Induction of neutralizing antibodies and gag-specific cellular immune responses to an R5 primary isolate of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in rhesus macaques
- PMID: 11390589
- PMCID: PMC114303
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.13.5879-5890.2001
Induction of neutralizing antibodies and gag-specific cellular immune responses to an R5 primary isolate of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in rhesus macaques
Abstract
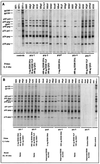
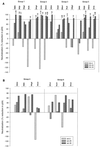
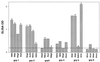
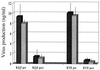
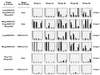
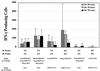
The ability to generate antibodies that cross-neutralize diverse primary isolates is an important goal for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) vaccine development. Most of the candidate HIV-1 vaccines tested in humans and nonhuman primates have failed in this regard. Past efforts have focused almost entirely on the envelope glycoproteins of a small number of T-cell line-adapted strains of the virus as immunogens. Here we assessed the immunogenicity of noninfectious virus-like particles (VLP) consisting of Gag, Pro (protease), and Env from R5 primary isolate HIV-1(Bx08). Immunogens were delivered to rhesus macaques in the form of either purified VLP, recombinant DNA and canarypox (ALVAC) vectors engineered to express VLP, or a combination of these products. Seroconversion to Gag and Pro was detected in all of the immunized animals. Antibodies that could neutralize HIV-1(Bx08) were detected in animals that received (i) coinoculations with DNA(Bx08) and VLP(Bx08), (ii) DNA(Bx08) followed by ALVAC(Bx08) boosting, and (iii) VLP(Bx08) alone. The neutralizing antibodies were highly strain specific despite the fact that they did not appear to be directed to linear epitopes in the V3 loop. Virus-specific cellular immune responses also were generated, as judged by the presence of Gag-specific gamma interferon (IFN-gamma)-producing cells. These cellular immune responses required the inclusion of DNA(Bx08) in the immunization modality, since few or no IFN-gamma-producing cells were detected in animals that received either VLP(Bx08) or ALVAC(Bx08) alone. The results demonstrate the feasibility of generating neutralizing antibodies and cellular immune responses that target an R5 primary HIV-1 isolate by vaccination in primates.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immunogenicity in Mamu-A*01 rhesus macaques of a CCR5-tropic human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope from the primary isolate (Bx08) after synthetic DNA prime and recombinant adenovirus 5 boost.J Gen Virol. 2003 Jan;84(Pt 1):203-213. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.18589-0. J Gen Virol. 2003. PMID: 12533717
-
Immune response in rhesus macaques after mixed modality immunisations with DNA, recombinant adenovirus and recombinant gp120 from human immunodeficiency virus type 1.APMIS. 2006 Oct;114(10):690-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0463.2006.apm_395.x. APMIS. 2006. PMID: 17004972
-
Comparison of HIV Type 1 ADA gp120 monomers versus gp140 trimers as immunogens for the induction of neutralizing antibodies.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2005 Jan;21(1):58-67. doi: 10.1089/aid.2005.21.58. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2005. PMID: 15665645
-
Head-to-Head Comparison of Poxvirus NYVAC and ALVAC Vectors Expressing Identical HIV-1 Clade C Immunogens in Prime-Boost Combination with Env Protein in Nonhuman Primates.J Virol. 2015 Aug;89(16):8525-39. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01265-15. Epub 2015 Jun 3. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26041302 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and immunogenicity of recombinant human immunodeficiency virus-like particles in rodents and rhesus macaques.Intervirology. 1996;39(1-2):93-103. doi: 10.1159/000150480. Intervirology. 1996. PMID: 8957675 Review.
Cited by
-
HIV-1 virus-like particles produced by stably transfected Drosophila S2 cells: a desirable vaccine component.J Virol. 2012 Jul;86(14):7662-76. doi: 10.1128/JVI.07164-11. Epub 2012 May 2. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22553333 Free PMC article.
-
Robust recall and long-term memory T-cell responses induced by prime-boost regimens with heterologous live viral vectors expressing human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Gag and Env proteins.J Virol. 2002 Aug;76(15):7506-17. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.15.7506-7517.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 12097563 Free PMC article.
-
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 env clones from acute and early subtype B infections for standardized assessments of vaccine-elicited neutralizing antibodies.J Virol. 2005 Aug;79(16):10108-25. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.16.10108-10125.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16051804 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of broad and potent anti-human immunodeficiency virus immune responses in rhesus macaques by priming with a DNA vaccine and boosting with protein-adsorbed polylactide coglycolide microparticles.J Virol. 2003 May;77(10):6087-92. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.10.6087-6092.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12719603 Free PMC article.
-
Immunization with a Mixture of HIV Env DNA and VLP Vaccines Augments Induction of CD8 T Cell Responses.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010;2010:497219. doi: 10.1155/2010/497219. Epub 2010 May 25. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20508832 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baba T W, Liska V, Hofmann-Lehmann R, Vlasak J, Xu W, Ayehunie S, Cavacini L A, Posner M R, Katinger H, Stiegler G, Bernacky B J, Rizvi T A, Schmidt R, Hill L R, Keeling M E, Lu Y, Wright J E, Chou T-C, Ruprecht R M. Human neutralizing monoclonal antibodies of the IgG1 subtype protect against mucosal simian-human immunodeficiency virus infection. Nat Med. 2000;6:200–206. - PubMed
-
- Barouch D H, Santra S, Schmitz J E, Kuroda M J, Fu T-M, Wagner W, Bilska M, Craiu A, Zheng X X, Krivulka G R, Beaudry K, Lifton M A, Nickerson C E, Trigona W L, Punt K, Freed D C, Guan L, Dubey S, Casimiro D, Simon A, Davies M-E, Chastain M, Strom T B, Gelman R S, Montefiori D C, Lewis M G, Emini E A, Shiver J W, Letvin N L. Control of viremia and prevention of clinical AIDS in rhesus monkeys by cytokine-augmented DNA vaccination. Science. 2000;290:486–492. - PubMed
-
- Beddows S, Lister S, Cheingsong R, Bruck C, Weber J. Comparison of the antibody repertoire generated in healthy volunteers following immunization with a monomeric recombinant gp120 construct derived from a CCR5/CXCR4-using human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolate with sera from naturally infected individuals. J Virol. 1999;73:1740–1745. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Belshe R B, Gorse G J, Mulligan M J, Evans T G, Keefer M C, Excler J-L, Duliege A-M, Tartaglia J, Cox W I, McNamara J, Hwang K-L, Bradney A, Montefiori D, Weinhold K J. Induction of immune responses to HIV-1 canarypox virus (ALVAC) HIV-1 and gp120 SF-2 recombinant vaccines in uninfected volunteers. AIDS. 1998;12:2407–2415. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

