Relaxin is essential for renal vasodilation during pregnancy in conscious rats
- PMID: 11390429
- PMCID: PMC209320
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI11975
Relaxin is essential for renal vasodilation during pregnancy in conscious rats
Abstract
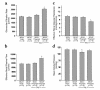
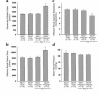
Marked vasodilation in the kidney and other nonreproductive organs is one of the earliest maternal adaptations to occur during pregnancy. Despite the recognition of this extraordinary physiology for over four decades, the gestational hormone responsible has remained elusive. Here we demonstrate a key role for relaxin, a member of the IGF family that is secreted by the corpus luteum in humans and rodents. Using a gravid rodent model, we employ two approaches to eliminate relaxin or its biological activity from the circulation: ovariectomy and administration of neutralizing antibodies. Both abrogate the gestational elevation in renal perfusion and glomerular filtration, as well as preventing the reduction in myogenic reactivity of isolated, small renal arteries. Osmoregulatory changes, another pregnancy adaptation, are also abolished. Our results indicate that relaxin mediates the renal vasodilatory responses to pregnancy and thus may be important for maternal and fetal health. They also raise the likelihood of a role for relaxin in other cardiovascular changes of pregnancy, and they suggest that, like estrogen, relaxin should be considered a regulator of cardiovascular function.
Figures
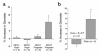
Similar articles
-
Essential role for vascular gelatinase activity in relaxin-induced renal vasodilation, hyperfiltration, and reduced myogenic reactivity of small arteries.Circ Res. 2003 Dec 12;93(12):1249-57. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000104086.43830.6C. Epub 2003 Oct 30. Circ Res. 2003. PMID: 14593002
-
The renal circulation in normal pregnancy and preeclampsia: is there a place for relaxin?Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2014 May 15;306(10):F1121-35. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00042.2014. Epub 2014 Mar 19. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24647709 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relaxin is essential for systemic vasodilation and increased global arterial compliance during early pregnancy in conscious rats.Endocrinology. 2006 Nov;147(11):5126-31. doi: 10.1210/en.2006-0567. Epub 2006 Jul 27. Endocrinology. 2006. PMID: 16873529
-
Endothelin mediates renal vasodilation and hyperfiltration during pregnancy in chronically instrumented conscious rats.Am J Physiol. 1999 May;276(5):F767-76. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1999.276.5.F767. Am J Physiol. 1999. PMID: 10330059
-
Emerging role of relaxin in the maternal adaptations to normal pregnancy: implications for preeclampsia.Semin Nephrol. 2011 Jan;31(1):15-32. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2010.10.003. Semin Nephrol. 2011. PMID: 21266262 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. XCV. Recent advances in the understanding of the pharmacology and biological roles of relaxin family peptide receptors 1-4, the receptors for relaxin family peptides.Pharmacol Rev. 2015;67(2):389-440. doi: 10.1124/pr.114.009472. Pharmacol Rev. 2015. PMID: 25761609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A single-chain derivative of the relaxin hormone is a functionally selective agonist of the G protein-coupled receptor, RXFP1.Chem Sci. 2016 Jun 1;7(6):3805-3819. doi: 10.1039/c5sc04754d. Epub 2016 Feb 26. Chem Sci. 2016. PMID: 30155023 Free PMC article.
-
Relaxin-2 in Cardiometabolic Diseases: Mechanisms of Action and Future Perspectives.Front Physiol. 2017 Aug 18;8:599. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00599. eCollection 2017. Front Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28868039 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Short-Term Administration of Serelaxin Produces Predominantly Vascular Benefits in the Angiotensin II/L-NAME Chronic Heart Failure Model.JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2017 Jun 26;2(3):285-296. doi: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2017.03.011. eCollection 2017 Jun. JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2017. PMID: 30062150 Free PMC article.
-
Relaxin as a natural agent for vascular health.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2008;4(3):515-24. doi: 10.2147/vhrm.s2177. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2008. PMID: 18827902 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Conrad, K.P., and Lindheimer, M.D. 1999. Renal and cardiovascular alterations. In Chesley’s hypertensive disorders in pregnancy. 2nd edition. M.D. Lindheimer, J.M. Roberts, and F.G. Cunningham, editors. Appleton & Lange. Stamford, Connecticut, USA. 263–326.
-
- Veille JC, Morton MJ, Burry K, Nemeth M, Speroff L. Estradiol and hemodynamics during ovulation induction. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986;63:721–724. - PubMed
-
- Magness RR, Phernetton TM, Zheng J. Systemic and uterine blood flow distribution during prolonged infusion of estradiol-17β. Am J Physiol. 1998;275:H731–H743. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

