Macaques with rapid disease progression and simian immunodeficiency virus encephalitis have a unique cytokine profile in peripheral lymphoid tissues
- PMID: 11287599
- PMCID: PMC114195
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.9.4448-4452.2001
Macaques with rapid disease progression and simian immunodeficiency virus encephalitis have a unique cytokine profile in peripheral lymphoid tissues
Abstract
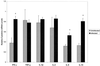
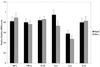
The influence of host cytokine response on viral load, disease progression, and neurologic lesions was investigated in the simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV)-infected macaque model of AIDS. Cytokine gene expression (interleukin-1beta [IL-1beta], IL-2, IL-6, IL-10, gamma interferon [IFN-gamma], and tumor necrosis factor alpha [TNF-alpha]) and viral loads were evaluated by semiquantitative reverse transcription-PCR in lymph nodes of 5 control animals and 28 animals infected with SIVmac251 at the terminal stages of AIDS. Infected animals showed higher expression of IFN-gamma, IL-6, and IL-10 mRNAs compared with controls. Levels of all cytokines were comparable between animals with rapid (survival, <200 days) or slow/normal (survival, >200 days) disease progression. However, among rapid progressors, the eight animals with SIV encephalitis had a unique cytokine profile (increased IL-2, IL-6, and IFN-gamma) that was associated with higher viral loads. These observations provide evidence that host cytokine responses may influence SIV neuropathogenesis independent of disease progression.
Figures

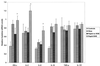
Similar articles
-
Enhanced expression of proinflammatory cytokines in the central nervous system is associated with neuroinvasion by simian immunodeficiency virus and the development of encephalitis.J Virol. 2002 Jun;76(11):5797-802. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.11.5797-5802.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 11992008 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of proinflammatory cytokines and its relationship with virus infection in the brain of macaques inoculated with macrophage-tropic simian immunodeficiency virus.Neuropathology. 2009 Feb;29(1):13-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1789.2008.00929.x. Epub 2008 May 27. Neuropathology. 2009. PMID: 18507770
-
Simian immunodeficiency virus encephalitis in rhesus macaques is associated with rapid disease progression.J Neurovirol. 1998 Jun;4(3):260-8. doi: 10.3109/13550289809114527. J Neurovirol. 1998. PMID: 9639069
-
Searching for clues: tracking the pathogenesis of human immunodeficiency virus central nervous system disease by use of an accelerated, consistent simian immunodeficiency virus macaque model.J Infect Dis. 2002 Dec 1;186 Suppl 2:S199-208. doi: 10.1086/344938. J Infect Dis. 2002. PMID: 12424698 Review.
-
Non-human primate models of SIV infection and CNS neuropathology.Curr Opin Virol. 2016 Aug;19:92-8. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2016.07.012. Epub 2016 Aug 18. Curr Opin Virol. 2016. PMID: 27544476 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A rapid progressor-specific variant clone of simian immunodeficiency virus replicates efficiently in vivo only in the absence of immune responses.J Virol. 2007 Sep;81(17):8891-904. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00614-07. Epub 2007 Jun 27. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17596304 Free PMC article.
-
Mucosal innate immune response associated with a timely humoral immune response and slower disease progression after oral transmission of simian immunodeficiency virus to rhesus macaques.J Virol. 2007 Jun;81(12):6175-86. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00042-07. Epub 2007 Apr 11. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17428863 Free PMC article.
-
Early control of highly pathogenic simian immunodeficiency virus/human immunodeficiency virus chimeric virus infections in rhesus monkeys usually results in long-lasting asymptomatic clinical outcomes.J Virol. 2003 Oct;77(20):10829-40. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.20.10829-10840.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 14512533 Free PMC article.
-
Gamma interferon-mediated inflammation is associated with lack of protection from intravaginal simian immunodeficiency virus SIVmac239 challenge in simian-human immunodeficiency virus 89.6-immunized rhesus macaques.J Virol. 2004 Jan;78(2):841-54. doi: 10.1128/jvi.78.2.841-854.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 14694116 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of HIV infection and HAART on inflammatory biomarkers in a population-based cohort of women.AIDS. 2011 Sep 24;25(15):1823-32. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e3283489d1f. AIDS. 2011. PMID: 21572306 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brice G T, Mayne A E, Villinger F, Ansari A A. A novel role for tumor necrosis factor-alpha in regulating susceptibility of activated CD4+ T cells from human and nonhuman primates for distinct coreceptor using lentiviruses. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2000;24:10–22. - PubMed
-
- Cheret A, Le Grand R, Caufour P, Dereuddre-Bosquet N, Matheux F, Neildez O, Theodoro F, Maestrali N, Benveniste O, Vaslin B, Dormont D. Cytokine mRNA expression in mononuclear cells from different tissues during acute SIVmac251 infection of macaques. AIDS Res Hum Retrovir. 1996;12:1263–1272. - PubMed
-
- Clerici M, Balotta C, Meroni L, Ferrario E, Riva C, Trabattoni D, Ridolfo A, Villa M, Shearer G M, Moroni M, Galli M. Type 1 cytokine production and low prevalence of viral isolation correlate with long-term nonprogression in HIV infection. AIDS Res Hum Retrovir. 1996;12:1053–1061. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

