Transcriptional repression by RB-E2F and regulation of anchorage-independent survival
- PMID: 11313458
- PMCID: PMC100254
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.21.10.3325-3335.2001
Transcriptional repression by RB-E2F and regulation of anchorage-independent survival
Abstract
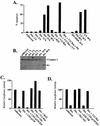
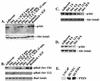
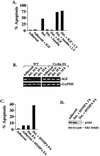
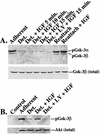
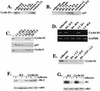
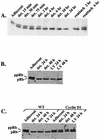
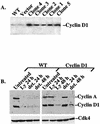
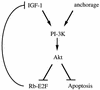
Mutations that lead to anchorage-independent survival are a hallmark of tumor cells. Adhesion of integrin receptors to extracellular matrix activates a survival signaling pathway in epithelial cells where Akt phosphorylates and blocks the activity of proapoptotic proteins such as the BCL2 family member Bad, the forkhead transcription factor FKHRL-1, and caspase 9. Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) is a well-established epithelial cell survival factor that also triggers activation of Akt and can maintain Akt activity after cells lose matrix contact. It is not until IGF-1 expression diminishes (~16 h after loss of matrix contact) that epithelial cells deprived of matrix contact undergo apoptosis. This suggests that IGF-1 expression is linked to cell adhesion and that it is the loss of IGF-1 which dictates the onset of apoptosis after cells lose matrix contact. Here, we examine the linkage between cell adhesion and IGF-1 expression. While IGF-1 is able to maintain Akt activity and phosphorylation of proapoptotic proteins in cells that have lost matrix contact, Akt is not able to phosphorylate and inactivate another of its substrates, glycogen synthase kinase 3beta (GSK-3beta), under these conditions. The reason for this appears to be a rapid translocation of active Akt away from GSK-3beta when cells lose matrix contact. One target of GSK-3beta is cyclin D, which is turned over in response to this phosphorylation. Therefore, cyclin D is rapidly lost when cells are deprived of matrix contact, leading to a loss of cyclin-dependent kinase 4 activity and accumulation of hypophosphorylated, active Rb. This facilitates assembly of a repressor complex containing histone deacetylase (HDAC), Rb, and E2F that blocks transcription of the gene for IGF-1, leading to loss of Akt activity, accumulation of active proapoptotic proteins, and apoptosis. This feedback loop containing GSK-3beta, cyclin D, HDAC-Rb-E2F, and IGF-1 then determines how long Akt will remain active after cells lose matrix contact, and thus it serves to regulate the onset of apoptosis in such cells.
Figures

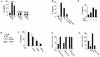
Similar articles
-
Cell anchorage regulates apoptosis through the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor/E2F pathway.J Biol Chem. 1997 Mar 28;272(13):8125-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.13.8125. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9079623
-
Retinoblastoma protein recruits histone deacetylase to repress transcription.Nature. 1998 Feb 5;391(6667):597-601. doi: 10.1038/35404. Nature. 1998. PMID: 9468139
-
Tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibits cyclin A expression and retinoblastoma hyperphosphorylation triggered by insulin-like growth factor-I induction of new E2F-1 synthesis.J Biol Chem. 2004 Feb 27;279(9):7438-46. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M310264200. Epub 2003 Dec 16. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14681231
-
Role of the Rb/E2F pathway in cell growth control.J Cell Physiol. 1997 Nov;173(2):233-6. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4652(199711)173:2<233::AID-JCP27>3.0.CO;2-F. J Cell Physiol. 1997. PMID: 9365528 Review. No abstract available.
-
The cell cycle-regulating transcription factors E2F-RB.Br J Cancer. 1999 Jul;80 Suppl 1:38-41. Br J Cancer. 1999. PMID: 10466760 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
To divide or not to divide: revisiting liver regeneration.Cell Div. 2013 Jun 20;8(1):8. doi: 10.1186/1747-1028-8-8. Cell Div. 2013. PMID: 23786799 Free PMC article.
-
Collagen-IV and laminin-1 regulate estrogen receptor alpha expression and function in mouse mammary epithelial cells.J Cell Sci. 2003 Jul 15;116(Pt 14):2975-86. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00523. J Cell Sci. 2003. PMID: 12808020 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular imaging metrics to evaluate response to preclinical therapeutic regimens.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2011 Jan 1;16(2):393-410. doi: 10.2741/3694. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2011. PMID: 21196177 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anoikis resistance: an essential prerequisite for tumor metastasis.Int J Cell Biol. 2012;2012:306879. doi: 10.1155/2012/306879. Epub 2012 Feb 23. Int J Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22505926 Free PMC article.
-
Sleeping Beauty and the Microenvironment Enchantment: Microenvironmental Regulation of the Proliferation-Quiescence Decision in Normal Tissues and in Cancer Development.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2018 Jun 7;6:59. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2018.00059. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2018. PMID: 29930939 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Andjelkovic M, Alessi D R, Meier R, Fernandez A, Lamb N J, Frech M, Cron P, Cohen P, Lucocq J M, Hemmings B A. Role of translocation in the activation and function of protein kinase B. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:31515–31524. - PubMed
-
- Baserga R, Sell C, Porcu P, Rubini M. The role of the IGF-1 receptor in the growth and transformation of mammalian cells. Cell Prolif. 1994;27:63–71. - PubMed
-
- Bellacosa A, de Feo D, Godwin A K, Bell D W, Cheng J Q, Altomare D A, Wan M, Dubeau L, Scambia G, Masciullo V, et al. Molecular alterations of the AKT2 oncogene in ovarian and breast carcinomas. Int J Cancer. 1995;64:280–285. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
