Molecular pathways in virus-induced cytokine production
- PMID: 11238989
- PMCID: PMC99022
- DOI: 10.1128/MMBR.65.1.131-150.2001
Molecular pathways in virus-induced cytokine production
Abstract
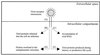
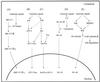
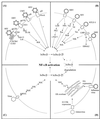
Virus infections induce a proinflammatory response including expression of cytokines and chemokines. The subsequent leukocyte recruitment and antiviral effector functions contribute to the first line of defense against viruses. The molecular virus-cell interactions initiating these events have been studied intensively, and it appears that viral surface glycoproteins, double-stranded RNA, and intracellular viral proteins all have the capacity to activate signal transduction pathways leading to the expression of cytokines and chemokines. The signaling pathways activated by viral infections include the major proinflammatory pathways, with the transcription factor NF-kappaB having received special attention. These transcription factors in turn promote the expression of specific inducible host proteins and participate in the expression of some viral genes. Here we review the current knowledge of virus-induced signal transduction by seven human pathogenic viruses and the most widely used experimental models for viral infections. The molecular mechanisms of virus-induced expression of cytokines and chemokines is also analyzed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Virus-cell interactions: impact on cytokine production, immune evasion and tumor growth.Eur Cytokine Netw. 2001 Jul-Sep;12(3):382-90. Eur Cytokine Netw. 2001. PMID: 11566618 Review.
-
The viral manipulation of the host cellular and immune environments to enhance propagation and survival: a focus on RNA viruses.J Leukoc Biol. 2002 Sep;72(3):429-39. J Leukoc Biol. 2002. PMID: 12223509 Review.
-
[Influenza viruses and intracellular signalling pathways].Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 2006 Mar-Apr;119(3-4):101-11. Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 2006. PMID: 16573200 Review. German.
-
Expression of cytokines in bacterial and viral infections and their biochemical aspects.J Biochem. 2000 Apr;127(4):525-30. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a022636. J Biochem. 2000. PMID: 10739941 Review.
-
Viral strategies in modulation of NF-kappaB activity.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2003;51(6):367-75. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2003. PMID: 14692658 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular mechanisms of human herpes viruses inferring with host immune surveillance.J Immunother Cancer. 2020 Jul;8(2):e000841. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-000841. J Immunother Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32616556 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Establishment of Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) Latent Gene-Expressing T-Cell Lines with an Expression Vector Harboring EBV Nuclear Antigen 1.Microorganisms. 2023 Oct 25;11(11):2624. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11112624. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 38004636 Free PMC article.
-
Intensive cytokine induction in pandemic H1N1 influenza virus infection accompanied by robust production of IL-10 and IL-6.PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e28680. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028680. Epub 2011 Dec 9. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22174866 Free PMC article.
-
NFκB1 Polymorphisms Are Associated with Severe Influenza A (H1N1) Virus Infection in a Canadian Population.Microorganisms. 2022 Sep 21;10(10):1886. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10101886. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36296162 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a new cell line permissive to porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus infection and replication which is phenotypically distinct from MARC-145 cell line.Virol J. 2012 Nov 13;9:267. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-9-267. Virol J. 2012. PMID: 23148668 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albrecht T, Boldogh I, Fons M, AbuBakar S, Deng C Z. Cell activation signals and the pathogenesis of human cytomegalovirus. Intervirology. 1990;31:68–75. - PubMed
-
- al-Wabel A, al-Janadi M, Raziuddin S. Cytokine profile of viral and autoimmune chronic active hepatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1993;92:902–908. - PubMed
-
- Ambrosino C, Ruocco M R, Chen X, Mallardo M R, Baudi F, Trematerra S, Quinto I, Ventura S, Scala G. HIV-1 Tat induces the expression of the interleukin-6 (IL6) gene by binding to the IL6 leader RNA and by interacting with CAAT enhancer-binding protein β (NF-IL6) transcription factors. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:14883–14892. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

