The role of Upf proteins in modulating the translation read-through of nonsense-containing transcripts
- PMID: 11179232
- PMCID: PMC145432
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.4.880
The role of Upf proteins in modulating the translation read-through of nonsense-containing transcripts
Abstract
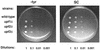
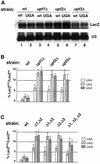
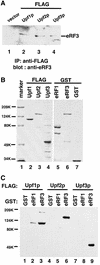
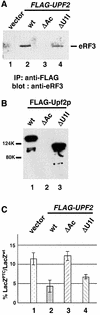
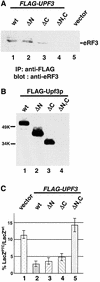
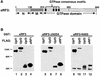
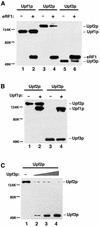
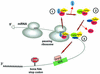
The yeast UPF1, UPF2 and UPF3 genes encode trans-acting factors of the nonsense-mediated mRNA decay pathway. In addition, the upf1Delta strain demonstrates a nonsense suppression phenotype and Upf1p has been shown to interact with the release factors eRF1 and eRF3. In this report, we show that both upf2Delta and upf3Delta strains demonstrate a nonsense suppression phenotype independent of their effect on mRNA turnover. We also demonstrate that Upf2p and Upf3p interact with eRF3, and that their ability to bind eRF3 correlates with their ability to complement the nonsense suppression phenotype. In vitro experiments demonstrate that Upf2p, Upf3p and eRF1 compete with each other for interacting with eRF3. Con versely, Upf1p binds to a different region of eRF3 and can form a complex with these factors. These results suggest a sequential surveillance complex assembly pathway, which occurs during the premature translation termination process. We propose that the observed nonsense suppression phenotype in the upfDelta strains can be attributed to a defect in the surveillance complex assembly.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification and characterization of mutations in the UPF1 gene that affect nonsense suppression and the formation of the Upf protein complex but not mRNA turnover.Mol Cell Biol. 1996 Oct;16(10):5491-506. doi: 10.1128/MCB.16.10.5491. Mol Cell Biol. 1996. PMID: 8816462 Free PMC article.
-
Upf1p control of nonsense mRNA translation is regulated by Nmd2p and Upf3p.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Jul;20(13):4591-603. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.13.4591-4603.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10848586 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of Upf1p compensates for mitochondrial splicing deficiency independently of its role in mRNA surveillance.Mol Microbiol. 2004 Feb;51(4):1129-42. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03889.x. Mol Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 14763985
-
NMD: At the crossroads between translation termination and ribosome recycling.Biochimie. 2015 Jul;114:2-9. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2014.10.027. Epub 2014 Nov 13. Biochimie. 2015. PMID: 25446649 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcript selection and the recruitment of mRNA decay factors for NMD in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.RNA. 2005 Sep;11(9):1333-9. doi: 10.1261/rna.2113605. Epub 2005 Jul 25. RNA. 2005. PMID: 16043493 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Features and factors that dictate if terminating ribosomes cause or counteract nonsense-mediated mRNA decay.J Biol Chem. 2022 Nov;298(11):102592. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102592. Epub 2022 Oct 13. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 36244451 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Translational competence of ribosomes released from a premature termination codon is modulated by NMD factors.RNA. 2010 Sep;16(9):1832-47. doi: 10.1261/rna.1987710. Epub 2010 Jul 30. RNA. 2010. PMID: 20675403 Free PMC article.
-
Human SMG-1, a novel phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related protein kinase, associates with components of the mRNA surveillance complex and is involved in the regulation of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay.Genes Dev. 2001 Sep 1;15(17):2215-28. doi: 10.1101/gad.913001. Genes Dev. 2001. PMID: 11544179 Free PMC article.
-
Ultraconserved elements are associated with homeostatic control of splicing regulators by alternative splicing and nonsense-mediated decay.Genes Dev. 2007 Mar 15;21(6):708-18. doi: 10.1101/gad.1525507. Genes Dev. 2007. PMID: 17369403 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of the hybrid state of ribosome in complex with the guanosine triphosphatase release factor 3.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Sep 20;108(38):15798-803. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1112185108. Epub 2011 Sep 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21903932 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Atkin A.L., Schenkman,L.R., Eastham,M., Dahlseid,J.N., Lelivelt,M.J. and Culbertson,M.R. (1997) Relationship between yeast polyribosomes and Upf proteins required for nonsense mRNA decay. J. Biol. Chem., 272, 22163–22172. - PubMed
-
- Cui Y., Hagan,K.W., Zhang,S. and Peltz,S.W. (1995) Identification and characterization of genes that are required for the accelerated degradation of mRNAs containing a premature translational termination codon. Genes Dev., 9, 423–436. - PubMed
-
- Czaplinski K., Ruiz-Echevarria,M.J., Paushkin,S.V., Han,X., Weng,Y., Perlick,H.A., Dietz,H.C., Ter-Avanesyan,M.D. and Peltz,S.W. (1998) The surveillance complex interacts with the translation release factors to enhance termination and degrade aberrant mRNAs. Genes Dev., 12, 1665–1677. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Czaplinski K., Ruiz-Echevarria,M.J., Gonzales,C.I. and Peltz,S.W. (1999) Should we kill the messenger? The role of the surveillance complex in translation termination and mRNA turnover. BioEssays, 21, 685–696. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

