Roles of salicylic acid, jasmonic acid, and ethylene in cpr-induced resistance in arabidopsis
- PMID: 11090217
- PMCID: PMC150166
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.12.11.2175
Roles of salicylic acid, jasmonic acid, and ethylene in cpr-induced resistance in arabidopsis
Abstract
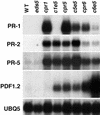
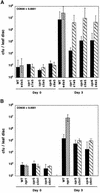
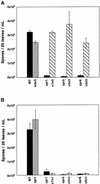
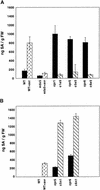
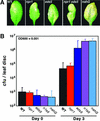
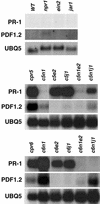
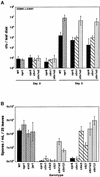
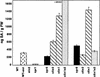
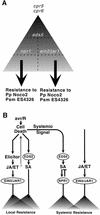
Disease resistance in Arabidopsis is regulated by multiple signal transduction pathways in which salicylic acid (SA), jasmonic acid (JA), and ethylene (ET) function as key signaling molecules. Epistasis analyses were performed between mutants that disrupt these pathways (npr1, eds5, ein2, and jar1) and mutants that constitutively activate these pathways (cpr1, cpr5, and cpr6), allowing exploration of the relationship between the SA- and JA/ET-mediated resistance responses. Two important findings were made. First, the constitutive disease resistance exhibited by cpr1, cpr5, and cpr6 is completely suppressed by the SA-deficient eds5 mutant but is only partially affected by the SA-insensitive npr1 mutant. Moreover, eds5 suppresses the SA-accumulating phenotype of the cpr mutants, whereas npr1 enhances it. These data indicate the existence of an SA-mediated, NPR1-independent resistance response. Second, the ET-insensitive mutation ein2 and the JA-insensitive mutation jar1 suppress the NPR1-independent resistance response exhibited by cpr5 and cpr6. Furthermore, ein2 potentiates SA accumulation in cpr5 and cpr5 npr1 while dampening SA accumulation in cpr6 and cpr6 npr1. These latter results indicate that cpr5 and cpr6 regulate resistance through distinct pathways and that SA-mediated, NPR1-independent resistance works in combination with components of the JA/ET-mediated response pathways.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ethylene and jasmonic acid signaling affect the NPR1-independent expression of defense genes without impacting resistance to Pseudomonas syringae and Peronospora parasitica in the Arabidopsis ssi1 mutant.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2003 Jul;16(7):588-99. doi: 10.1094/MPMI.2003.16.7.588. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2003. PMID: 12848424
-
Early responses in the Arabidopsis-Verticillium longisporum pathosystem are dependent on NDR1, JA- and ET-associated signals via cytosolic NPR1 and RFO1.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2006 Sep;19(9):958-69. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-19-0958. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2006. PMID: 16941900
-
Components of Arabidopsis defense- and ethylene-signaling pathways regulate susceptibility to Cauliflower mosaic virus by restricting long-distance movement.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2007 Jun;20(6):659-70. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-20-6-0659. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2007. PMID: 17555274
-
NPR1: the spider in the web of induced resistance signaling pathways.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2004 Aug;7(4):456-64. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2004.05.006. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2004. PMID: 15231270 Review.
-
NPR1, all things considered.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2004 Oct;7(5):547-52. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2004.07.005. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2004. PMID: 15337097 Review.
Cited by
-
Oxo-phytodienoic acid-containing galactolipids in Arabidopsis: jasmonate signaling dependence.Plant Physiol. 2007 Dec;145(4):1658-69. doi: 10.1104/pp.107.104752. Epub 2007 Oct 19. Plant Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17951463 Free PMC article.
-
Induced expression of oryzain alpha gene encoding a cysteine proteinase under stress conditions.J Plant Res. 2007 May;120(3):465-9. doi: 10.1007/s10265-007-0080-5. Epub 2007 Apr 3. J Plant Res. 2007. PMID: 17404686
-
Systemic gene expression in Arabidopsis during an incompatible interaction with Alternaria brassicicola.Plant Physiol. 2003 Jun;132(2):999-1010. doi: 10.1104/pp.103.021683. Epub 2003 May 1. Plant Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12805628 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular cloning and differential expression of an gamma-aminobutyrate transaminase gene, OsGABA-T, in rice (Oryza sativa) leaves infected with blast fungus.J Plant Res. 2006 Nov;119(6):663-9. doi: 10.1007/s10265-006-0018-3. Epub 2006 Aug 8. J Plant Res. 2006. PMID: 16896530
-
Identification of Arabidopsis ethylene-responsive element binding factors with distinct induction kinetics after pathogen infection.Plant Physiol. 2002 Apr;128(4):1313-22. doi: 10.1104/pp.010862. Plant Physiol. 2002. PMID: 11950980 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alanso, J.M., Hirayama, T., Roman, G., Nourizadeh, S., and Ecker, J.R. (1999). EIN2, a bifunctional transducer of ethylene and stress responses in Arabidopsis. Science 284, 2148–2152. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel, F.M., Brent, R., Kingston, R.E., Moore, D.D., Seidman, J.G., Smith, J.A., and Struhl, K., eds (1994). Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. (New York: Greene Publishing Association/Wiley Interscience).
-
- Baker, B., Zambryski, P., Staskawicz, B., and Dinesh-Kumar, S.P. (1997). Signaling in plant–microbe interactions. Science 276, 726–733. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

