Kinetics of murine gammaherpesvirus 68 gene expression following infection of murine cells in culture and in mice
- PMID: 11333874
- PMCID: PMC114898
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.11.4955-4963.2001
Kinetics of murine gammaherpesvirus 68 gene expression following infection of murine cells in culture and in mice
Abstract
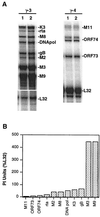
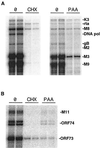
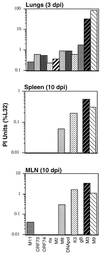
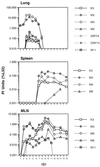
A model system to study the pathogenesis of gammaherpesvirus infections is the infection of mice with murine gammaherpesvirus 68 (MHV-68). To define the kinetics of infection, we developed an RNase protection assay to quantitate gene expression from lytic (K3, Rta, M8, DNA polymerase [DNA pol], and gB) and candidate latency (M2, M3, M9, M11, ORF73, and ORF74) genes. All candidate latency genes were expressed during lytic infection of 3T3 cells. Four kinetic classes of transcripts were observed following infection of 3T3 cells: immediate-early (K3, Rta, M8, and ORF73), early (DNA pol), early-late (M3, M11, and ORF74), and late (M2, M9, and gB). To assess the kinetics of viral gene expression in vivo, lungs, spleens, and mediastinal lymph nodes (MLN) were harvested from MHV-68-infected mice. All transcripts were expressed between 3 and 6 days postinfection (dpi) in the lungs. In the spleen, K3, M3, M8, and M9 transcripts were expressed between 10 and 16 dpi when latency is established. The K3, M3, M8, M9, and M11 transcripts were detected in the MLN from 2 through 16 dpi. This is the first demonstration of MHV-68 gene expression in the MLN. Importantly, our data showed that MHV-68 has different kinetics of gene expression at different sites of infection. Furthermore, we demonstrated that K3, a gene recently shown to encode a protein that downregulates major histocompatibility complex class I on the surface of cells, is expressed during latency, which argues for a role of K3 in immune evasion during latent infection.
Figures


Similar articles
-
In vivo activation of toll-like receptor-9 induces an age-dependent abortive lytic cycle reactivation of murine gammaherpesvirus-68.Viral Immunol. 2010 Dec;23(6):547-55. doi: 10.1089/vim.2010.0055. Viral Immunol. 2010. PMID: 21142440 Free PMC article.
-
The m4 gene of murine gammaherpesvirus modulates productive and latent infection in vivo.J Virol. 2004 Jan;78(2):758-67. doi: 10.1128/jvi.78.2.758-767.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 14694108 Free PMC article.
-
Three distinct regions of the murine gammaherpesvirus 68 genome are transcriptionally active in latently infected mice.J Virol. 1999 Mar;73(3):2321-32. doi: 10.1128/JVI.73.3.2321-2332.1999. J Virol. 1999. PMID: 9971815 Free PMC article.
-
Murine herpesvirus pathogenesis: a model for the analysis of molecular mechanisms of human gamma herpesvirus infections.Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung. 2005;52(1):41-71. doi: 10.1556/AMicr.52.2005.1.2. Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung. 2005. PMID: 15957234 Review.
-
Gamma herpesviruses: pathogenesis of infection and cell signaling.Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2003;48(3):291-318. doi: 10.1007/BF02931360. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2003. PMID: 12879740 Review.
Cited by
-
Murine gammaherpesvirus 68 LANA is essential for virus reactivation from splenocytes but not long-term carriage of viral genome.J Virol. 2010 Jul;84(14):7214-24. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00133-10. Epub 2010 May 5. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20444892 Free PMC article.
-
Gammaherpesvirus modulation of mouse adenovirus type 1 pathogenesis.Virology. 2008 Oct 25;380(2):182-90. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2008.07.031. Epub 2008 Sep 2. Virology. 2008. PMID: 18768196 Free PMC article.
-
Gammaherpesvirus lytic gene expression as characterized by DNA array.J Virol. 2002 Jun;76(12):6244-56. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.12.6244-6256.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 12021358 Free PMC article.
-
Differential activation of murine herpesvirus 68- and Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-encoded ORF74 G protein-coupled receptors by human and murine chemokines.J Virol. 2004 Apr;78(7):3343-51. doi: 10.1128/jvi.78.7.3343-3351.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15016856 Free PMC article.
-
Relevance of BET Family Proteins in SARS-CoV-2 Infection.Biomolecules. 2021 Jul 30;11(8):1126. doi: 10.3390/biom11081126. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34439792 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chomczynski P, Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987;162:156–159. - PubMed
-
- Flano E, Husain S M, Sample J T, Woodland D L, Blackman M A. Latent murine gamma-herpesvirus infection is established in activated B cells, dendritic cells, and macrophages. J Immunol. 2000;165:1074–1081. - PubMed
-
- Hobbs M V, Weigle W O, Noonan D J, Torbett B E, McEvilly R J, Koch R J, Cardenas G J, Ernst D N. Patterns of cytokine gene expression by CD4+ T cells from young and old mice. J Immunol. 1993;150:3602–3614. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

