Bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in fibrinogen-null mice
- PMID: 11104787
- PMCID: PMC381464
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI10531
Bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in fibrinogen-null mice
Abstract
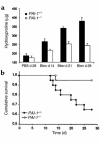
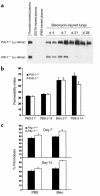
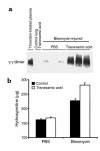
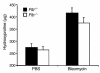
Mice deleted for the plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) gene are relatively protected from developing pulmonary fibrosis induced by bleomycin. We hypothesized that PAI-1 deficiency reduces fibrosis by promoting plasminogen activation and accelerating the clearance of fibrin matrices that accumulate within the damaged lung. In support of this hypothesis, we found that the lungs of PAI-1(-/-) mice accumulated less fibrin after injury than wild-type mice, due in part to enhanced fibrinolytic activity. To further substantiate the importance of fibrin removal as the mechanism by which PAI-1 deficiency limited bleomycin-induced fibrosis, bleomycin was administered to mice deficient in the gene for the Aalpha-chain of fibrinogen (fib). Contrary to our expectation, fib(-/-) mice developed pulmonary fibrosis to a degree similar to fib(+/-) littermate controls, which have a plasma fibrinogen level that is 70% of that of wild-type mice. Although elimination of fibrin from the lung was not in itself protective, the beneficial effect of PAI-1 deficiency was still associated with proteolytic activity of the plasminogen activation system. In particular, inhibition of plasmin activation and/or activity by tranexamic acid reversed both the accelerated fibrin clearance and the protective effect of PAI-1 deficiency. We conclude that protection from fibrosis by PAI-1 deficiency is dependent upon increased proteolytic activity of the plasminogen activation system; however, complete removal of fibrin is not sufficient to protect the lung.
Figures
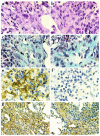
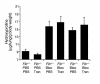
Comment in
-
PAI-1, fibrosis, and the elusive provisional fibrin matrix.J Clin Invest. 2000 Dec;106(12):1441-3. doi: 10.1172/JCI11765. J Clin Invest. 2000. PMID: 11120750 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
The development of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice deficient for components of the fibrinolytic system.Am J Pathol. 2000 Jul;157(1):177-87. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64529-4. Am J Pathol. 2000. PMID: 10880388 Free PMC article.
-
PAI-1, fibrosis, and the elusive provisional fibrin matrix.J Clin Invest. 2000 Dec;106(12):1441-3. doi: 10.1172/JCI11765. J Clin Invest. 2000. PMID: 11120750 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in transgenic mice that either lack or overexpress the murine plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 gene.J Clin Invest. 1996 Jan 1;97(1):232-7. doi: 10.1172/JCI118396. J Clin Invest. 1996. PMID: 8550840 Free PMC article.
-
Development of pulmonary fibrosis in fibrinogen-deficient mice.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001;936:542-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2001.tb03542.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001. PMID: 11460513 Review.
-
The fibrogenic actions of the coagulant and plasminogen activation systems in pulmonary fibrosis.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2018 Apr;97:108-117. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2018.02.016. Epub 2018 Feb 21. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29474926 Review.
Cited by
-
The Temporal Evolution of Airways Hyperresponsiveness and Inflammation.J Allergy Ther. 2012 Jan 25;1(5):1-7. doi: 10.4172/2155-6121.S1-005. J Allergy Ther. 2012. PMID: 23565340 Free PMC article.
-
Antifibrotic effect of heparin on liver fibrosis model in rats.World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. 2012 Dec 6;3(6):86-92. doi: 10.4292/wjgpt.v3.i6.86. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. 2012. PMID: 23494756 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial-mesenchymal interactions in pulmonary fibrosis.Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2006 Dec;27(6):600-12. doi: 10.1055/s-2006-957332. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2006. PMID: 17195137 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A mutant, noninhibitory plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 decreases matrix accumulation in experimental glomerulonephritis.J Clin Invest. 2003 Aug;112(3):379-88. doi: 10.1172/JCI18038. J Clin Invest. 2003. PMID: 12897205 Free PMC article.
-
An essential role for fibronectin extra type III domain A in pulmonary fibrosis.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008 Mar 15;177(6):638-45. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200708-1291OC. Epub 2007 Dec 20. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008. PMID: 18096707 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fein A, et al. The value of edema fluid protein measurement in patients with pulmonary edema. Am J Med. 1979;67:32–38. - PubMed
-
- Idell S, et al. Bronchoalveolar lavage procoagulant activity in bleomycin-induced lung injury in marmosets. Characterization and relationship to fibrin deposition and fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987;136:124–133. - PubMed
-
- Sisson TH, Hattori N, Xu Y, Simon RH. Treatment of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by transfer of urokinase-type plasminogen activator genes. Hum Gene Ther. 1999;10:2315–2323. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

