Binding of recombinant feline immunodeficiency virus surface glycoprotein to feline cells: role of CXCR4, cell-surface heparans, and an unidentified non-CXCR4 receptor
- PMID: 11312323
- PMCID: PMC114206
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.10.4528-4539.2001
Binding of recombinant feline immunodeficiency virus surface glycoprotein to feline cells: role of CXCR4, cell-surface heparans, and an unidentified non-CXCR4 receptor
Abstract
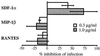
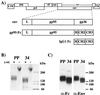
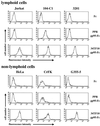
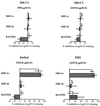
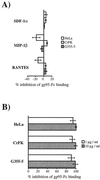
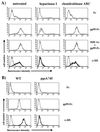
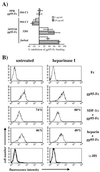
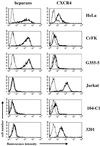
To address the role of CXCR4 in the cell-surface attachment of the feline immunodeficency virus (FIV), a soluble fusion protein, gp95-Fc, consisting of the surface glycoprotein (SU, gp95) of either a primary (PPR) or cell line-adapted (34TF10) FIV strain was fused in frame with the Fc domain of human immunoglobulin G1. The recombinant SU-immunoadhesins were used as probes to investigate the cellular binding of FIV SU. In agreement with the host cell range properties of both viruses, binding of 34TF10 gp95-Fc was observed for all cell lines tested, whereas PPR gp95-Fc bound only to primary feline T cells. 34TF10 gp95-Fc also bound to Jurkat and HeLa cells, consistent with the ability of FIV to use human CXCR4 as a fusion receptor. As expected, 34TF10 gp95-Fc binding to Jurkat cells was blocked by addition of stromal cell-derived factor 1alpha (SDF-1alpha), as was binding to the 3201 feline lymphoma cell line. However, SDF-1alpha, RANTES, macrophage inflammatory protein 1beta, and heparin all failed to inhibit the binding of either gp95-Fc to primary T cells, suggesting that a non-CXCR4 receptor is involved in the binding of FIV SU. In this regard, an unidentified 40-kDa protein species from the surface of primary T cells but not Jurkat and 3201 cells specifically coprecipitated with both gp95-Fc. Yet another type of binding of 34TF10 gp95-Fc to adherent kidney cells was noted. SDF-1alpha failed to block the binding of 34TF10 gp95-Fc to either HeLa, Crandel feline leukemia, or G355-5 cells. However, binding was severely impaired in the presence of soluble heparin, as well as after enzymatic removal of surface heparans or on cells deficient in heparan expression. These overall findings suggest that in addition to CXCR4, a non-CXCR4 receptor and cell-surface heparans also play an important role in FIV gp95 cell surface interactions on specific target cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Factors that increase the effective concentration of CXCR4 dictate feline immunodeficiency virus tropism and kinetics of replication.J Virol. 2004 Sep;78(17):9132-43. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.17.9132-9143.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15308709 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of amino acid residues important for heparan sulfate proteoglycan interaction within variable region 3 of the feline immunodeficiency virus surface glycoprotein.J Virol. 2011 Jul;85(14):7108-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00573-11. Epub 2011 May 4. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21543468 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping of the CXCR4 binding site within variable region 3 of the feline immunodeficiency virus surface glycoprotein.J Virol. 2008 Sep;82(18):9134-42. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00394-08. Epub 2008 Jul 2. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18596086 Free PMC article.
-
The virus-receptor interaction in the replication of feline immunodeficiency virus (FIV).Curr Opin Virol. 2013 Dec;3(6):670-5. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2013.08.003. Epub 2013 Aug 28. Curr Opin Virol. 2013. PMID: 23992667 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 in infection with feline immunodeficiency virus.Mol Membr Biol. 1999 Jan-Mar;16(1):67-72. doi: 10.1080/096876899294779. Mol Membr Biol. 1999. PMID: 10332739 Review.
Cited by
-
Methamphetamine enhances cell-associated feline immunodeficiency virus replication in astrocytes.J Neurovirol. 2002 Jun;8(3):240-9. doi: 10.1080/13550280290049660. J Neurovirol. 2002. PMID: 12053278
-
Specific interaction of feline immunodeficiency virus surface glycoprotein with human DC-SIGN.J Virol. 2004 Mar;78(5):2597-600. doi: 10.1128/jvi.78.5.2597-2600.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 14963164 Free PMC article.
-
Improved health and survival of FIV-infected cats is associated with the presence of autoantibodies to the primary receptor, CD134.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Nov 24;106(47):19980-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0911307106. Epub 2009 Nov 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19901342 Free PMC article.
-
Plectin regulates the signaling and trafficking of the HIV-1 co-receptor CXCR4 and plays a role in HIV-1 infection.Exp Cell Res. 2008 Feb 1;314(3):590-602. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2007.10.032. Epub 2007 Nov 17. Exp Cell Res. 2008. PMID: 18155192 Free PMC article.
-
Domestic cat microsphere immunoassays: detection of antibodies during feline immunodeficiency virus infection.J Immunol Methods. 2013 Oct 31;396(1-2):74-86. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2013.08.001. Epub 2013 Aug 14. J Immunol Methods. 2013. PMID: 23954271 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alkhatib G, Combadiere C, Broder C C, Feng Y, Kennedy P E, Murphy P M, Berger E A. CC CKR5: a RANTES, MIP-1alpha, MIP-1beta receptor as a fusion cofactor for macrophage-tropic HIV-1. Science. 1996;272:1955–1958. - PubMed
-
- Altin J G, Pagler E B. A one-step procedure for biotinylation and chemical cross-linking of lymphocyte surface and intracellular membrane-associated molecules. Anal Biochem. 1995;224:382–389. - PubMed
-
- Aruffo A, Stamenkovic I, Melnick M, Underhill C B, Seed B. CD44 is the principal cell surface receptor for hyaluronate. Cell. 1990;61:1303–1313. - PubMed
-
- Batinic D, Robey F A. The V3 region of the envelope glycoprotein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 binds sulfated polysaccharides and CD4-derived synthetic peptides. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:6664–6671. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

