Regulation of macropinocytosis by p21-activated kinase-1
- PMID: 11029040
- PMCID: PMC14996
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.11.10.3341
Regulation of macropinocytosis by p21-activated kinase-1
Abstract
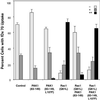
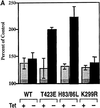
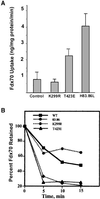
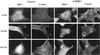
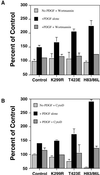
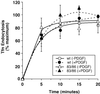
The process of macropinocytosis is an essential aspect of normal cell function, contributing to both growth and motile processes of cells. p21-activated kinases (PAKs) are targets for activated Rac and Cdc42 guanosine 5'-triphosphatases and have been shown to regulate the actin-myosin cytoskeleton. In fibroblasts PAK1 localizes to areas of membrane ruffling, as well as to amiloride-sensitive pinocytic vesicles. Expression of a PAK1 kinase autoinhibitory domain blocked both platelet-derived growth factor- and RacQ61L-stimulated uptake of 70-kDa dextran particles, whereas an inactive version of this domain did not, indicating that PAK kinase activity is required for normal growth factor-induced macropinocytosis. The mechanisms by which PAK modulate macropinocytosis were examined in NIH3T3 cell lines expressing various PAK1 constructs under the control of a tetracycline-responsive transactivator. Cells expressing PAK1 (H83,86L), a mutant that dramatically stimulates formation of dorsal membrane ruffles, exhibited increased macropinocytic uptake of 70-kDa dextran particles in the absence of additional stimulation. This effect was not antagonized by coexpression of dominant-negative Rac1-T17N. In the presence of platelet-derived growth factor, both PAK1 (H83,86L) and a highly kinase active PAK1 (T423E) mutant dramatically enhanced the uptake of 70-kDa dextran. Neither wild-type PAK1 nor vector controls exhibited enhanced macropinocytosis, nor did PAK1 (H83,86L) affect clathrin-dependent endocytic mechanisms. Active versions of PAK1 enhanced both growth factor-stimulated 70-kDa dextran uptake and efflux, suggesting that PAK1 activity modulated pinocytic vesicle cycling. These data indicate that PAK1 plays an important regulatory role in the process of macropinocytosis, perhaps related to the requirement for PAK in directed cell motility.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Localization of p21-activated kinase 1 (PAK1) to pinocytic vesicles and cortical actin structures in stimulated cells.J Cell Biol. 1997 Sep 22;138(6):1265-78. doi: 10.1083/jcb.138.6.1265. J Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9298982 Free PMC article.
-
Association of PI-3 kinase with PAK1 leads to actin phosphorylation and cytoskeletal reorganization.Mol Biol Cell. 2002 Aug;13(8):2946-62. doi: 10.1091/mbc.02-01-0599. Mol Biol Cell. 2002. PMID: 12181358 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal and spatial distribution of activated Pak1 in fibroblasts.J Cell Biol. 2000 Dec 25;151(7):1449-58. doi: 10.1083/jcb.151.7.1449. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 11134074 Free PMC article.
-
Spatiotemporal regulation of the Pak1 kinase.Biochem Soc Trans. 2005 Aug;33(Pt 4):646-8. doi: 10.1042/BST0330646. Biochem Soc Trans. 2005. PMID: 16042564 Review.
-
p21-Activated kinase 1 (PAK1) in aging and longevity: An overview.Ageing Res Rev. 2021 Nov;71:101443. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2021.101443. Epub 2021 Aug 12. Ageing Res Rev. 2021. PMID: 34390849 Review.
Cited by
-
Macropinocytosis of type XVII collagen induced by bullous pemphigoid IgG is regulated via protein kinase C.Lab Invest. 2016 Dec;96(12):1301-1310. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2016.108. Epub 2016 Oct 24. Lab Invest. 2016. PMID: 27775687
-
Endocytosis unplugged: multiple ways to enter the cell.Cell Res. 2010 Mar;20(3):256-75. doi: 10.1038/cr.2010.19. Epub 2010 Feb 2. Cell Res. 2010. PMID: 20125123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Tat regulates endothelial cell actin cytoskeletal dynamics through PAK1 activation and oxidant production.J Virol. 2004 Jan;78(2):779-89. doi: 10.1128/jvi.78.2.779-789.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 14694110 Free PMC article.
-
Macropinosomes as units of signal transduction.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2019 Feb 4;374(1765):20180157. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2018.0157. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30967006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanism of ribonuclease A endocytosis: analogies to cell-penetrating peptides.Biochemistry. 2011 Oct 4;50(39):8374-82. doi: 10.1021/bi2009079. Epub 2011 Sep 7. Biochemistry. 2011. PMID: 21827164 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bagrodia S, Derijard B, Davis RJ, Cerione RA. Cdc42, and PAK-mediated signaling leads to Jun kinase and p38MAP kinase activation. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:27995–27998. - PubMed
-
- Bar-Sagi D, Feramisco JR. Induction of membrane ruffling and fluid-phase pinocytosis in quiescent fibroblast by ras proteins. Science. 1986;233:1061–1068. - PubMed
-
- Bretscher MS. Getting membrane flow and the cytoskeleton to cooperate in moving cells. Cell. 1996;87:601–606. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

