Allogeneic transplantation induces expression of cytomegalovirus immediate-early genes in vivo: a model for reactivation from latency
- PMID: 11312353
- PMCID: PMC114236
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.10.4814-4822.2001
Allogeneic transplantation induces expression of cytomegalovirus immediate-early genes in vivo: a model for reactivation from latency
Abstract
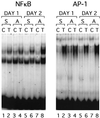
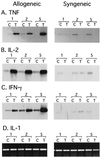
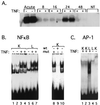
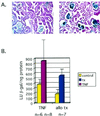
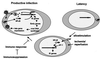
Reactivation of cytomegalovirus (CMV) from latency is a frequent complication of organ transplantation, and the molecular mechanism by which this occurs is unknown. Previous studies have shown that allogeneic stimulation induces reactivation of human CMV (HCMV) in vitro (64). We find that transplantation of vascularized allogeneic kidneys induces murine CMV (MCMV) and HCMV immediate-early (ie) gene expression. This induction is accompanied by increased expression of transcripts encoding inflammatory cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor (TNF), interleukin-2, and gamma interferon, and by activation of NF-kappaB. TNF alone can substitute for allogeneic transplantation in inducing HCMV and MCMV ie gene expression in some tissues. Our studies suggest that reactivation is a multistep process which is initiated by factors that induce ie gene expression, including TNF and NF-kappaB. Allogeneic transplantation combined with immunosuppression may be required to achieve complete reactivation in vivo.
Figures
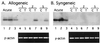
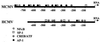
Similar articles
-
A model for reactivation of CMV from latency.J Clin Virol. 2002 Aug;25 Suppl 2:S123-36. doi: 10.1016/s1386-6532(02)00088-4. J Clin Virol. 2002. PMID: 12361763 Review.
-
Transplant-induced reactivation of murine cytomegalovirus immediate early gene expression is associated with recruitment of NF-κB and AP-1 to the major immediate early promoter.J Gen Virol. 2016 Apr;97(4):941-954. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.000407. Epub 2016 Jan 20. J Gen Virol. 2016. PMID: 26795571 Free PMC article.
-
Role for tumor necrosis factor alpha in murine cytomegalovirus transcriptional reactivation in latently infected lungs.J Virol. 2005 Jan;79(1):326-40. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.1.326-340.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15596827 Free PMC article.
-
CD8 T cells control cytomegalovirus latency by epitope-specific sensing of transcriptional reactivation.J Virol. 2006 Nov;80(21):10436-56. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01248-06. Epub 2006 Aug 23. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16928768 Free PMC article.
-
Mouse models of cytomegalovirus latency: overview.J Clin Virol. 2002 Aug;25 Suppl 2:S23-36. doi: 10.1016/s1386-6532(02)00087-2. J Clin Virol. 2002. PMID: 12361754 Review.
Cited by
-
TRIM22 inhibits HIV-1 transcription independently of its E3 ubiquitin ligase activity, Tat, and NF-kappaB-responsive long terminal repeat elements.J Virol. 2011 May;85(10):5183-96. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02302-10. Epub 2011 Feb 23. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21345949 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of cytomegalovirus load on host response to sepsis.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2019 Aug;208(3-4):295-303. doi: 10.1007/s00430-019-00603-y. Epub 2019 Apr 11. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30976913 Review.
-
The cytomegaloviral protein pUL138 acts as potentiator of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor 1 surface density to enhance ULb'-encoded modulation of TNF-α signaling.J Virol. 2011 Dec;85(24):13260-70. doi: 10.1128/JVI.06005-11. Epub 2011 Oct 5. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21976655 Free PMC article.
-
A myeloid progenitor cell line capable of supporting human cytomegalovirus latency and reactivation, resulting in infectious progeny.J Virol. 2012 Sep;86(18):9854-65. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01278-12. Epub 2012 Jul 3. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22761372 Free PMC article.
-
MCMV Dissemination from Latently-Infected Allografts Following Transplantation into Pre-Tolerized Recipients.Pathogens. 2020 Jul 26;9(8):607. doi: 10.3390/pathogens9080607. Pathogens. 2020. PMID: 32722544 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abecassis M M, Jiang X, O'Neil M E, Bale J F., Jr Detection of murine cytomegalovirus (MCMV) DNA in skin using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) Microb Pathog. 1993;15:17–22. - PubMed
-
- Baldwin A S. The NF-kB and IkB proteins: new discoveries and insights. Annu Rev Immunol. 1996;14:649–681. - PubMed
-
- Barnes P J, Karin M. Nuclear factor-kappaB: a pivotal transcription factor in chronic inflammatory diseases. N Engl J Med. 1997;336:1066–1071. - PubMed
-
- Baskar J F, Smith P P, Nilaver G, Jupp R A, Hoffmann S, Peffer N J, Tenney D J, Colberg-Poley A M, Ghazal P, Nelson J A. The enhancer domain of the human cytomegalovirus major immediate-early promoter determines cell type-specific expression in transgenic mice. J Virol. 1996;70:3207–3214. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bevan I S, Sammons C C, Sweet C. Investigation of murine cytomegalovirus latency and reactivation in mice using viral mutants and the polymerase chain reaction. J Med Virol. 1996;48:308–320. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

