. 2004. PMID: 15598880 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA-215 Regulates Fibroblast Function: Insights from a Human Fibrotic Disease.Cell Cycle. 2015;14(12):1973-84. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2014.998077. Cell Cycle. 2015. PMID: 25565137 Free PMC article.
-
Cdc25A regulates matrix metalloprotease 1 through Foxo1 and mediates metastasis of breast cancer cells.Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Aug;31(16):3457-71. doi: 10.1128/MCB.05523-11. Epub 2011 Jun 13. Mol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21670150 Free PMC article.
-
A review of the mammalian unfolded protein response.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2011 Dec;108(12):2777-93. doi: 10.1002/bit.23282. Epub 2011 Aug 9. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2011. PMID: 21809331 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AIP1 mediates TNF-alpha-induced ASK1 activation by facilitating dissociation of ASK1 from its inhibitor 14-3-3.J Clin Invest. 2003 Jun;111(12):1933-43. doi: 10.1172/JCI17790. J Clin Invest. 2003. PMID: 12813029 Free PMC article.
-
A human cancer-predisposing polymorphism in Cdc25A is embryonic lethal in the mouse and promotes ASK-1 mediated apoptosis.Cell Div. 2011 Feb 10;6(1):4. doi: 10.1186/1747-1028-6-4. Cell Div. 2011. PMID: 21310058 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adler V, Yin Z, Tew K D, Ronai Z. Role of redox potential and reactive oxygen species in stress signaling. Oncogene. 1999;18:6104–6111. - PubMed
-
- Behrens A, Sibilia M, Wagner E F. Amino-terminal phosphorylation of c-Jun regulates stress-induced apoptosis and cellular proliferation. Nat Genet. 1999;21:326–329. - PubMed
-
- Biguet C, Wakasugi N, Mishal Z, Holmgren A, Chouaib S, Tursz T, Wakasugi H. Thioredoxin increases the proliferation of human B-cell lines through a protein kinase C-dependent mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:28865–28870. - PubMed
-
- Bunz F, Dutriaux A, Lengauer C, Waldman T, Zhou S, Brown J P, Sedivy J M, Kinzler K W, Vogelstein B. Requirement for p53 and p21 to sustain G2 arrest after DNA damage. Science. 1998;282:1497–1501. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
