Platelet-derived growth factor receptor association with Na(+)/H(+) exchanger regulatory factor potentiates receptor activity
- PMID: 11046132
- PMCID: PMC102142
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.20.22.8352-8363.2000
Platelet-derived growth factor receptor association with Na(+)/H(+) exchanger regulatory factor potentiates receptor activity
Abstract
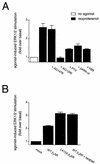
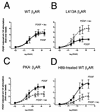
Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) is a potent mitogen for many cell types. The PDGF receptor (PDGFR) is a receptor tyrosine kinase that mediates the mitogenic effects of PDGF by binding to and/or phosphorylating a variety of intracellular signaling proteins upon PDGF-induced receptor dimerization. We show here that the Na(+)/H(+) exchanger regulatory factor (NHERF; also known as EBP50), a protein not previously known to interact with the PDGFR, binds to the PDGFR carboxyl terminus (PDGFR-CT) with high affinity via a PDZ (PSD-95/Dlg/Z0-1 homology) domain-mediated interaction and potentiates PDGFR autophosphorylation and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) activation in cells. A point-mutated version of the PDGFR, with the terminal leucine changed to alanine (L1106A), cannot bind NHERF in vitro and is markedly impaired relative to the wild-type receptor with regard to PDGF-induced autophosphorylation and activation of ERK in cells. NHERF potentiation of PDGFR signaling depends on the capacity of NHERF to oligomerize. NHERF oligomerizes in vitro when bound with PDGFR-CT, and a truncated version of the first NHERF PDZ domain that can bind PDGFR-CT but which does not oligomerize reduces PDGFR tyrosine kinase activity when transiently overexpressed in cells. PDGFR activity in cells can also be regulated in a NHERF-dependent fashion by stimulation of the beta(2)-adrenergic receptor, a known cellular binding partner for NHERF. These findings reveal that NHERF can directly bind to the PDGFR and potentiate PDGFR activity, thus elucidating both a novel mechanism by which PDGFR activity can be regulated and a new cellular role for the PDZ domain-containing adapter protein NHERF.
Figures
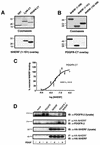
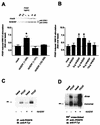
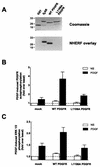

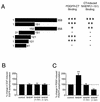
Similar articles
-
Oligomerization of NHERF-1 and NHERF-2 PDZ domains: differential regulation by association with receptor carboxyl-termini and by phosphorylation.Biochemistry. 2001 Jul 24;40(29):8572-80. doi: 10.1021/bi0103516. Biochemistry. 2001. PMID: 11456497
-
Ezrin-radixin-moesin-binding phosphoprotein-50/Na+/H+ exchanger regulatory factor (EBP50/NHERF) blocks U50,488H-induced down-regulation of the human kappa opioid receptor by enhancing its recycling rate.J Biol Chem. 2002 Jul 26;277(30):27545-52. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M200058200. Epub 2002 May 9. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12004055
-
Ligand-induced recruitment of Na+/H+-exchanger regulatory factor to the PDGF (platelet-derived growth factor) receptor regulates actin cytoskeleton reorganization by PDGF.Biochem J. 2003 Dec 1;376(Pt 2):505-10. doi: 10.1042/BJ20030385. Biochem J. 2003. PMID: 12967325 Free PMC article.
-
Assembly of signaling complexes by the sodium-hydrogen exchanger regulatory factor family of PDZ-containing proteins.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 1999 Sep;8(5):603-8. doi: 10.1097/00041552-199909000-00012. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 1999. PMID: 10541224 Review.
-
NHERF: targeting and trafficking membrane proteins.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2001 Mar;280(3):F389-95. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.2001.280.3.F389. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11181400 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel bioactivity of NHERF1 in corneal neovascularization.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2012 Nov;250(11):1615-25. doi: 10.1007/s00417-012-2094-5. Epub 2012 Jul 10. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2012. PMID: 22777301
-
New functions for the NHERF family of proteins.J Clin Invest. 2001 Jul;108(2):185-6. doi: 10.1172/JCI13518. J Clin Invest. 2001. PMID: 11457870 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The transmembrane protein CBP plays a role in transiently anchoring small clusters of Thy-1, a GPI-anchored protein, to the cytoskeleton.J Cell Sci. 2009 Nov 1;122(Pt 21):3966-72. doi: 10.1242/jcs.049346. Epub 2009 Oct 13. J Cell Sci. 2009. PMID: 19825940 Free PMC article.
-
The PDZ scaffold NHERF-2 interacts with mGluR5 and regulates receptor activity.J Biol Chem. 2006 Oct 6;281(40):29949-61. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M602262200. Epub 2006 Aug 4. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16891310 Free PMC article.
-
ERM-1 Phosphorylation and NRFL-1 Redundantly Control Lumen Formation in the C. elegans Intestine.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Feb 7;10:769862. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.769862. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35198555 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anan K, Morisaki T, Katano M, Ikubo A, Kitsuki H, Uchiyama A, Kuroki S, Tanaka M, Torisu M. Vascular endothelial growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor are potential angiogenic and metastatic factors in human breast cancer. Surgery. 1996;119:333–339. - PubMed
-
- Ariad S, Seymour L, Bezwoda W R. Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) in plasma of breast cancer patients: correlation with stage and rate of progression. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1991;20:11–17. - PubMed
-
- Brenman J E, Chao D S, Gee S H, McGee A W, Craven S E, Santillano D R, Wu Z, Huang F, Xia H, Peters M F, Froehner S C, Bredt D S. Interaction of nitric oxide syntahse with the postsynaptic density protein PSD-95 and α1-syntrophin mediated by PDZ domains. Cell. 1996;84:757–767. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
