Inhibition of T1/ST2 during respiratory syncytial virus infection prevents T helper cell type 2 (Th2)- but not Th1-driven immunopathology
- PMID: 11283151
- PMCID: PMC2193366
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.193.7.785
Inhibition of T1/ST2 during respiratory syncytial virus infection prevents T helper cell type 2 (Th2)- but not Th1-driven immunopathology
Abstract
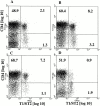
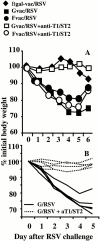
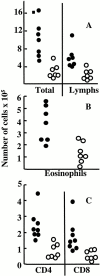
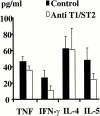
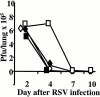
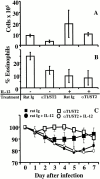
T cells secreting interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-5 (T helper cell type 2 [Th2] cells) play a detrimental role in a variety of diseases, but specific methods of regulating their activity remain elusive. T1/ST2 is a surface ligand of the IL-1 receptor family, expressed on Th2- but not on interferon (IFN)-gamma-producing Th1 cells. Prior exposure of BALB/c mice to the attachment (G) or fusion (F) protein of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) increases illness severity during intranasal RSV challenge, due to Th2-driven lung eosinophilia and exuberant Th1-driven pulmonary infiltration, respectively. We used these polar models of viral illness to study the recruitment of T1/ST2 cells to the lung and to test the effects of anti-T1/ST2 treatment in vivo. T1/ST2 was present on a subset of CD4(+) cells from mice with eosinophilic lung disease. Monoclonal anti-T1/ST2 treatment reduced lung inflammation and the severity of illness in mice with Th2 (but not Th1) immunopathology. These results show that inhibition of T1/ST2 has a specific effect on virally induced Th2 responses and suggests that therapy targeted at this receptor might be of value in treating Th2-driven illness.
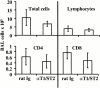
Figures
Similar articles
-
Crucial role of the interleukin 1 receptor family member T1/ST2 in T helper cell type 2-mediated lung mucosal immune responses.J Exp Med. 1999 Oct 4;190(7):895-902. doi: 10.1084/jem.190.7.895. J Exp Med. 1999. PMID: 10510079 Free PMC article.
-
IL-33 Receptor (ST2) Signalling is Important for Regulation of Th2-Mediated Airway Inflammation in a Murine Model of Acute Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection.Scand J Immunol. 2015 Jun;81(6):494-501. doi: 10.1111/sji.12284. Scand J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25721734
-
Natural helper cells contribute to pulmonary eosinophilia by producing IL-13 via IL-33/ST2 pathway in a murine model of respiratory syncytial virus infection.Int Immunopharmacol. 2015 Sep;28(1):337-43. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2015.05.035. Epub 2015 Jun 1. Int Immunopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26044350
-
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) evades the human adaptive immune system by skewing the Th1/Th2 cytokine balance toward increased levels of Th2 cytokines and IgE, markers of allergy--a review.Virus Genes. 2006 Oct;33(2):235-52. doi: 10.1007/s11262-006-0064-x. Virus Genes. 2006. PMID: 16972040 Review.
-
IL-33/ST2 axis in inflammation and immunopathology.Immunol Res. 2012 Apr;52(1-2):89-99. doi: 10.1007/s12026-012-8283-9. Immunol Res. 2012. PMID: 22392053 Review.
Cited by
-
Signaling through the T1/ST2 molecule is not necessary for Th2 differentiation but is important for the regulation of type 1 responses in nonhealing Leishmania major infection.Infect Immun. 2003 Apr;71(4):1961-71. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.4.1961-1971.2003. Infect Immun. 2003. PMID: 12654814 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenicity and efficacy of recombinant RSV-F vaccine in a mouse model.Vaccine. 2007 Aug 14;25(33):6211-23. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2007.05.068. Epub 2007 Jun 26. Vaccine. 2007. PMID: 17629376 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptors and the eye.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006 Apr;47(4):1255-63. doi: 10.1167/iovs.05-0956. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006. PMID: 16565355 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Pulmonary immunity and immunopathology: lessons from respiratory syncytial virus.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2008 Oct;7(8):1239-55. doi: 10.1586/14760584.7.8.1239. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2008. PMID: 18844597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Il4ra-independent vaginal eosinophil accumulation following helminth infection exacerbates epithelial ulcerative pathology of HSV-2 infection.Cell Host Microbe. 2021 Apr 14;29(4):579-593.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2021.02.004. Cell Host Microbe. 2021. PMID: 33857419 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sher A., Coffman R.L. Regulation of immunity to parasites by T cells and T cell-derived cytokines. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1992;10:385–409. - PubMed
-
- Abbas A.K., Murphy K.M., Sher A. Functional diversity of helper T lymphocytes. Nature. 1996;383:787–793. - PubMed
-
- Mosmann T.R., Sad S. The expanding universe of T-cell subsetsTh1, Th2 and more. Immunol. Today. 1996;17:138–146. - PubMed
-
- Loetscher P., Uguccioni M., Bordoli L., Baggiolini M., Moser B., Chizzolini C., Dayer J.M. CCR5 is characteristic of Th1 lymphocytes. Nature. 1998;391:344–345. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

