Acetylation of TAF(I)68, a subunit of TIF-IB/SL1, activates RNA polymerase I transcription
- PMID: 11250901
- PMCID: PMC145524
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.6.1353
Acetylation of TAF(I)68, a subunit of TIF-IB/SL1, activates RNA polymerase I transcription
Abstract
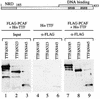
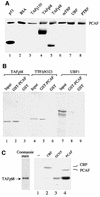
Mammalian rRNA genes are preceded by a terminator element that is recognized by the transcription termination factor TTF-I. In exploring the functional significance of the promoter-proximal terminator, we found that TTF-I associates with the p300/CBP-associated factor PCAF, suggesting that TTF-I may target histone acetyltransferase to the rDNA promoter. We demonstrate that PCAF acetylates TAF(I)68, the second largest subunit of the TATA box-binding protein (TBP)-containing factor TIF-IB/SL1, and acetylation enhances binding of TAF(I)68 to the rDNA promoter. Moreover, PCAF stimulates RNA polymerase I (Pol I) transcription in a reconstituted in vitro system. Consistent with acetylation of TIF-IB/SL1 being required for rDNA transcription, the NAD(+)-dependent histone deacetylase mSir2a deacetylates TAF(I)68 and represses Pol I transcription. The results demonstrate that acetylation of the basal Pol I transcription machinery has functional consequences and suggest that reversible acetylation of TIF-IB/SL1 may be an effective means to regulate rDNA transcription in response to external signals.
Figures
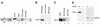
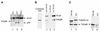
Similar articles
-
A TBP-containing multiprotein complex (TIF-IB) mediates transcription specificity of murine RNA polymerase I.Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Sep 11;21(18):4180-6. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.18.4180. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993. PMID: 8414971 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstitution of human rRNA gene transcription in mouse cells by a complete SL1 complex.J Cell Sci. 2014 Aug 1;127(Pt 15):3309-19. doi: 10.1242/jcs.146787. Epub 2014 Jun 13. J Cell Sci. 2014. PMID: 24928901
-
Species specificity of ribosomal gene transcription: a factor associated with human RNA polymerase I prevents transcription of mouse rDNA.DNA Cell Biol. 1996 Feb;15(2):167-73. doi: 10.1089/dna.1996.15.167. DNA Cell Biol. 1996. PMID: 8634144
-
Distinct GCN5/PCAF-containing complexes function as co-activators and are involved in transcription factor and global histone acetylation.Oncogene. 2007 Aug 13;26(37):5341-57. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210604. Oncogene. 2007. PMID: 17694077 Review.
-
Acetylation of general transcription factors by histone acetyltransferases.Curr Biol. 1997 Sep 1;7(9):689-92. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(06)00296-x. Curr Biol. 1997. PMID: 9285713 Review.
Cited by
-
Pro-autophagic polyphenols reduce the acetylation of cytoplasmic proteins.Cell Cycle. 2012 Oct 15;11(20):3851-60. doi: 10.4161/cc.22027. Cell Cycle. 2012. PMID: 23070521 Free PMC article.
-
Cooperative Action of Cdk1/cyclin B and SIRT1 Is Required for Mitotic Repression of rRNA Synthesis.PLoS Genet. 2015 May 29;11(5):e1005246. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005246. eCollection 2015 May. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 26023773 Free PMC article.
-
The functional significance of nuclear receptor acetylation.Steroids. 2007 Feb;72(2):221-30. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2006.12.001. Epub 2007 Feb 7. Steroids. 2007. PMID: 17291555 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The chromatin remodeling complex NoRC targets HDAC1 to the ribosomal gene promoter and represses RNA polymerase I transcription.EMBO J. 2002 Sep 2;21(17):4632-40. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdf460. EMBO J. 2002. PMID: 12198165 Free PMC article.
-
Hormonal control of androgen receptor function through SIRT1.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Nov;26(21):8122-35. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00289-06. Epub 2006 Aug 21. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16923962 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bazett-Jones D.P., Leblanc,B., Herfort,M. and Moss.T. (1994) Short-range DNA looping by the Xenopus HMG-box transcription factor, xUBF. Science, 264, 1134–1137. - PubMed
-
- Beckmann H., Chen,J.L., O’Brien,T. and Tjian,R. (1995) Coactivator and promoter-selective properties of RNA polymerase I TAFs. Science, 270, 1506–1509. - PubMed
-
- Boyes J., Byfield,P., Nakatani,Y. and Ogryzko,V. (1998) Regulation of activity of the transcription factor GATA-1 by acetylation. Nature, 396, 594–598. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

