The Exocytosis-regulatory protein synaptotagmin VII mediates cell invasion by Trypanosoma cruzi
- PMID: 11342594
- PMCID: PMC2193425
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.193.9.1097
The Exocytosis-regulatory protein synaptotagmin VII mediates cell invasion by Trypanosoma cruzi
Abstract
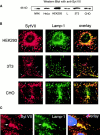
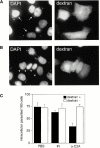
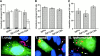
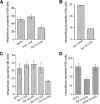
The intracellular protozoan parasite Trypanosoma cruzi causes Chagas' disease, which affects millions of people in Latin America. T. cruzi enters a large number of cell types by an unusual mechanism that involves Ca(2+)-triggered fusion of lysosomes with the plasma membrane. Here we show that synaptotagmin VII (Syt VII), a ubiquitously expressed synaptotagmin isoform that regulates exocytosis of lysosomes, is localized on the membranes of intracellular vacuoles containing T. cruzi. Antibodies against the C(2)A domain of Syt VII or recombinant peptides including this domain inhibit cell entry by T. cruzi, but not by Toxoplasma gondii or Salmonella typhimurium. The C(2)A domains of other ubiquitously expressed synaptotagmin isoforms have no effect on T. cruzi invasion, and mutation of critical residues on Syt VII C(2)A abolish its inhibitory activity. These findings indicate that T. cruzi exploits the Syt VII-dependent, Ca(2+)-regulated lysosomal exocytic pathway for invading host cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synaptotagmin VII regulates Ca(2+)-dependent exocytosis of lysosomes in fibroblasts.J Cell Biol. 2000 Mar 20;148(6):1141-49. doi: 10.1083/jcb.148.6.1141. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10725327 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptotagmin VII is targeted to dense-core vesicles and regulates their Ca2+ -dependent exocytosis in PC12 cells.J Biol Chem. 2004 Dec 10;279(50):52677-84. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M409241200. Epub 2004 Sep 28. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15456748
-
Plasma membrane repair is mediated by Ca(2+)-regulated exocytosis of lysosomes.Cell. 2001 Jul 27;106(2):157-69. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00421-4. Cell. 2001. PMID: 11511344
-
Don't bother to knock--the cell invasion strategy of Trypanosoma cruzi.Trends Parasitol. 2002 Oct;18(10):427-8. doi: 10.1016/s1471-4922(02)02368-1. Trends Parasitol. 2002. PMID: 12377585 Review.
-
Synaptotagmin regulates mast cell functions.Immunol Rev. 2001 Feb;179:25-34. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-065x.2001.790103.x. Immunol Rev. 2001. PMID: 11292024 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular and cellular mechanisms involved in the Trypanosoma cruzi/host cell interplay.IUBMB Life. 2012 May;64(5):387-96. doi: 10.1002/iub.1019. Epub 2012 Mar 27. IUBMB Life. 2012. PMID: 22454195 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of cellular invasion by intracellular parasites.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014 Apr;71(7):1245-63. doi: 10.1007/s00018-013-1491-1. Epub 2013 Nov 13. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 24221133 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms Associated with Trypanosoma cruzi Host Target Cell Adhesion, Recognition and Internalization.Life (Basel). 2021 Jun 9;11(6):534. doi: 10.3390/life11060534. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34207491 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Membrane traffic and synaptic cross-talk during host cell entry by Trypanosoma cruzi.Cell Microbiol. 2012 Sep;14(9):1345-53. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2012.01818.x. Epub 2012 Jul 4. Cell Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22646288 Free PMC article.
-
A new cruzipain-mediated pathway of human cell invasion by Trypanosoma cruzi requires trypomastigote membranes.Infect Immun. 2004 Oct;72(10):5892-902. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.10.5892-5902.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15385491 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tardieux I., Webster P., Ravesloot J., Boron W., Lunn J.A., Heuser J.E., Andrews N.W. Lysosome recruitment and fusion are early events required for trypanosome invasion of mammalian cells. Cell. 1992;71:1117–1130. - PubMed
-
- Dorta M.L., Ferreira A.T., Oshiro M.E.M., Yoshida N. Ca2+ signal induced by Trypanosoma cruzi metacyclic trypomastigote surface molecules implicated in mammalian cell invasion. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1995;73:285–289. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

