The ADP ribosylation factor-nucleotide exchange factors Gea1p and Gea2p have overlapping, but not redundant functions in retrograde transport from the Golgi to the endoplasmic reticulum
- PMID: 11294905
- PMCID: PMC32285
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.12.4.1035
The ADP ribosylation factor-nucleotide exchange factors Gea1p and Gea2p have overlapping, but not redundant functions in retrograde transport from the Golgi to the endoplasmic reticulum
Abstract
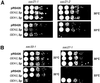
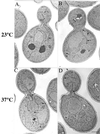
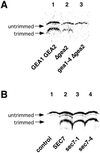
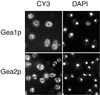
The activation of the small ras-like GTPase Arf1p requires the action of guanine nucleotide exchange factors. Four Arf1p guanine nucleotide exchange factors have been identified in yeast: Sec7p, Syt1p, Gea1p, and its homologue Gea2p. We identified GEA2 as a multicopy suppressor of a sec21-3 temperature-sensitive mutant. SEC21 encodes the gamma-subunit of coatomer, a heptameric protein complex that together with Arf1p forms the COPI coat. GEA1 and GEA2 have at least partially overlapping functions, because deletion of either gene results in no obvious phenotype, whereas the double null mutant is inviable. Conditional mutants defective in both GEA1 and GEA2 accumulate endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi membranes under restrictive conditions. The two genes do not serve completely overlapping functions because a Deltagea1 Deltaarf1 mutant is not more sickly than a Deltaarf1 strain, whereas Deltagea2 Deltaarf1 is inviable. Biochemical experiments revealed similar distributions and activities for the two proteins. Gea1p and Gea2p exist both in membrane-bound and in soluble forms. The membrane-bound forms, at least one of which, Gea2p, can be visualized on Golgi structures, are both required for vesicle budding and protein transport from the Golgi to the endoplasmic reticulum. In contrast, Sec7p, which is required for protein transport within the Golgi, is not required for retrograde protein trafficking.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A role for GEA1 and GEA2 in the organization of the actin cytoskeleton in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2003 Nov;165(3):985-95. doi: 10.1093/genetics/165.3.985. Genetics. 2003. PMID: 14668359 Free PMC article.
-
The ARF exchange factors Gea1p and Gea2p regulate Golgi structure and function in yeast.J Cell Sci. 2001 Jun;114(Pt 12):2241-53. doi: 10.1242/jcs.114.12.2241. J Cell Sci. 2001. PMID: 11493664
-
Mutations in a highly conserved region of the Arf1p activator GEA2 block anterograde Golgi transport but not COPI recruitment to membranes.Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Aug;16(8):3786-99. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e05-04-0289. Epub 2005 Jun 1. Mol Biol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15930122 Free PMC article.
-
The role of ADP-ribosylation factor and SAR1 in vesicular trafficking in plants.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004 Jul 1;1664(1):9-30. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2004.04.005. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004. PMID: 15238254 Review.
-
The structure of COPI vesicles and regulation of vesicle turnover.FEBS Lett. 2023 Mar;597(6):819-835. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.14560. Epub 2022 Dec 30. FEBS Lett. 2023. PMID: 36513395 Review.
Cited by
-
Arf1 directly recruits the Pik1-Frq1 PI4K complex to regulate the final stages of Golgi maturation.Mol Biol Cell. 2021 May 1;32(10):1064-1080. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E21-02-0069. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Mol Biol Cell. 2021. PMID: 33788598 Free PMC article.
-
GTPase networks in membrane traffic.Annu Rev Biochem. 2012;81:637-59. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-052810-093700. Epub 2012 Mar 29. Annu Rev Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22463690 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel Golgi membrane protein is a partner of the ARF exchange factors Gea1p and Gea2p.Mol Biol Cell. 2003 Jun;14(6):2357-71. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e02-10-0693. Epub 2003 Mar 7. Mol Biol Cell. 2003. PMID: 12808035 Free PMC article.
-
The small GTPase Arf1 modulates mitochondrial morphology and function.EMBO J. 2014 Nov 18;33(22):2659-75. doi: 10.15252/embj.201489039. Epub 2014 Sep 4. EMBO J. 2014. PMID: 25190516 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Arf activation occurs via distinct mechanisms at early and late Golgi compartments.Mol Biol Cell. 2017 Dec 1;28(25):3660-3671. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E17-06-0370. Epub 2017 Oct 4. Mol Biol Cell. 2017. PMID: 28978742 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baker D, Hicke L, Rexach M, Schleyer M, Schekman R. Reconstitution of SEC gene product-dependent intercompartmental protein transport. Cell. 1988;54:335–344. - PubMed
-
- Barlowe C, Orci L, Yeung T, Hosobuchi M, Hamamoto S, Salama N, Rexach MF, Ravazzola M, Amherdt M, Schekman R. COPII: a membrane coat formed by Sec proteins that drive vesicle budding from the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1994;77:895–907. - PubMed
-
- Bednarek SY, Ravazzola M, Hosobuchi M, Amherdt M, Perrelet A, Schekman R, Orci L. COPI- and COPII-coated vesicles bud directly from the endoplasmic reticulum in yeast. Cell. 1995;83:1183–1196. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

