Epstein-Barr virus LMP2A transforms epithelial cells, inhibits cell differentiation, and activates Akt
- PMID: 11044112
- PMCID: PMC110942
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.74.22.10681-10689.2000
Epstein-Barr virus LMP2A transforms epithelial cells, inhibits cell differentiation, and activates Akt
Abstract
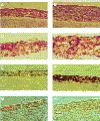
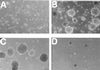
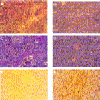
The Epstein-Barr virus LMP2A protein was expressed in a human keratinocyte cell line, HaCaT, and effects on epithelial cell growth were detected in organotypic raft cultures and in vivo in nude mice. Raft cultures derived from LMP2A-expressing cells were hyperproliferative, and epithelial differentiation was inhibited. The LMP2A-expressing HaCaT cells were able to grow anchorage independently and formed colonies in soft agar. HaCaT cells expressing LMP2A were highly tumorigenic and formed aggressive tumors in nude mice. The LMP2A tumors were poorly differentiated and highly proliferative, in contrast to occasional tumors that arose from parental HaCaT cells and vector control cells, which grew slowly and remained highly differentiated. Animals injected with LMP2A-expressing cells developed frequent metastases, which predominantly involved lymphoid organs. Involucrin, a marker of epithelial differentiation, and E-cadherin, involved in the maintenance of intercellular contact, were downregulated in LMP2A tumors. Whereas activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway was not observed, phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3-kinase)-dependent activation of the serine-threonine kinase Akt was detected in LMP2A-expressing cells and LMP2A tumors. Inhibition of this pathway blocked growth in soft agar. These data indicate that LMP2A greatly affects cell growth and differentiation pathways in epithelial cells, in part through activation of the PI3-kinase-Akt pathway.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 2A mediates transformation through constitutive activation of the Ras/PI3-K/Akt Pathway.J Virol. 2007 Sep;81(17):9299-306. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00537-07. Epub 2007 Jun 20. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17582000 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 2A activates beta-catenin signaling in epithelial cells.J Virol. 2003 Nov;77(22):12276-84. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.22.12276-12284.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 14581564 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) LMP2A mediates B-lymphocyte survival through constitutive activation of the Ras/PI3K/Akt pathway.Oncogene. 2004 Nov 11;23(53):8619-28. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207905. Oncogene. 2004. PMID: 15361852
-
Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein-2A induces ITAM/Syk- and Akt-dependent epithelial migration through αv-integrin membrane translocation.J Virol. 2012 Oct;86(19):10308-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00853-12. Epub 2012 Jul 25. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22837212 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus protein LMP2A regulates reactivation from latency by negatively regulating tyrosine kinases involved in sIg-mediated signal transduction.Infect Agents Dis. 1994 Apr-Jun;3(2-3):128-36. Infect Agents Dis. 1994. PMID: 7812651 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptional downregulation of p27KIP1 through regulation of E2F function during LMP1-mediated transformation.J Virol. 2009 Dec;83(24):12671-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01422-09. Epub 2009 Oct 14. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19828622 Free PMC article.
-
A cancer-associated Epstein-Barr virus BZLF1 promoter variant enhances lytic infection.PLoS Pathog. 2018 Jul 27;14(7):e1007179. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007179. eCollection 2018 Jul. PLoS Pathog. 2018. PMID: 30052684 Free PMC article.
-
Vasculogenic mimicry formation in EBV-associated epithelial malignancies.Nat Commun. 2018 Nov 27;9(1):5009. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07308-5. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30479336 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of autophagy-like processes by tumor viruses.Cells. 2012 Jun 25;1(3):204-47. doi: 10.3390/cells1030204. Cells. 2012. PMID: 24710474 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 2 effects on epithelial acinus development reveal distinct requirements for the PY and YEEA motifs.J Virol. 2013 Dec;87(24):13803-15. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02203-13. Epub 2013 Oct 9. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 24109232 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alessi D R, Kozlowski M T, Weng Q P, Morrice N, Avruch J. 3-Phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 (PDK1) phosphorylates and activates the p70 S6 kinase in vivo and in vitro. Curr Biol. 1998;8:69–81. - PubMed
-
- Assilineau D, Prunieras M. Reconstruction of ‘simplified’ skin: control of fabrication. Br J Dermatol. 1984;111:219–222. - PubMed
-
- Balendran A, Currie R, Armstrong C G, Avruch J, Alessi D R. Evidence that 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 mediates phosphorylation of p70 S6 kinase in vivo at Thr-412 as well as Thr-252. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:37400–37406. - PubMed
-
- Behrens J. Cadherins and catenins: role in signal transduction and tumor progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1999;18:15–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

