Cross-talk between catalytic and regulatory elements in a DEAD motor domain is essential for SecA function
- PMID: 11230120
- PMCID: PMC145479
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.5.961
Cross-talk between catalytic and regulatory elements in a DEAD motor domain is essential for SecA function
Abstract
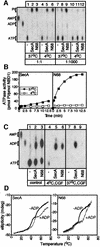
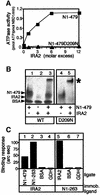
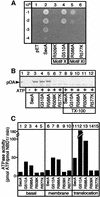
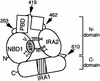
SecA, the motor subunit of bacterial polypeptide translocase, is an RNA helicase. SecA comprises a dimerization C-terminal domain fused to an ATPase N-terminal domain containing conserved DEAD helicase motifs. We show that the N-terminal domain is organized like the motor core of DEAD proteins, encompassing two subdomains, NBD1 and IRA2. NBD1, a rigid nucleotide-binding domain, contains the minimal ATPase catalytic machinery. IRA2 binds to NBD1 and acts as an intramolecular regulator of ATP hydrolysis by controlling ADP release and optimal ATP catalysis at NBD1. IRA2 is flexible and can undergo changes in its alpha-helical content. The C-terminal domain associates with NBD1 and IRA2 and restricts IRA2 activator function. Thus, cytoplasmic SecA is maintained in the thermally stabilized ADP-bound state and unnecessary ATP hydrolysis cycles are prevented. Two DEAD family motifs in IRA2 are essential for IRA2-NBD1 binding, optimal nucleotide turnover and polypeptide translocation. We propose that translocation ligands alleviate C-terminal domain suppression, allowing IRA2 to stimulate nucleotide turnover at NBD1. DEAD motors may employ similar mechanisms to translocate different enzymes along chemically unrelated biopolymers.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A molecular switch in SecA protein couples ATP hydrolysis to protein translocation.Mol Microbiol. 1999 Dec;34(5):1133-45. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1999.01686.x. Mol Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10594836
-
Structure of dimeric SecA, the Escherichia coli preprotein translocase motor.J Mol Biol. 2007 Mar 9;366(5):1545-57. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.12.049. Epub 2006 Dec 23. J Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17229438
-
Global co-ordination of protein translocation by the SecA IRA1 switch.J Biol Chem. 2004 May 21;279(21):22490-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M401008200. Epub 2004 Mar 7. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15007058
-
SecA: the ubiquitous component of preprotein translocase in prokaryotes.Microbes Infect. 1999 Oct;1(12):993-1004. doi: 10.1016/s1286-4579(99)80517-6. Microbes Infect. 1999. PMID: 10617931 Review.
-
Autogenous translation regulation by Escherichia coli ATPase SecA may be mediated by an intrinsic RNA helicase activity of this protein.FEBS Lett. 1992 Feb 17;298(1):6-8. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80009-6. FEBS Lett. 1992. PMID: 1531961 Review.
Cited by
-
SecA: a potential antimicrobial target.Future Med Chem. 2015;7(8):989-1007. doi: 10.4155/fmc.15.42. Future Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 26062397 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ATPase active-site electrostatic interactions control the global conformation of the 100 kDa SecA translocase.J Am Chem Soc. 2013 Feb 27;135(8):2999-3010. doi: 10.1021/ja306361q. Epub 2013 Feb 14. J Am Chem Soc. 2013. PMID: 23167435 Free PMC article.
-
Role of a conserved glutamate residue in the Escherichia coli SecA ATPase mechanism.J Biol Chem. 2005 Apr 15;280(15):14611-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M414224200. Epub 2005 Feb 14. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15710614 Free PMC article.
-
Preprotein-controlled catalysis in the helicase motor of SecA.EMBO J. 2007 Jun 20;26(12):2904-14. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601721. Epub 2007 May 24. EMBO J. 2007. PMID: 17525736 Free PMC article.
-
A unifying mechanism for protein transport through the core bacterial Sec machinery.Open Biol. 2023 Aug;13(8):230166. doi: 10.1098/rsob.230166. Epub 2023 Aug 30. Open Biol. 2023. PMID: 37643640 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ali J.A. and Lohman,T.M. (1997) Kinetic measurement of the step size of DNA unwinding by Escherichia coli UvrD helicase. Science, 275, 377–380. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel F.M., Brent,R., Kingston,R.E., Moore,D.D., Smith,J.A., Seidman,J.G. and Struhl,K. (1994) Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. John Wiley and Sons, NY.
-
- Bailey T.L. and Gribskov,M. (1999) Combining evidence using P-values: application to sequence homology searches. Bioinformatics, 14, 48–54. - PubMed
-
- Bianco P.R. and Kowalczykowski,S.C. (2000) Translocation step size and mechanism of the RecBC DNA helicase. Nature, 405, 368–372. - PubMed
-
- Breukink E., Nouwen,N., van Raalte,A., Mizushima,S., Tommassen,J. and de Kruijff,B. (1995) The C terminus of SecA is involved in both lipid binding and SecB binding. J. Biol. Chem., 270, 7902–7907. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

