Physical and functional interactions of Galphaq with Rho and its exchange factors
- PMID: 11278452
- PMCID: PMC1761691
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M008961200
Physical and functional interactions of Galphaq with Rho and its exchange factors
Abstract
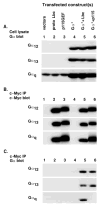
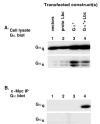
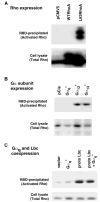
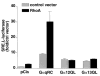
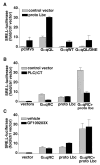
Recent reports have shown that several heterotrimeric protein-coupled receptors that signal through Galpha(q) can induce Rho-dependent responses, but the pathways that mediate the interaction between Galpha(q) and Rho have not yet been identified. In this report we present evidence that Galpha(q) expressed in COS-7 cells coprecipitates with the Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) Lbc. Furthermore, Galpha(q) expression enhances Rho-dependent responses. Coexpressed Galpha(q) and Lbc have a synergistic effect on the Rho-dependent rounding of 1321N1 astrocytoma cells. In addition, serum response factor-dependent gene expression, as assessed by the SRE.L reporter gene, is synergistically activated by Galpha(q) and Rho GEFs. The synergistic effect of Galpha(q) on this response is inhibited by C3 exoenzyme and requires phospholipase C activation. Surprisingly, expression of Galpha(q), in contrast to that of Galpha(12) and Galpha(13), does not increase the amount of activated Rho. We also observe that Galpha(q) enhances SRE.L stimulation by activated Rho, indicating that the effect of Galpha(q) occurs downstream of Rho activation. Thus, Galpha(q) interacts physically and/or functionally with Rho GEFs; however this does not appear to lead to or result from increased activation of Rho. We suggest that Galpha(q)-generated signals enhance responses downstream of Rho activation.
Figures
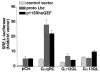

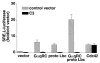
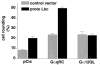
Similar articles
-
Potent activation of RhoA by Galpha q and Gq-coupled receptors.J Biol Chem. 2002 Jul 26;277(30):27130-4. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M204715200. Epub 2002 May 16. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12016230
-
LARG links histamine-H1-receptor-activated Gq to Rho-GTPase-dependent signaling pathways.Cell Signal. 2012 Mar;24(3):652-63. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2011.10.014. Epub 2011 Nov 10. Cell Signal. 2012. PMID: 22100544
-
Galphaq signaling is required for Rho-dependent transcriptional activation of the cyclooxygenase-2 promoter in fibroblasts.J Cell Physiol. 2003 Feb;194(2):127-38. doi: 10.1002/jcp.10195. J Cell Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12494451
-
Structure and function of heterotrimeric G protein-regulated Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factors.Mol Pharmacol. 2010 Feb;77(2):111-25. doi: 10.1124/mol.109.061234. Epub 2009 Oct 30. Mol Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 19880753 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The GAPs, GEFs, and GDIs of heterotrimeric G-protein alpha subunits.Int J Biol Sci. 2005;1(2):51-66. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.1.51. Epub 2005 Apr 1. Int J Biol Sci. 2005. PMID: 15951850 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Low concentration of ethanol induce apoptosis in HepG2 cells: role of various signal transduction pathways.Int J Med Sci. 2006 Oct 31;3(4):160-7. doi: 10.7150/ijms.3.160. Int J Med Sci. 2006. PMID: 17088943 Free PMC article.
-
Gastrin-stimulated Gα13 Activation of Rgnef Protein (ArhGEF28) in DLD-1 Colon Carcinoma Cells.J Biol Chem. 2015 Jun 12;290(24):15197-209. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.628164. Epub 2015 Apr 28. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25922072 Free PMC article.
-
The Lbc Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor α-catulin axis functions in serotonin-induced vascular smooth muscle cell mitogenesis and RhoA/ROCK activation.J Biol Chem. 2010 Oct 22;285(43):32919-32926. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.062513. Epub 2010 Aug 9. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20696764 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of the matricellular protein CCN1 through RhoA and MRTF-A contributes to ischemic cardioprotection.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014 Oct;75:152-61. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2014.07.017. Epub 2014 Aug 8. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 25106095 Free PMC article.
-
Substance P receptor antagonism: a potential novel treatment option for viral-myocarditis.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:645153. doi: 10.1155/2015/645153. Epub 2015 Mar 2. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 25821814 Free PMC article.
References
-
- van Biesen T, Luttrell LM, Hawes BE, Lefkowitz RJ. Endocr Rev. 1996;17:698–714. - PubMed
-
- Ridley AJ, Hall A. Cell. 1992;70:389–399. - PubMed
-
- Gohla A, Harhammer R, Schultz G. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:4653–4659. - PubMed
-
- Majumdar M, Seasholtz TM, Goldstein D, de Lanerolle P, Brown JH. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:10099–10106. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

