Determination of the binding constants of the centromere protein Cbf1 to all 16 centromere DNAs of Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 11222754
- PMCID: PMC29730
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/29.5.1054
Determination of the binding constants of the centromere protein Cbf1 to all 16 centromere DNAs of Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
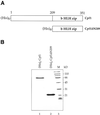
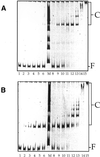
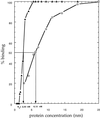
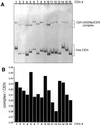
Cbf1p is a Saccharomyces cerevisiae chromatin protein belonging to the basic region helix-loop-helix leucine zipper (bHLHzip) family of DNA binding proteins. Cbf1p binds to a conserved element in the 5'-flanking region of methionine biosynthetic genes and to centromere DNA element I (CDEI) of S.cerevisiae centromeric DNA. We have determined the apparent equilibrium dissociation constants of Cbf1p binding to all 16 CDEI DNAs in gel retardation assays. Binding constants of full-length Cbf1p vary between 1.7 and 3.8 nM. However, the dissociation constants of a Cbf1p deletion variant that has been shown to be fully sufficient for Cbf1p function in vivo vary in a range between 3.2 and 12 nM. In addition, native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis revealed distinct changes in the 3D structure of the Cbf1p/CEN complexes. We also show that the previously reported DNA binding stimulation activity of the centromere protein p64 functions on both the Cbf1 full-length protein and a deletion variant containing only the bHLHzip domain of Cbf1p. Our results suggest that centromeric DNA outside the consensus CDEI sequence and interaction of Cbf1p with adjacent centromere proteins contribute to the complex formation between Cbf1p and CEN DNA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interaction of yeast kinetochore proteins with centromere-protein/transcription factor Cbf1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Nov 7;97(23):12583-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.23.12583. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 11070082 Free PMC article.
-
Multifunctional centromere binding factor 1 is essential for chromosome segregation in the human pathogenic yeast Candida glabrata.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Aug;21(15):4875-88. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.15.4875-4888.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11438645 Free PMC article.
-
The yeast centromere CDEI/Cpf1 complex: differences between in vitro binding and in vivo function.Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Jul 25;22(14):2791-800. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.14.2791. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994. PMID: 8052535 Free PMC article.
-
The centromere of budding yeast.Bioessays. 1993 Jul;15(7):451-60. doi: 10.1002/bies.950150704. Bioessays. 1993. PMID: 8379948 Review.
-
Metabolism of sulfur amino acids in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 1997 Dec;61(4):503-32. doi: 10.1128/mmbr.61.4.503-532.1997. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 1997. PMID: 9409150 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Concatemer Assisted Stoichiometry Analysis (CASA): targeted mass spectrometry for protein quantification.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 27:2024.07.26.605382. doi: 10.1101/2024.07.26.605382. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Life Sci Alliance. 2024 Dec 31;8(3):e202403007. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202403007. PMID: 39091769 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Differential regulation of ceramide synthase components LAC1 and LAG1 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Eukaryot Cell. 2004 Aug;3(4):880-92. doi: 10.1128/EC.3.4.880-892.2004. Eukaryot Cell. 2004. PMID: 15302821 Free PMC article.
-
Basic helix-loop-helix pioneer factors interact with the histone octamer to invade nucleosomes and generate nucleosome-depleted regions.Mol Cell. 2023 Apr 20;83(8):1251-1263.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2023.03.006. Epub 2023 Mar 29. Mol Cell. 2023. PMID: 36996811 Free PMC article.
-
Dissociation rate compensation mechanism for budding yeast pioneer transcription factors.Elife. 2019 Mar 19;8:e43008. doi: 10.7554/eLife.43008. Elife. 2019. PMID: 30888317 Free PMC article.
-
Determining physical constraints in transcriptional initiation complexes using DNA sequence analysis.PLoS One. 2007 Nov 21;2(11):e1199. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001199. PLoS One. 2007. PMID: 18030333 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Choo K.H.A. (1997) The Centromere. Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK.
-
- Lee C., Wevrick,R., Fisher,R.B., Ferguson-Smith,M.A. and Lin,C.C. (1997) Human centromeric DNAs. Hum. Genet., 100, 291–304. - PubMed
-
- Hegemann J.H. and Fleig,U.N. (1993) The centromere of budding yeast. Bioessays, 15, 451–460. - PubMed
-
- Craig J.M., Earnshaw,W.C. and Vagnarelli,P. (1999) Mammalian centromeres: DNA sequence, protein composition and role in cell cycle progression. Exp. Cell Res., 246, 249–262. - PubMed
-
- Lechner J. and Ortiz,J. (1996) The Saccharomyces cerevisiae kinetochore. FEBS Lett., 389, 70–74. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

