Neurogenesis in dentate subgranular zone and rostral subventricular zone after focal cerebral ischemia in the rat
- PMID: 11296300
- PMCID: PMC31899
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.081011098
Neurogenesis in dentate subgranular zone and rostral subventricular zone after focal cerebral ischemia in the rat
Abstract
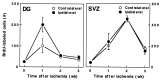
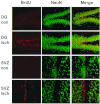
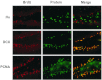
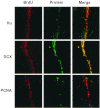
Because neurogenesis persists in the adult mammalian brain and can be regulated by physiological and pathological events, we investigated its possible involvement in the brain's response to focal cerebral ischemia. Ischemia was induced by occlusion of the middle cerebral artery in the rat for 90 min, and proliferating cells were labeled with 5-bromo-2'-deoxyuridine-5'-monophosphate (BrdUrd) over 2-day periods before sacrificing animals 1, 2 or 3 weeks after ischemia. Ischemia increased the incorporation of BrdUrd into cells in two neuroproliferative regions-the subgranular zone of the dentate gyrus and the rostral subventricular zone. Both effects were bilateral, but that in the subgranular zone was more prominent on the ischemic side. Cells labeled with BrdUrd coexpressed the immature neuronal markers doublecortin and proliferating cell nuclear antigen but did not express the more mature cell markers NeuN and Hu, suggesting that they were nascent neurons. These results support a role for ischemia-induced neurogenesis in what may be adaptive processes that contribute to recovery after stroke.
Figures
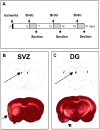
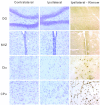
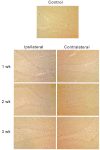
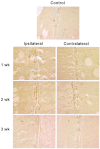
Similar articles
-
Sustained increase in adult neurogenesis in the rat hippocampal dentate gyrus after transient brain ischemia.Neurosci Lett. 2011 Jan 13;488(1):70-5. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2010.10.079. Epub 2010 Nov 5. Neurosci Lett. 2011. PMID: 21056620
-
Temporal profile of neurogenesis in the subventricular zone, dentate gyrus and cerebral cortex following transient focal cerebral ischemia.Neurol Res. 2009 Nov;31(9):969-76. doi: 10.1179/174313209X383312. Epub 2009 Jan 9. Neurol Res. 2009. PMID: 19138475
-
Proliferation and differentiation of progenitor cells in the cortex and the subventricular zone in the adult rat after focal cerebral ischemia.Neuroscience. 2001;105(1):33-41. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(01)00117-8. Neuroscience. 2001. PMID: 11483298
-
Lithium fails to enhance neurogenesis in subventricular zone and dentate subgranular zone after intracerebral hemorrhage in rats.Neurol Res. 2014 Jan;36(1):79-85. doi: 10.1179/1743132813Y.0000000265. Epub 2013 Dec 6. Neurol Res. 2014. PMID: 24107386
-
N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-mediated increase of neurogenesis in adult rat dentate gyrus following stroke.Eur J Neurosci. 2001 Jul;14(1):10-8. doi: 10.1046/j.0953-816x.2001.01611.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11488944
Cited by
-
Delayed hyperbaric oxygen therapy induces cell proliferation through stabilization of cAMP responsive element binding protein in the rat model of MCAo-induced ischemic brain injury.Neurobiol Dis. 2013 Mar;51:133-43. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2012.11.003. Epub 2012 Nov 10. Neurobiol Dis. 2013. PMID: 23146993 Free PMC article.
-
Rit GTPase signaling promotes immature hippocampal neuronal survival.J Neurosci. 2012 Jul 18;32(29):9887-97. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0375-12.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22815504 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective mechanism of Lycium barbarum polysaccharides against hippocampal-dependent spatial memory deficits in a rat model of obstructive sleep apnea.PLoS One. 2015 Feb 25;10(2):e0117990. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117990. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25714473 Free PMC article.
-
Intravenous injection of neural progenitor cells improved depression-like behavior after cerebral ischemia.Transl Psychiatry. 2011 Aug 9;1(8):e29. doi: 10.1038/tp.2011.32. Transl Psychiatry. 2011. PMID: 22832603 Free PMC article.
-
Mutant alpha-synuclein exacerbates age-related decrease of neurogenesis.Neurobiol Aging. 2008 Jun;29(6):913-25. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2006.12.016. Epub 2007 Jan 31. Neurobiol Aging. 2008. PMID: 17275140 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McKay R. Science. 1997;276:66–71. - PubMed
-
- Martinez-Serrano A, Bjorklund A. Trends Neurosci. 1997;20:530–538. - PubMed
-
- Scheffler B, Horn M, Blumcke I, Laywell E D, Coomes D, Kukekov V G, Steindler D A. Trends Neurosci. 1999;22:348–357. - PubMed
-
- van der Kooy D, Weiss S. Science. 2000;287:1439–1441. - PubMed
-
- Gage F H. Science. 2000;287:1433–1438. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

