Increased serum concentrations of advanced glycation end products: a marker of coronary artery disease activity in type 2 diabetic patients
- PMID: 11119472
- PMCID: PMC1729572
- DOI: 10.1136/heart.85.1.87
Increased serum concentrations of advanced glycation end products: a marker of coronary artery disease activity in type 2 diabetic patients
Abstract
Objective: To assess whether the concentrations of serum advanced glycation end products (AGE) in diabetic patients with obstructive coronary artery disease differ from those in type 2 diabetic patients without obstructive coronary artery disease.
Design: Serum AGE concentrations were measured in type 2 diabetic patients and in non-diabetic patients, both with and without obstructive coronary artery disease, and the relation between these values and coronary disease severity was evaluated.
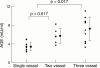
Results: Mean (SD) serum AGE concentrations were higher (p < 0.0125) in type 2 diabetic patients with obstructive coronary artery disease (5.5 (2.5) mU/ml, n = 30) than in patients without obstructive coronary artery disease (2.8 (0. 5) mU/ml, n = 12), and higher than in non-diabetic patients with (3. 4 (1.0) mU/ml, n = 28) and without (3.2 (0.4) mU/ml, n = 13) obstructive coronary artery disease. Serum AGE was associated with the degree of coronary arteriosclerosis in type 2 diabetic patients with obstructive coronary artery disease (single vessel: n = 13, 3.4 (0.9) mU/m; two vessel: n = 6, 5.7 (1.6) mU/m; three vessel: n = 11, 7.2 (2.5) mU/ml). Serum AGE was positively correlated with serum mean four year HbA(1C) (r = 0.46, p < 0.01), but not with recent serum HbA(1C) (r = 0.24). The four groups did not differ in the other coronary risk factors.
Conclusions: Serum AGE concentrations may be associated with long term poor glycaemic control and reflect the severity of coronary arteriosclerosis in type 2 diabetic patients.
Figures
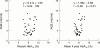

Similar articles
-
Increased serum glycated albumin level is associated with the presence and severity of coronary artery disease in type 2 diabetic patients.Circ J. 2007 Jul;71(7):1067-73. doi: 10.1253/circj.71.1067. Circ J. 2007. PMID: 17587712
-
Glycated albumin is superior to hemoglobin A1c for evaluating the presence and severity of coronary artery disease in type 2 diabetic patients.Cardiology. 2012;123(2):84-90. doi: 10.1159/000342055. Epub 2012 Sep 25. Cardiology. 2012. PMID: 23018602
-
Serum advanced glycation end-products and receptors as prognostic biomarkers in diabetics undergoing coronary artery stent implantation.Can J Cardiol. 2012 Nov-Dec;28(6):737-43. doi: 10.1016/j.cjca.2012.08.015. Epub 2012 Oct 13. Can J Cardiol. 2012. PMID: 23073352
-
Association of Advanced Glycation End Products with coronary Artery Calcification in Japanese Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes as Assessed by Skin Autofluorescence.J Atheroscler Thromb. 2016 Oct 1;23(10):1178-1187. doi: 10.5551/jat.30155. Epub 2016 Mar 10. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2016. PMID: 26961217 Free PMC article.
-
Glucose Variability and Coronary Artery Disease.Heart Lung Circ. 2019 Apr;28(4):553-559. doi: 10.1016/j.hlc.2018.10.019. Epub 2018 Nov 12. Heart Lung Circ. 2019. PMID: 30527849 Review.
Cited by
-
Advanced Glycation End Products: A Sweet Flavor That Embitters Cardiovascular Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 22;23(5):2404. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052404. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35269546 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AGE-RAGE Stress and Coronary Artery Disease.Int J Angiol. 2021 Mar;30(1):4-14. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1721813. Epub 2021 Jan 21. Int J Angiol. 2021. PMID: 34025091 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increased serum levels of advanced glycation endproducts predict total, cardiovascular and coronary mortality in women with type 2 diabetes: a population-based 18 year follow-up study.Diabetologia. 2007 Jul;50(7):1409-17. doi: 10.1007/s00125-007-0687-z. Epub 2007 May 4. Diabetologia. 2007. PMID: 17479244
-
The clinical relevance of assessing advanced glycation endproducts accumulation in diabetes.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2008 Oct 7;7:29. doi: 10.1186/1475-2840-7-29. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2008. PMID: 18840258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Correlation between Gensini Score and Duration of Diabetes in Patients Undergoing Coronary Angiography.Cureus. 2019 Feb 4;11(2):e4010. doi: 10.7759/cureus.4010. Cureus. 2019. PMID: 31001464 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
