Epstein-Barr virus that lacks glycoprotein gN is impaired in assembly and infection
- PMID: 11070013
- PMCID: PMC113204
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.74.23.11162-11172.2000
Epstein-Barr virus that lacks glycoprotein gN is impaired in assembly and infection
Abstract
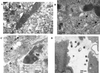
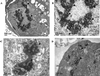
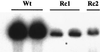
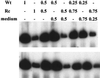
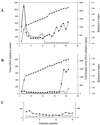
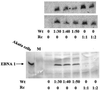
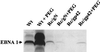
The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) glycoproteins N and M (gN and gM) are encoded by the BLRF1 and BBRF3 genes. To examine the function of the EBV gN-gM complex, recombinant virus was constructed in which the BLRF1 gene was interrupted with a neomycin resistance cassette. Recombinant virus lacked not only gN but also detectable gM. A significant proportion of the recombinant virus capsids remained associated with condensed chromatin in the nucleus of virus-producing cells, and cytoplasmic vesicles containing enveloped virus were scarce. Virus egress was impaired, and sedimentation analysis revealed that the majority of the virus that was released lacked a complete envelope. The small amount of virus that could bind to cells was also impaired in infectivity at a step following fusion. These data are consistent with the hypothesis that the predicted 78-amino-acid cytoplasmic tail of gM, which is highly charged and rich in prolines, interacts with the virion tegument. It is proposed that this interaction is important both for association of capsids with cell membrane to assemble and release enveloped particles and for dissociation of the capsid from the membrane of the newly infected cell on its way to the cell nucleus. The phenotype of EBV lacking the gN-gM complex is more striking than that of most alphaherpesviruses lacking the same complex but resembles in many respects the phenotype of pseudorabies virus lacking glycoproteins gM, gE, and gI. Since EBV does not encode homologs for gE and gI, this suggests that functions that may have some redundancy in alphaherpesviruses have been concentrated in fewer proteins in EBV.
Figures



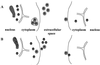
Similar articles
-
The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) gN homolog BLRF1 encodes a 15-kilodalton glycoprotein that cannot be authentically processed unless it is coexpressed with the EBV gM homolog BBRF3.J Virol. 1998 Jul;72(7):5559-64. doi: 10.1128/JVI.72.7.5559-5564.1998. J Virol. 1998. PMID: 9621013 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the cytoplasmic tail of pseudorabies virus glycoprotein E in virion formation.J Virol. 2000 May;74(9):4004-16. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.9.4004-4016.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10756012 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus glycoprotein gM can interact with the cellular protein p32 and knockdown of p32 impairs virus.Virology. 2016 Feb;489:223-32. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2015.12.019. Epub 2016 Jan 13. Virology. 2016. PMID: 26773383 Free PMC article.
-
Varicella-zoster virus glycoprotein M.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2010;342:147-54. doi: 10.1007/82_2010_30. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20373090 Review.
-
Tegument proteins of Epstein-Barr virus: Diverse functions, complex networks, and oncogenesis.Tumour Virus Res. 2023 Jun;15:200260. doi: 10.1016/j.tvr.2023.200260. Epub 2023 May 9. Tumour Virus Res. 2023. PMID: 37169175 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Envelope glycoprotein gB of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus is essential for egress from infected cells.J Virol. 2005 Sep;79(17):10952-67. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.17.10952-10967.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16103147 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus shed in saliva is high in B-cell-tropic glycoprotein gp42.J Virol. 2006 Jul;80(14):7281-3. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00497-06. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16809335 Free PMC article.
-
Gastric epithelial attachment of Helicobacter pylori induces EphA2 and NMHC-IIA receptors for Epstein-Barr virus.Cancer Sci. 2021 Nov;112(11):4799-4811. doi: 10.1111/cas.15121. Epub 2021 Sep 13. Cancer Sci. 2021. PMID: 34449934 Free PMC article.
-
Complete nucleotide sequence of the rhesus lymphocryptovirus: genetic validation for an Epstein-Barr virus animal model.J Virol. 2002 Jan;76(1):421-6. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.1.421-426.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 11739708 Free PMC article.
-
HCMV-encoded glycoprotein M (UL100) interacts with Rab11 effector protein FIP4.Traffic. 2009 Oct;10(10):1439-57. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2009.00967.x. Traffic. 2009. PMID: 19761540 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams R, Cunningham C, Davison M D, MacLean C A, Davison A J. Characterization of the protein encoded by the gene UL49A of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1998;78:813–823. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel F M, Brent R, Kingston R E, Moore D D, Siedman J G, Smith J A, Struhl K. Current protocols in molecular biology. New York, N.Y: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; 1997.
-
- Baer R, Bankier A T, Biggin M D, Deininger P L, Farrell P J, Gibson T J, Hatfull G, Hudson G S, Satchwell S C, Seguin C, Tuffnell P S, Barrell B G. DNA sequence and expression of the B95–8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984;310:207–211. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

