Genomewide studies of histone deacetylase function in yeast
- PMID: 11095743
- PMCID: PMC17640
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.250477697
Genomewide studies of histone deacetylase function in yeast
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2001 Apr 24;98(9):5368
Abstract
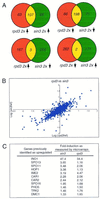
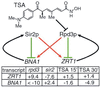
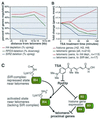
The trichostatin A (TSA)-sensitive histone deacetylase (HDAC) Rpd3p exists in a complex with Sin3p and Sap30p in yeast that is recruited to target promoters by transcription factors including Ume6p. Sir2p is a TSA-resistant HDAC that mediates yeast silencing. The transcription profile of rpd3 is similar to the profiles of sin3, sap30, ume6, and TSA-treated wild-type yeast. A Ume6p-binding site was identified in the promoters of genes up-regulated in the sin3 strain. Two genes appear to participate in feedback loops that modulate HDAC activity: ZRT1 encodes a zinc transporter and is repressed by RPD3 (Rpd3p is zinc-dependent); BNA1 encodes a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD)-biosynthesis enzyme and is repressed by SIR2 (Sir2p is NAD-dependent). Although HDACs are transcriptional repressors, deletion of RPD3 down-regulates certain genes. Many of these are down-regulated rapidly by TSA, indicating that Rpd3p may also activate transcription. Deletion of RPD3 previously has been shown to repress ("silence") reporter genes inserted near telomeres. The profiles demonstrate that 40% of endogenous genes located within 20 kb of telomeres are down-regulated by RPD3 deletion. Rpd3p appears to activate telomeric genes sensitive to histone depletion indirectly by repressing transcription of histone genes. Rpd3p also appears to activate telomeric genes repressed by the silent information regulator (SIR) proteins directly, possibly by deacetylating lysine 12 of histone H4. Finally, bioinformatic analyses indicate that the yeast HDACs RPD3, SIR2, and HDA1 play distinct roles in regulating genes involved in cell cycle progression, amino acid biosynthesis, and carbohydrate transport and utilization, respectively.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Rpd3p relocation mediates a transcriptional response to rapamycin in yeast.Chem Biol. 2004 Mar;11(3):295-9. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2004.03.001. Chem Biol. 2004. PMID: 15123258
-
Genome-wide binding map of the histone deacetylase Rpd3 in yeast.Nat Genet. 2002 Jul;31(3):248-54. doi: 10.1038/ng907. Epub 2002 Jun 24. Nat Genet. 2002. PMID: 12089521
-
Global histone acetylation and deacetylation in yeast.Nature. 2000 Nov 23;408(6811):495-8. doi: 10.1038/35044127. Nature. 2000. PMID: 11100734
-
Structure and chemistry of the Sir2 family of NAD+-dependent histone/protein deactylases.Biochem Soc Trans. 2004 Dec;32(Pt 6):904-9. doi: 10.1042/BST0320904. Biochem Soc Trans. 2004. PMID: 15506920 Review.
-
Sound silencing: the Sir2 protein and cellular senescence.Bioessays. 2001 Apr;23(4):327-32. doi: 10.1002/bies.1047. Bioessays. 2001. PMID: 11268038 Review.
Cited by
-
Recruitment of Rpd3 to the telomere depends on the protein arginine methyltransferase Hmt1.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e44656. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044656. Epub 2012 Aug 31. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22953000 Free PMC article.
-
Rfm1, a novel tethering factor required to recruit the Hst1 histone deacetylase for repression of middle sporulation genes.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Mar;23(6):2009-16. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.6.2009-2016.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12612074 Free PMC article.
-
Global and specific transcriptional repression by the histone H3 amino terminus in yeast.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Apr 1;100(7):4084-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0637524100. Epub 2003 Mar 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12649325 Free PMC article.
-
Histone deacetylase 4 interacts with 53BP1 to mediate the DNA damage response.J Cell Biol. 2003 Mar 31;160(7):1017-27. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200209065. J Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12668657 Free PMC article.
-
An epigenetically altered tumor cell vaccine.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2004 Aug;53(8):748-54. doi: 10.1007/s00262-004-0513-0. Epub 2004 Feb 28. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2004. PMID: 14997346 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

