Redistribution of Golgi stacks and other organelles during mitosis and cytokinesis in plant cells
- PMID: 10982429
- PMCID: PMC59129
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.124.1.135
Redistribution of Golgi stacks and other organelles during mitosis and cytokinesis in plant cells
Abstract
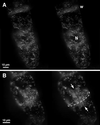
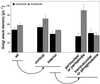
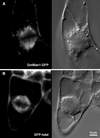
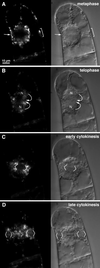
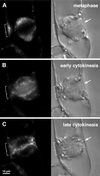
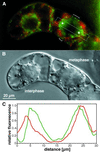
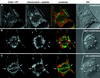
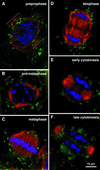
We have followed the redistribution of Golgi stacks during mitosis and cytokinesis in living tobacco BY-2 suspension culture cells by means of a green fluorescent protein-tagged soybean alpha-1,2 mannosidase, and correlated the findings to cytoskeletal rearrangements and to the redistribution of endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, and plastids. In preparation for cell division, when the general streaming of Golgi stacks stops, about one-third of the peripheral Golgi stacks redistributes to the perinuclear cytoplasm, the phragmosome, thereby reversing the ratio of interior to cortical Golgi from 2:3 to 3:2. During metaphase, approximately 20% of all Golgi stacks aggregate in the immediate vicinity of the mitotic spindle and a similar number becomes concentrated in an equatorial region under the plasma membrane. This latter localization, the "Golgi belt," accurately predicts the future site of cell division, and thus forms a novel marker for this region after the disassembly of the preprophase band. During telophase and cytokinesis, many Golgi stacks redistribute around the phragmoplast where the cell plate is formed. At the end of cytokinesis, the daughter cells have very similar Golgi stack densities. The sites of preferential Golgi stack localization are specific for this organelle and largely exclude mitochondria and plastids, although some mitochondria can approach the phragmoplast. This segregation of organelles is first observed in metaphase and persists until completion of cytokinesis. Maintenance of the distinct localizations does not depend on intact actin filaments or microtubules, although the mitotic spindle appears to play a major role in organizing the organelle distribution patterns. The redistribution of Golgi stacks during mitosis and cytokinesis is consistent with the hypothesis that Golgi stacks are repositioned to ensure equal partitioning between daughter cells as well as rapid cell plate assembly.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Reorganization of the Golgi complex in association with mitosis: redistribution of mannosidase II to the endoplasmic reticulum and effects of brefeldin A.J Submicrosc Cytol Pathol. 1992 Oct;24(4):495-508. J Submicrosc Cytol Pathol. 1992. PMID: 1458437
-
Role of microtubules in the organization of the Golgi complex.Exp Cell Res. 1999 Feb 1;246(2):263-79. doi: 10.1006/excr.1998.4326. Exp Cell Res. 1999. PMID: 9925741 Review.
-
An ordered inheritance strategy for the Golgi apparatus: visualization of mitotic disassembly reveals a role for the mitotic spindle.J Cell Biol. 1998 May 18;141(4):955-66. doi: 10.1083/jcb.141.4.955. J Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9585414 Free PMC article.
-
Partitioning of cytoplasmic organelles during mitosis with special reference to the Golgi complex.Microsc Res Tech. 1998 Mar 1;40(5):354-68. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0029(19980301)40:5<354::AID-JEMT3>3.0.CO;2-R. Microsc Res Tech. 1998. PMID: 9527046 Review.
-
Microtubules and the organization of the Golgi complex.Exp Cell Res. 1985 Jul;159(1):1-16. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(85)80032-x. Exp Cell Res. 1985. PMID: 3896822 Review.
Cited by
-
The secretory system of Arabidopsis.Arabidopsis Book. 2008;6:e0116. doi: 10.1199/tab.0116. Epub 2008 Sep 30. Arabidopsis Book. 2008. PMID: 22303241 Free PMC article.
-
Putative p24 complexes in Arabidopsis contain members of the delta and beta subfamilies and cycle in the early secretory pathway.J Exp Bot. 2013 Aug;64(11):3147-67. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ert157. J Exp Bot. 2013. PMID: 23918961 Free PMC article.
-
The association of peroxisomes with the developing cell plate in dividing onion root cells depends on actin microfilaments and myosin.Planta. 2003 Dec;218(2):204-16. doi: 10.1007/s00425-003-1096-2. Epub 2003 Aug 21. Planta. 2003. PMID: 12937986
-
The role of GRASP55 in Golgi fragmentation and entry of cells into mitosis.Mol Biol Cell. 2008 Jun;19(6):2579-87. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e07-10-0998. Epub 2008 Apr 2. Mol Biol Cell. 2008. PMID: 18385516 Free PMC article.
-
Subcellular positioning during cell division and cell plate formation in maize.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Jul 7;14:1204889. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1204889. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37484472 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andersland JM, Fisher DD, Wymer CL, Cyr RJ, Parthasarathy MV. Characterization of a monoclonal antibody prepared against plant actin. Cell Motil Cytoskel. 1994;29:339–344. - PubMed
-
- Andreeva AV, Kutuzov MA, Evans DE, Hawes CR. The structure and function of the Golgi apparatus: a hundred years of questions. J Exp Bot. 1998;49:1281–1291.
-
- Binarová P, Hause B, Dolezel J, Dráber P. Association of γ-tubulin with kinetochore/centromeric region of plant chromosomes. Plant J. 1998;14:751–757.
-
- Driouich A, Staehelin LA. The plant Golgi apparatus: structural organization and functional properties. In: Berger EG, Roth J, editors. The Golgi apparatus. Basel: Birkhäuser-Verlag; 1997. pp. 275–301.
-
- Dupree P, Sherrier DJ. The plant Golgi apparatus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998;1404:259–270. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

