Fatty acids and hypolipidemic drugs regulate peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors alpha - and gamma-mediated gene expression via liver fatty acid binding protein: a signaling path to the nucleus
- PMID: 11226238
- PMCID: PMC30137
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.051619898
Fatty acids and hypolipidemic drugs regulate peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors alpha - and gamma-mediated gene expression via liver fatty acid binding protein: a signaling path to the nucleus
Abstract
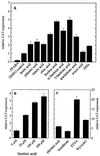
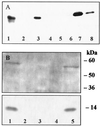
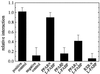
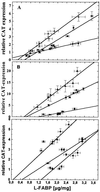
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha) is a key regulator of lipid homeostasis in hepatocytes and target for fatty acids and hypolipidemic drugs. How these signaling molecules reach the nuclear receptor is not known; however, similarities in ligand specificity suggest the liver fatty acid binding protein (L-FABP) as a possible candidate. In localization studies using laser-scanning microscopy, we show that L-FABP and PPARalpha colocalize in the nucleus of mouse primary hepatocytes. Furthermore, we demonstrate by pull-down assay and immunocoprecipitation that L-FABP interacts directly with PPARalpha. In a cell biological approach with the aid of a mammalian two-hybrid system, we provide evidence that L-FABP interacts with PPARalpha and PPARgamma but not with PPARbeta and retinoid X receptor-alpha by protein-protein contacts. In addition, we demonstrate that the observed interaction of both proteins is independent of ligand binding. Final and quantitative proof for L-FABP mediation was obtained in transactivation assays upon incubation of transiently and stably transfected HepG2 cells with saturated, monounsaturated, and polyunsaturated fatty acids as well as with hypolipidemic drugs. With all ligands applied, we observed strict correlation of PPARalpha and PPARgamma transactivation with intracellular concentrations of L-FABP. This correlation constitutes a nucleus-directed signaling by fatty acids and hypolipidemic drugs where L-FABP acts as a cytosolic gateway for these PPARalpha and PPARgamma agonists. Thus, L-FABP and the respective PPARs could serve as targets for nutrients and drugs to affect expression of PPAR-sensitive genes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phytanic acid is ligand and transcriptional activator of murine liver fatty acid binding protein.J Lipid Res. 1999 Apr;40(4):708-14. J Lipid Res. 1999. PMID: 10191295
-
Differential involvement of peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptors alpha and delta in fibrate and fatty-acid-mediated inductions of the gene encoding liver fatty-acid-binding protein in the liver and the small intestine.Biochem J. 2001 Apr 15;355(Pt 2):481-8. doi: 10.1042/0264-6021:3550481. Biochem J. 2001. PMID: 11284737 Free PMC article.
-
Functional analysis of peroxisome-proliferator-responsive element motifs in genes of fatty acid-binding proteins.Biochem J. 2004 Aug 15;382(Pt 1):239-45. doi: 10.1042/BJ20031340. Biochem J. 2004. PMID: 15130092 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of mitogenesis by liver fatty acid binding protein.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1994 Dec;13(3-4):317-36. doi: 10.1007/BF00666102. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1994. PMID: 7712594 Review.
-
Role of fatty acid binding proteins and long chain fatty acids in modulating nuclear receptors and gene transcription.Lipids. 2008 Jan;43(1):1-17. doi: 10.1007/s11745-007-3111-z. Epub 2007 Sep 19. Lipids. 2008. PMID: 17882463 Review.
Cited by
-
Liver fatty acid binding protein gene-ablation exacerbates weight gain in high-fat fed female mice.Lipids. 2013 May;48(5):435-48. doi: 10.1007/s11745-013-3777-3. Epub 2013 Mar 29. Lipids. 2013. PMID: 23539345 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear localization of 5-lipoxygenase as a determinant of leukotriene B4 synthetic capacity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 14;100(21):12165-70. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2133253100. Epub 2003 Oct 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 14530386 Free PMC article.
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: lipid binding proteins controling gene expression.Mol Cell Biochem. 2002 Oct;239(1-2):131-8. Mol Cell Biochem. 2002. PMID: 12479578 Review.
-
Drosophila HNF4 regulates lipid mobilization and beta-oxidation.Cell Metab. 2009 Mar;9(3):228-39. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2009.01.009. Cell Metab. 2009. PMID: 19254568 Free PMC article.
-
PPARγ agonists regulate tobacco smoke-induced Toll like receptor 4 expression in alveolar macrophages.Respir Res. 2014 Mar 11;15(1):28. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-15-28. Respir Res. 2014. PMID: 24612634 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bocos C, Göttlicher M, Gearing K, Banner C, Enmark E, Teboul M, Crickmore A, Gustafsson J A. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1995;53:467–473. - PubMed
-
- Krey G, Braissant O, L'Horset F, Kalkhoven E, Perroud M, Parker M G, Wahli W. Mol Endocrinol. 1997;11:779–791. - PubMed
-
- Ellinghaus P, Wolfrum C, Assmann G, Spener F, Seedorf U. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:2766–2772. - PubMed
-
- Issemann I, Green S. Nature (London) 1990;347:645–650. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

