Involvement of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in spatial memory formation and maintenance in a radial arm maze test in rats
- PMID: 10995859
- PMCID: PMC6772840
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-18-07116.2000
Involvement of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in spatial memory formation and maintenance in a radial arm maze test in rats
Abstract
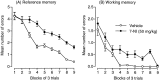
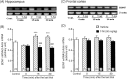
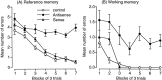
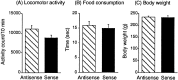
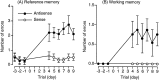
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) regulates both short-term synaptic functions and activity-dependent synaptic plasticity such as long-term potentiation. In the present study, we investigated the role of BDNF in the spatial reference and working memory in a radial arm maze test. The radial arm maze training resulted in a significant increase in the BDNF mRNA expression in the hippocampus, although the expression in the frontal cortex did not change. When spatial learning was inhibited by treatment with 7-nitroindazole, an inhibitor of brain nitric oxide synthase, the increase in the hippocampal BDNF mRNA did not occur. To clarify the causal relation between BDNF mRNA expression and spatial memory formation, we examined the effects of antisense BDNF treatment on spatial learning and memory. A continuous intracerebroventricular infusion of antisense BDNF oligonucleotide resulted in an impairment of spatial learning, although the sense oligonucleotide had no effect. Treatment with antisense, but not sense, BDNF oligonucleotide was associated with a significant reduction of BDNF mRNA and protein levels in the hippocampus. Furthermore, treatment with antisense BDNF oligonucleotide in rats, which had previously acquired spatial memory by an extensive training, impaired both reference and working memory. There were no differences in locomotor activity, food consumption, and body weight between the antisense and sense oligonucleotide-treated rats. These results suggest that BDNF plays an important role not only in the formation, but also in the retention and/or recall, of spatial memory.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase: a molecule mediating BDNF-dependent spatial memory formation.Mol Psychiatry. 2003 Feb;8(2):217-24. doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4001215. Mol Psychiatry. 2003. PMID: 12610654
-
Learning upregulates brain-derived neurotrophic factor messenger ribonucleic acid: a mechanism to facilitate encoding and circuit maintenance?Behav Neurosci. 1998 Aug;112(4):1012-9. doi: 10.1037//0735-7044.112.4.1012. Behav Neurosci. 1998. PMID: 9733207
-
Bidirectional changes in water-maze learning following recombinant adenovirus-associated viral vector (rAAV)-mediated brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in the rat hippocampus.Behav Pharmacol. 2007 Sep;18(5-6):533-47. doi: 10.1097/FBP.0b013e3282da0bf6. Behav Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17762522
-
The effect of a selective neuronal nitric oxide synthase inhibitor 3-bromo 7-nitroindazole on spatial learning and memory in rats.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2015 Apr;131:19-25. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2015.01.013. Epub 2015 Jan 28. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2015. PMID: 25636602
-
Use it and boost it with physical and mental activity.Hippocampus. 2013 Nov;23(11):1125-35. doi: 10.1002/hipo.22197. Hippocampus. 2013. PMID: 23996382 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neurotropic activity of ACTH(7-10)PGP, an analog of an ACTH fragment.Dokl Biol Sci. 2011 Sep-Oct;440:270-4. doi: 10.1134/S0012496611050140. Epub 2011 Dec 2. Dokl Biol Sci. 2011. PMID: 22134808 No abstract available.
-
The neurotrophins and their role in Alzheimer's disease.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2011 Dec;9(4):559-73. doi: 10.2174/157015911798376190. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2011. PMID: 22654716 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in hippocampus: complexity of steroid hormone-growth factor interactions in the adult CNS.Front Neuroendocrinol. 2006 Dec;27(4):415-35. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2006.09.004. Epub 2006 Oct 20. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2006. PMID: 17055560 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Short- and long-term effects of intermittent social defeat stress on brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in mesocorticolimbic brain regions.Neuroscience. 2010 May 19;167(3):598-607. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.02.064. Epub 2010 Mar 3. Neuroscience. 2010. PMID: 20206238 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Ficus umbellata (Moraceae) Aqueous Extract and 7-Methoxycoumarin on Scopolamine-Induced Spatial Memory Impairment in Ovariectomized Wistar Rats.Behav Neurol. 2018 Sep 30;2018:5751864. doi: 10.1155/2018/5751864. eCollection 2018. Behav Neurol. 2018. PMID: 30363978 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acheson A, Conover JC, Fandl JP, DeChiare TM, Russell M, Thadani A, Squinto SP, Yancopoulos GD, Lindsay RM. A BDNF autocrine loop in adult sensory neurons prevents cell death. Nature. 1995;374:450–453. - PubMed
-
- Barnes CA. Involvement of LTP in memory: are we “searching under the street light”? Neuron. 1995;15:751–754. - PubMed
-
- Berninger B, Poo MM. Fast actions of neurotrophic factors. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1996;6:324–330. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
