Pathogenic function of IL-1 beta in psoriasiform skin lesions of flaky skin (fsn/fsn) mice
- PMID: 11298140
- PMCID: PMC1906010
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2001.01421.x
Pathogenic function of IL-1 beta in psoriasiform skin lesions of flaky skin (fsn/fsn) mice
Abstract
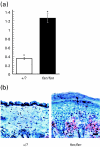
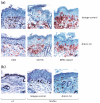
IL-1 acts on many cells as an inflammatory mediator. Its two forms, IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta, are regulated differentially within hyperproliferative inflammatory skin conditions, such as psoriasis. While IL-1 alpha is down-regulated within psoriatic lesions, the levels of IL-1 beta are increased. However, some investigators have described an inactive form of IL-1 beta in psoriasis, while others have detected increased IL-1 beta activity within these lesions. Thus, its in vivo role remains unclear. We have assessed expression and function of IL-1 beta within psoriasiform skin lesions of the spontaneous mouse mutation flaky skin (fsn/fsn ). It was found that IL-1 beta was increased by 357% within psoriasiform lesions of fsn/fsn mice compared with their wild-type or heterozygous (+/?) littermates (P < 0.00001). When the IL-1 beta function was inhibited by i.p. injection with a neutralizing MoAb, no effects were seen in +/? mice. In contrast, psoriasiform features in fsn/fsn mice were alleviated dramatically, as demonstrated by a 40% decrease of the epidermal thickness and a diminished number of intra-epidermal microabscesses. In addition, infiltrating epidermal CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells were decreased by 68% and 81%, respectively (P < 0.05), and epidermal Langerhans cells also were reduced by 36% (P < 0.005). In contrast, mast cells were not affected, suggesting differential responses of various cutaneous cell types. Our results demonstrate an important in vivo role of IL-1 beta for the generation of hyperproliferative inflammatory skin lesions in the fsn/fsn model.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Critical role of neutrophils for the generation of psoriasiform skin lesions in flaky skin mice.J Invest Dermatol. 2000 May;114(5):976-83. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1747.2000.00953.x. J Invest Dermatol. 2000. PMID: 10771480
-
Dysregulated expression of CD69 and IL-2 receptor alpha and beta chains on CD8+ T lymphocytes in flaky skin mice.Immunol Cell Biol. 2000 Dec;78(6):596-602. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1711.2000.00945.x. Immunol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 11114969
-
Development and progression of psoriasiform dermatitis and systemic lesions in the flaky skin (fsn) mouse mutant.Pathobiology. 1997;65(5):271-86. doi: 10.1159/000164138. Pathobiology. 1997. PMID: 9459497
-
Animal models of psoriasis - what can we learn from them?J Invest Dermatol. 1999 Apr;112(4):405-10. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1747.1999.00538.x. J Invest Dermatol. 1999. PMID: 10201521 Review.
-
Psoriasiform dermatoses.Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2008 Mar-Apr;74(2):94-9. doi: 10.4103/0378-6323.39688. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2008. PMID: 18388363 Review.
Cited by
-
Involvement of Neuro-Immune Interactions in Pruritus With Special Focus on Receptor Expressions.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Feb 18;8:627985. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.627985. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33681256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A new model for dermatitis herpetiformis that uses HLA-DQ8 transgenic NOD mice.J Clin Invest. 2004 Oct;114(8):1090-7. doi: 10.1172/JCI21055. J Clin Invest. 2004. PMID: 15489956 Free PMC article.
-
Human Langerhans Cells with Pro-inflammatory Features Relocate within Psoriasis Lesions.Front Immunol. 2018 Feb 22;9:300. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00300. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29520279 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like dermatitis in mice by herbal extracts from some Indian medicinal plants.Protoplasma. 2016 Mar;253(2):503-15. doi: 10.1007/s00709-015-0829-y. Epub 2015 May 28. Protoplasma. 2016. PMID: 26016607
-
Dissolving Candlelit Microneedle for Chronic Inflammatory Skin Diseases.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021 May 7;8(14):2004873. doi: 10.1002/advs.202004873. eCollection 2021 Jul. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021. PMID: 34306973 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Christophers E, Sterry W. Psoriasis. In: Fitzpatrick TB, Eisen AZ, Wolff K, Freedberg IM, Austen KF, editors. Dermatology in general medicine. New York: McGraw-Hill Inc.; 1993. pp. 489–514.
-
- Nickoloff BJ. The cytokine network of psoriasis. Arch Dermatol. 1991;127:871–84. - PubMed
-
- Kim N-I, Cooper KD, Fisher GJ, et al. Psoriatic skin reveals the in vivo presence of an epidermal IL-1 inhibitor. Arch Dermatol Res. 1992;284:71–76. - PubMed
-
- Prens EP, Benne K, van Damme J, et al. Interleukin-1 and interleukin-6 in psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol. 1990;95:121S–124S. - PubMed
-
- Uyemura K, Yamamura M, Fivenson DF, et al. The cytokine network in lesional and lesion-free psoriatic skin is characterized by a T-helper type 1 cell-mediated response. J Invest Dermatol. 1993;101:701–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

