RNA tertiary interactions in the large ribosomal subunit: the A-minor motif
- PMID: 11296253
- PMCID: PMC33135
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.081082398
RNA tertiary interactions in the large ribosomal subunit: the A-minor motif
Abstract
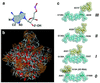
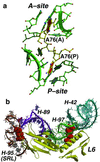
Analysis of the 2.4-A resolution crystal structure of the large ribosomal subunit from Haloarcula marismortui reveals the existence of an abundant and ubiquitous structural motif that stabilizes RNA tertiary and quaternary structures. This motif is termed the A-minor motif, because it involves the insertion of the smooth, minor groove edges of adenines into the minor groove of neighboring helices, preferentially at C-G base pairs, where they form hydrogen bonds with one or both of the 2' OHs of those pairs. A-minor motifs stabilize contacts between RNA helices, interactions between loops and helices, and the conformations of junctions and tight turns. The interactions between the 3' terminal adenine of tRNAs bound in either the A site or the P site with 23S rRNA are examples of functionally significant A-minor interactions. The A-minor motif is by far the most abundant tertiary structure interaction in the large ribosomal subunit; 186 adenines in 23S and 5S rRNA participate, 68 of which are conserved. It may prove to be the universally most important long-range interaction in large RNA structures.
Figures
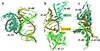
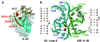
Similar articles
-
The complete atomic structure of the large ribosomal subunit at 2.4 A resolution.Science. 2000 Aug 11;289(5481):905-20. doi: 10.1126/science.289.5481.905. Science. 2000. PMID: 10937989
-
Sequence and structural conservation in RNA ribose zippers.J Mol Biol. 2002 Jul 12;320(3):455-74. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(02)00515-6. J Mol Biol. 2002. PMID: 12096903
-
The structures of four macrolide antibiotics bound to the large ribosomal subunit.Mol Cell. 2002 Jul;10(1):117-28. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(02)00570-1. Mol Cell. 2002. PMID: 12150912
-
Progress toward an understanding of the structure and enzymatic mechanism of the large ribosomal subunit.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2001;66:33-42. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2001.66.33. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2001. PMID: 12762006 Review. No abstract available.
-
High-resolution structures of large ribosomal subunits from mesophilic eubacteria and halophilic archaea at various functional States.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2002 Feb;3(1):67-78. doi: 10.2174/1389203023380828. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2002. PMID: 12370012 Review.
Cited by
-
The structure and catalytic mechanism of a pseudoknot-containing hammerhead ribozyme.Nat Commun. 2024 Aug 5;15(1):6628. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-50892-y. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39103372 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and mechanism of purine-binding riboswitches.Q Rev Biophys. 2012 Aug;45(3):345-81. doi: 10.1017/S0033583512000078. Epub 2012 Jul 31. Q Rev Biophys. 2012. PMID: 22850604 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chaperna: linking the ancient RNA and protein worlds.RNA Biol. 2021 Jan;18(1):16-23. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2020.1801199. Epub 2020 Aug 11. RNA Biol. 2021. PMID: 32781880 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure of the RNA claw of the DNA packaging motor of bacteriophage Φ29.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Oct;40(19):9953-63. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks724. Epub 2012 Aug 8. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22879380 Free PMC article.
-
RNAMotifProfile: a graph-based approach to build RNA structural motif profiles.NAR Genom Bioinform. 2024 Sep 26;6(3):lqae128. doi: 10.1093/nargab/lqae128. eCollection 2024 Sep. NAR Genom Bioinform. 2024. PMID: 39328267 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

