Induction of beta3-integrin gene expression by sustained activation of the Ras-regulated Raf-MEK-extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathway
- PMID: 11287623
- PMCID: PMC86954
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.21.9.3192-3205.2001
Induction of beta3-integrin gene expression by sustained activation of the Ras-regulated Raf-MEK-extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathway
Abstract
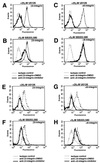
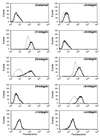
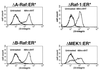
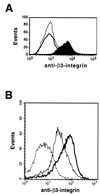
Alterations in the expression of integrin receptors for extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins are strongly associated with the acquisition of invasive and/or metastatic properties by human cancer cells. Despite this, comparatively little is known of the biochemical mechanisms that regulate the expression of integrin genes in cells. Here we demonstrate that the Ras-activated Raf-MEK-extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling pathway can specifically control the expression of individual integrin subunits in a variety of human and mouse cell lines. Pharmacological inhibition of MEK1 in a number of human melanoma and pancreatic carcinoma cell lines led to reduced cell surface expression of alpha6- and beta3-integrin. Consistent with this, conditional activation of the Raf-MEK-ERK pathway in NIH 3T3 cells led to a 5 to 20-fold induction of cell surface alpha6- and beta3-integrin expression. Induced beta3-integrin was expressed on the cell surface as a heterodimer with alphav-integrin; however, the overall level of alphav-integrin expression was not altered by Ras or Raf. Raf-induced beta3-integrin was observed in primary and established mouse fibroblast lines and in mouse and human endothelial cells. Consistent with previous reports of the ability of the Raf-MEK-ERK signaling pathway to induce beta3-integrin gene transcription in human K-562 erythroleukemia cells, Raf activation in NIH 3T3 cells led to elevated beta3-integrin mRNA. However, unlike immediate-early Raf targets such as heparin binding epidermal growth factor and Mdm2, beta3-integrin mRNA was induced by Raf in a manner that was cycloheximide sensitive. Surprisingly, activation of the Raf-MEK-ERK signaling pathway by growth factors and mitogens had little or no effect on beta3-integrin expression, suggesting that the expression of this gene requires sustained activation of this signaling pathway. In addition, despite the robust induction of cell surface alphavbeta3-integrin expression by Raf in NIH 3T3 cells, such cells display decreased spreading and adhesion, with a loss of focal adhesions and actin stress fibers. These data suggest that oncogene-induced alterations in integrin gene expression may participate in the changes in cell adhesion and migration that accompany the process of oncogenic transformation.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Radicicol suppresses transformation and restores tropomyosin-2 expression in both ras- and MEK-transformed cells without inhibiting the Raf/MEK/ERK signaling cascade.Cell Growth Differ. 2001 Nov;12(11):543-50. Cell Growth Differ. 2001. PMID: 11714635
-
Different effects of point mutations within the B-Raf glycine-rich loop in colorectal tumors on mitogen-activated protein/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase and nuclear factor kappaB pathway and cellular transformation.Cancer Res. 2004 May 15;64(10):3428-35. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-03-3591. Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15150094
-
The Ras/Raf/MEK/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway induces autocrine-paracrine growth inhibition via the leukemia inhibitory factor/JAK/STAT pathway.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Jan;23(2):543-54. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.2.543-554.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12509453 Free PMC article.
-
[Roles of targeting Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathways in the treatment of esophageal carcinoma].Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2013 May;48(5):635-41. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2013. PMID: 23888683 Review. Chinese.
-
Roles of the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in cell growth, malignant transformation and drug resistance.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007 Aug;1773(8):1263-84. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2006.10.001. Epub 2006 Oct 7. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007. PMID: 17126425 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA 9-3p targets β1 integrin to sensitize claudin-low breast cancer cells to MEK inhibition.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Jun;33(11):2260-74. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00269-13. Epub 2013 Mar 25. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23530058 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting mutant BRAF in melanoma: current status and future development of combination therapy strategies.Cancer J. 2012 Mar-Apr;18(2):124-31. doi: 10.1097/PPO.0b013e31824b436e. Cancer J. 2012. PMID: 22453012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increased expression levels of integrin alphavbeta5 on scleroderma fibroblasts.Am J Pathol. 2004 Apr;164(4):1275-92. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)63215-4. Am J Pathol. 2004. PMID: 15039216 Free PMC article.
-
Augmentation of therapeutic responses in melanoma by inhibition of IRAK-1,-4.Cancer Res. 2012 Dec 1;72(23):6209-16. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-0337. Epub 2012 Oct 4. Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 23041547 Free PMC article.
-
Feeling Things Out: Bidirectional Signaling of the Cell-ECM Interface, Implications in the Mechanobiology of Cell Spreading, Migration, Proliferation, and Differentiation.Adv Healthc Mater. 2020 Apr;9(8):e1901445. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201901445. Epub 2020 Feb 9. Adv Healthc Mater. 2020. PMID: 32037719 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Albelda S M, Mette S A, Elder D E, Stewart R, Damjanovich L, Herlyn M, Buck C A. Integrin distribution in malignant melanoma: association of the beta 3 subunit with tumor progression. Cancer Res. 1990;50:6757–6764. - PubMed
-
- Alberts A S, Geneste O, Treisman R. Activation of SRF-regulated chromosomal templates by Rho-family GTPases requires a signal that also induces H4 hyperacetylation. Cell. 1998;92:475–487. - PubMed
-
- Albino A P, Shea C R, McNutt N S. Oncogenes in melanomas. J Dermatol. 1992;19:853–867. - PubMed
-
- Barnard J A, Graves-Deal R, Pittelkow M R, DuBois R, Cook P, Ramsey G W, Bishop P R, Damstrup L, Coffey R J. Auto- and cross-induction within the mammalian epidermal growth factor-related peptide family. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:22817–22822. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
