A Glanzmann's mutation in beta 3 integrin specifically impairs osteoclast function
- PMID: 11342577
- PMCID: PMC209281
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI12040
A Glanzmann's mutation in beta 3 integrin specifically impairs osteoclast function
Abstract
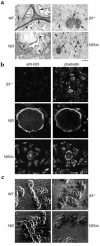
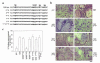
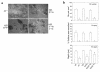
Osteoclastic bone resorption requires cell-matrix contact, an event mediated by the alpha v beta 3 integrin. The structural components of the integrin that mediate osteoclast function are, however, not in hand. To address this issue, we generated mice lacking the beta 3 integrin gene, which have dysfunctional osteoclasts. Here, we show the full rescue of beta 3(-/-) osteoclast function following expression of a full-length beta 3 integrin. In contrast, truncated beta 3, lacking a cytoplasmic domain (h beta 3c), is completely ineffective in restoring function to beta 3(-/-) osteoclasts. To identify the components of the beta 3 cytoplasmic domain regulating osteoclast function, we generated six point mutants known, in other circumstances, to mediate beta integrin signaling. Of the six, only the S(752)P substitution, which also characterizes a form of the human bleeding disorder Glanzmann's thrombasthenia, fails to rescue beta 3(-/-) osteoclasts or restore ligand-activated signaling in the form of c-src activation. Interestingly, the double mutation Y(747)F/Y(759)F, which disrupts platelet function, does not affect the osteoclast. Thus similarities and distinctions exist in the mechanisms by which the beta 3 integrin regulates platelets and osteoclasts.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Dynamic changes in the osteoclast cytoskeleton in response to growth factors and cell attachment are controlled by beta3 integrin.J Cell Biol. 2003 Aug 4;162(3):499-509. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200212082. J Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12900398 Free PMC article.
-
Critical role of beta3 integrin in experimental postmenopausal osteoporosis.J Bone Miner Res. 2005 Dec;20(12):2116-23. doi: 10.1359/JBMR.050724. Epub 2005 Jul 25. J Bone Miner Res. 2005. PMID: 16294265
-
Mice lacking beta3 integrins are osteosclerotic because of dysfunctional osteoclasts.J Clin Invest. 2000 Feb;105(4):433-40. doi: 10.1172/JCI8905. J Clin Invest. 2000. PMID: 10683372 Free PMC article.
-
Blockade of osteoclast-mediated bone resorption through occupancy of the integrin receptor: a potential approach to the therapy of osteoporosis.J Cell Biochem. 1994 Nov;56(3):323-30. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240560308. J Cell Biochem. 1994. PMID: 7876325 Review.
-
Genetic analysis of integrin function in man: LAD-1 and other syndromes.Matrix Biol. 2000 Jul;19(3):211-22. doi: 10.1016/s0945-053x(00)00066-4. Matrix Biol. 2000. PMID: 10936446 Review.
Cited by
-
Talin1 and Rap1 are critical for osteoclast function.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Feb;33(4):830-44. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00790-12. Epub 2012 Dec 10. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23230271 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor activator of NF-{kappa}B (RANK) cytoplasmic IVVY535-538 motif plays an essential role in tumor necrosis factor-{alpha} (TNF)-mediated osteoclastogenesis.J Biol Chem. 2010 Nov 26;285(48):37427-35. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.149484. Epub 2010 Sep 24. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20870724 Free PMC article.
-
Prostate cancer specific integrin alphavbeta3 modulates bone metastatic growth and tissue remodeling.Oncogene. 2007 Sep 13;26(42):6238-43. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210429. Epub 2007 Mar 19. Oncogene. 2007. PMID: 17369840 Free PMC article.
-
c-Src links a RANK/αvβ3 integrin complex to the osteoclast cytoskeleton.Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Jul;32(14):2943-53. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00077-12. Epub 2012 May 21. Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22615494 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic changes in the osteoclast cytoskeleton in response to growth factors and cell attachment are controlled by beta3 integrin.J Cell Biol. 2003 Aug 4;162(3):499-509. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200212082. J Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12900398 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Teitelbaum, S.L., Tondravi, M.M., and Ross, F.P. 1996. Osteoclast Biology. In Osteoporosis. R. Marcus, D. Feldman, and J. Kelsey, editors. Academic Press. San Diego, California, USA. 61–94.
-
- Suda T, et al. Modulation of osteoclast differentiation and function by the new members of the tumor necrosis factor receptor and ligand families. Endocr Rev. 1999;20:345–357. - PubMed
-
- Hynes RO. Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell. 1992;69:11–25. - PubMed
-
- Horton MA, Taylor ML, Arnett TR, Helfrich MH. Arg-gly-asp (RGD) peptides and the anti-vitronectin receptor antibody 23C6 inhibit dentine resorption and cell spreading by osteoclasts. Exp Cell Res. 1991;195:368–375. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

