Phospholipase D1: a key factor for the exocytotic machinery in neuroendocrine cells
- PMID: 11350931
- PMCID: PMC125248
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.10.2424
Phospholipase D1: a key factor for the exocytotic machinery in neuroendocrine cells
Abstract
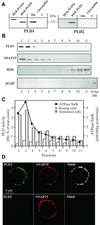
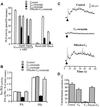
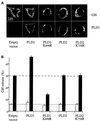
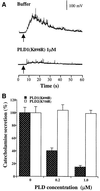
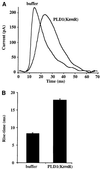
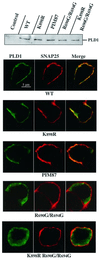
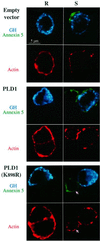
Phospholipase D (PLD) has been proposed to mediate cytoskeletal remodeling and vesicular trafficking along the secretory pathway. We recently described the activation of an ADP ribosylation factor-regulated PLD at the plasma membrane of chromaffin cells undergoing secretagogue-stimulated exocytosis. We show here that the isoform involved is PLD1b, and, using a real-time assay for individual cells, that PLD activation and exocytosis are closely correlated. Moreover, overexpressed PLD1, but not PLD2, increases stimulated exocytosis in a phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate-dependent manner, whereas catalytically inactive PLD1 inhibits it. These results provide the first direct evidence that PLD1 is an important component of the exocytotic machinery in neuroendocrine cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
betaPIX-activated Rac1 stimulates the activation of phospholipase D, which is associated with exocytosis in neuroendocrine cells.J Cell Sci. 2009 Mar 15;122(Pt 6):798-806. doi: 10.1242/jcs.038109. J Cell Sci. 2009. PMID: 19261846
-
Calcium-regulated exocytosis of dense-core vesicles requires the activation of ADP-ribosylation factor (ARF)6 by ARF nucleotide binding site opener at the plasma membrane.J Cell Biol. 2002 Oct 14;159(1):79-89. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200203027. Epub 2002 Oct 14. J Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12379803 Free PMC article.
-
Examination of the role of ADP-ribosylation factor and phospholipase D activation in regulated exocytosis in chromaffin and PC12 cells.J Neurochem. 1998 Nov;71(5):2023-33. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1998.71052023.x. J Neurochem. 1998. PMID: 9798927
-
Synthesis of fusogenic lipids through activation of phospholipase D1 by GTPases and the kinase RSK2 is required for calcium-regulated exocytosis in neuroendocrine cells.Biochem Soc Trans. 2010 Feb;38(Pt 1):167-71. doi: 10.1042/BST0380167. Biochem Soc Trans. 2010. PMID: 20074053 Review.
-
Phospholipase D in calcium-regulated exocytosis: lessons from chromaffin cells.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 Sep;1791(9):936-41. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2009.02.016. Epub 2009 Mar 13. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009. PMID: 19289180 Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphatidic acid induces conformational changes in Sec18 protomers that prevent SNARE priming.J Biol Chem. 2019 Mar 1;294(9):3100-3116. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.006552. Epub 2019 Jan 7. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30617180 Free PMC article.
-
A role for Phospholipase D in Drosophila embryonic cellularization.BMC Dev Biol. 2006 Dec 7;6:60. doi: 10.1186/1471-213X-6-60. BMC Dev Biol. 2006. PMID: 17156430 Free PMC article.
-
The Coffin-Lowry syndrome-associated protein RSK2 and neurosecretion.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2010 Nov;30(8):1401-6. doi: 10.1007/s10571-010-9578-9. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2010. PMID: 21061166 Review.
-
Lipid signaling on the mitochondrial surface.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 Sep;1791(9):839-44. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2009.05.012. Epub 2009 Jun 18. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009. PMID: 19540356 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A role for phosphatidic acid in the formation of "supersized" lipid droplets.PLoS Genet. 2011 Jul;7(7):e1002201. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002201. Epub 2011 Jul 28. PLoS Genet. 2011. PMID: 21829381 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abousalham A., Liossis,C., O’Brien,L. and Brindley,D.N. (1997) Cell-permeable ceramides prevent the activation of phospholipase D by ADP-ribosylation factor and RhoA. J. Biol. Chem., 272, 1069–1075. - PubMed
-
- Albillos A., Dernick,G., Horstmann,H., Almers,W., Alvarez de Toledo, G. and Lindau,M. (1997) The exocytotic event in chromaffin cells revealed by patch amperometry. Nature, 389, 509–512. - PubMed
-
- Bi K., Roth,M.G. and Ktistakis,N.T. (1997) Phosphatidic acid formation by phospholipase D is required for transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi complex. Curr. Biol., 7, 301–307. - PubMed
-
- Brown F.D., Thompson,N., Saqib,K., Clark,J.M., Powner,D., Thompson,N.T., Solari,R. and Wakelam,M.J.O. (1998) Phospholipase D1 localises to secretory granules and lysosomes and is plasma-membrane translocated on cellular stimulation. Curr. Biol., 8, 835–838. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

