Endothelial cell laminin isoforms, laminins 8 and 10, play decisive roles in T cell recruitment across the blood-brain barrier in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
- PMID: 11381080
- PMCID: PMC2174323
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.153.5.933
Endothelial cell laminin isoforms, laminins 8 and 10, play decisive roles in T cell recruitment across the blood-brain barrier in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
Abstract
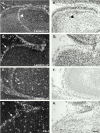
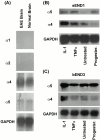
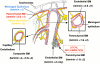
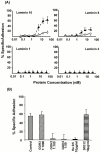
An active involvement of blood-brain barrier endothelial cell basement membranes in development of inflammatory lesions in the central nervous system (CNS) has not been considered to date. Here we investigated the molecular composition and possible function of the extracellular matrix encountered by extravasating T lymphocytes during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). Endothelial basement membranes contained laminin 8 (alpha4beta1gamma1) and/or 10 (alpha5beta1gamma1) and their expression was influenced by proinflammatory cytokines or angiostatic agents. T cells emigrating into the CNS during EAE encountered two biochemically distinct basement membranes, the endothelial (containing laminins 8 and 10) and the parenchymal (containing laminins 1 and 2) basement membranes. However, inflammatory cuffs occurred exclusively around endothelial basement membranes containing laminin 8, whereas in the presence of laminin 10 no infiltration was detectable. In vitro assays using encephalitogenic T cell lines revealed adhesion to laminins 8 and 10, whereas binding to laminins 1 and 2 could not be induced. Downregulation of integrin alpha6 on cerebral endothelium at sites of T cell infiltration, plus a high turnover of laminin 8 at these sites, suggested two possible roles for laminin 8 in the endothelial basement membrane: one at the level of the endothelial cells resulting in reduced adhesion and, thereby, increased penetrability of the monolayer; and secondly at the level of the T cells providing direct signals to the transmigrating cells.
Figures
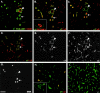
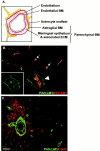
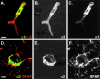
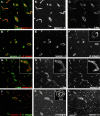
Similar articles
-
The endothelial basement membrane acts as a checkpoint for entry of pathogenic T cells into the brain.J Exp Med. 2020 Jul 6;217(7):e20191339. doi: 10.1084/jem.20191339. J Exp Med. 2020. PMID: 32379272 Free PMC article.
-
Blockade of MCAM/CD146 impedes CNS infiltration of T cells over the choroid plexus.J Neuroinflammation. 2018 Aug 22;15(1):236. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1276-4. J Neuroinflammation. 2018. PMID: 30134924 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and function of laminins in the embryonic and mature vasculature.Physiol Rev. 2005 Jul;85(3):979-1000. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00014.2004. Physiol Rev. 2005. PMID: 15987800 Review.
-
Beneficial effect of modified peptide inhibitor of alpha4 integrins on experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in Lewis rats.J Neurosci Res. 2002 Jan 15;67(2):191-9. doi: 10.1002/jnr.10095. J Neurosci Res. 2002. PMID: 11782963
-
The role of basement membrane laminins in vascular function.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2020 Oct;127:105823. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2020.105823. Epub 2020 Aug 8. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32781135 Review.
Cited by
-
Inflammation modulates expression of laminin in the central nervous system following ischemic injury.J Neuroinflammation. 2012 Jul 3;9:159. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-9-159. J Neuroinflammation. 2012. PMID: 22759265 Free PMC article.
-
Mycolactone causes destructive Sec61-dependent loss of the endothelial glycocalyx and vessel basement membrane: a new indirect mechanism driving tissue necrosis in Mycobacterium ulcerans infection.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 1:2023.02.21.529382. doi: 10.1101/2023.02.21.529382. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 36865118 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Laminin Triggers Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs) and Modulates NET Release Induced by Leishmania amazonensis.Biomedicines. 2022 Feb 23;10(3):521. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10030521. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35327324 Free PMC article.
-
Lymph node fibroblastic reticular cells preserve a tolerogenic niche in allograft transplantation through laminin α4.J Clin Invest. 2022 Jul 1;132(13):e156994. doi: 10.1172/JCI156994. J Clin Invest. 2022. PMID: 35775481 Free PMC article.
-
Organotypic vibrosections: novel whole sagittal brain cultures.J Neurosci Methods. 2011 Sep 30;201(1):131-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2011.07.021. Epub 2011 Jul 30. J Neurosci Methods. 2011. PMID: 21835204 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alcolado R., Weller R.O., Parrish E.P., Garrod D. The cranial arachnoid and piamater in mananatomical and ultrastructural observations. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 1988;14:1–17. - PubMed
-
- Boado R.J., Pardridge W.M. Differential expression of alpha-actin mRNA and immunoreactive protein in brain microvascular pericytes and smooth muscle cells. J. Neurosci. Res. 1994;39:430–435. - PubMed
-
- Breier G., Albrecht U., Sterrer S., Risau W. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor during embryonic angiogenesis and endothelial cell differentiation. Development. 1992;114:521–532. - PubMed
-
- Chandler S., Miller K.M., Clements J.M., Lury J., Corkill D., Anthony D.C.C., Adams S.E., Gearing A.J.H. Matrix metalloproteinases, tumor necrosis factor and multiple sclerosisan overview. J. Neuroimmunol. 1997;72:155–161. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

