Efficacy and safety studies of a recombinant chimeric respiratory syncytial virus FG glycoprotein vaccine in cotton rats
- PMID: 11044072
- PMCID: PMC110902
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.74.22.10287-10292.2000
Efficacy and safety studies of a recombinant chimeric respiratory syncytial virus FG glycoprotein vaccine in cotton rats
Abstract
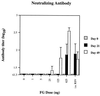
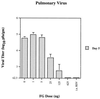
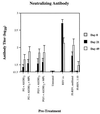
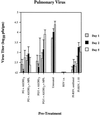
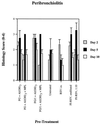
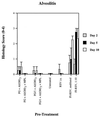
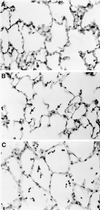
Several formulations of a recombinant chimeric respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) vaccine consisting of the extramembrane domains of the F and G glycoproteins (FG) were tested in cotton rats to evaluate efficacy and safety. The FG vaccine was highly immunogenic, providing nearly complete resistance to pulmonary infection at doses as low as 25 ng in spite of inducing relatively low levels of serum neutralizing antibody at low vaccine doses. Upon RSV challenge animals primed with FG vaccine showed quite mild alveolitis and interstitial pneumonitis, which were eliminated by the addition of monophosphoryl lipid A to the formulation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Virus-like particle vaccines containing F or F and G proteins confer protection against respiratory syncytial virus without pulmonary inflammation in cotton rats.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2017 May 4;13(5):1031-1039. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2016.1272743. Epub 2017 Jan 27. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2017. PMID: 28129031 Free PMC article.
-
A Single-Dose Recombinant Parainfluenza Virus 5-Vectored Vaccine Expressing Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) F or G Protein Protected Cotton Rats and African Green Monkeys from RSV Challenge.J Virol. 2017 May 12;91(11):e00066-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00066-17. Print 2017 Jun 1. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28298602 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccination with a heterologous respiratory syncytial virus chimeric FG glycoprotein demonstrates significant subgroup cross-reactivity.Vaccine. 1993;11(10):1040-8. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(93)90131-g. Vaccine. 1993. PMID: 8212825
-
Respiratory syncytial virus vaccines for otitis media.Vaccine. 2000 Dec 8;19 Suppl 1:S59-65. doi: 10.1016/s0264-410x(00)00280-2. Vaccine. 2000. PMID: 11163465 Review.
-
Cotton rat model for testing vaccines and antivirals against respiratory syncytial virus.Antivir Chem Chemother. 2018 Jan-Dec;26:2040206618770518. doi: 10.1177/2040206618770518. Antivir Chem Chemother. 2018. PMID: 29768937 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
New insights for development of a safe and protective RSV vaccine.Hum Vaccin. 2010 Jun;6(6):482-92. doi: 10.4161/hv.6.6.11562. Epub 2010 Jun 1. Hum Vaccin. 2010. PMID: 20671419 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human metapneumovirus: enhanced pulmonary disease in cotton rats immunized with formalin-inactivated virus vaccine and challenged.Vaccine. 2007 Jun 28;25(27):5034-40. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2007.04.075. Epub 2007 May 15. Vaccine. 2007. PMID: 17543425 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenesis of human metapneumovirus lung infection in BALB/c mice and cotton rats.J Virol. 2005 Jul;79(14):8894-903. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.14.8894-8903.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15994783 Free PMC article.
-
Active immunoprophylaxis with a synthetic DNA-encoded monoclonal anti-respiratory syncytial virus scFv-Fc fusion protein confers protection against infection and durable activity.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2020 Sep 1;16(9):2165-2175. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2020.1748979. Epub 2020 Jun 16. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2020. PMID: 32544376 Free PMC article.
-
Dual role of interleukin-10 in the regulation of respiratory syncitial virus (RSV)-induced lung inflammation.Clin Exp Immunol. 2013 May;172(2):263-79. doi: 10.1111/cei.12059. Clin Exp Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23574323 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bastien N, Trudel M, Simard C. Complete protection of mice from respiratory syncytial virus infection following mucosal delivery of synthetic peptide vaccine. Vaccine. 1999;17:832–836. - PubMed
-
- Baybutt H N, Pringle C R. Molecular cloning and sequencing of the F and 22K membrane protein genes of the RSS-2 strain of respiratory syncytial virus. J Gen Virol. 1987;68:2789–2796. - PubMed
-
- Belshe R B, Van Voris L P, Mufson M A. Parenteral administration of live respiratory syncytial virus vaccine: results of a field trial. J Infect Dis. 1982;145:311–319. - PubMed
-
- Brideau R J, Walters R R, Stier M A, Wathen M W. Protection of cotton rats against human respiratory syncytial virus by vaccination with a novel chimeric FG glycoprotein. J Gen Virol. 1989;70:2637–2644. - PubMed
-
- Cano F, Plotnicky-Gilquin H, Nguyen T N, Liljeqvist S, Samuelson P, Bonnefoy J-Y, Ståhl S, Robert A. Partial protection to respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) elicited in mice by intranasal immunization using live staphylococci with surface-displayed RSV-peptides. Vaccine. 2000;18:2743–2752. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

