High-resolution genetic and physical map of the Lgn1 interval in C57BL/6J implicates Naip2 or Naip5 in Legionella pneumophila pathogenesis
- PMID: 10958634
- PMCID: PMC310929
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.10.8.1158
High-resolution genetic and physical map of the Lgn1 interval in C57BL/6J implicates Naip2 or Naip5 in Legionella pneumophila pathogenesis
Abstract
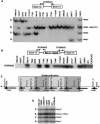
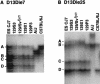
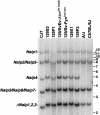
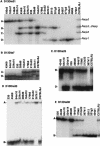
Prior genetic and physical mapping has shown that the Naip gene cluster on mouse chromosome 13D1-D3 contains a gene, Lgn1, that is responsible for determining the permissivity of ex vivo macrophages to Legionella pneumophila replication. We have identified differences in the structure of the Naip array among commonly used inbred mouse strains, although these gross structural differences do not correlate with differences in L. pneumophila permissiveness. A physical map of the region employing clones of the C57BL/6J haplotype confirms that there are fewer copies of Naip in this strain than are in the physical map of the 129 haplotype. We have also refined the genetic location of Lgn1, leaving only Naip2 and Naip5 as candidates for Lgn1. Our genetic map suggests the presence of two hotspots of recombination within the Naip array, indicating that the 3' portion of Naip may be involved in the genomic instability at this locus.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Birc1e is the gene within the Lgn1 locus associated with resistance to Legionella pneumophila.Nat Genet. 2003 Jan;33(1):55-60. doi: 10.1038/ng1065. Epub 2002 Dec 16. Nat Genet. 2003. PMID: 12483212
-
Naip5 affects host susceptibility to the intracellular pathogen Legionella pneumophila.Curr Biol. 2003 Jan 8;13(1):27-36. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(02)01359-3. Curr Biol. 2003. PMID: 12526741
-
Evolutionary divergence of the mouse and human Lgn1/SMA repeat structures.Genomics. 2000 Feb 15;64(1):62-81. doi: 10.1006/geno.1999.6111. Genomics. 2000. PMID: 10708519
-
Naip5/Birc1e and susceptibility to Legionella pneumophila.Trends Microbiol. 2005 Jul;13(7):328-35. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2005.05.007. Trends Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15935674 Review.
-
[Control of intracellular Legionella pneumophila growth--with special reference to the Lgn1/Naip5/Birc1e gene--].Nihon Saikingaku Zasshi. 2009 Dec;64(2-4):319-30. doi: 10.3412/jsb.64.319. Nihon Saikingaku Zasshi. 2009. PMID: 19628930 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
A 360° view of the inflammasome: Mechanisms of activation, cell death, and diseases.Cell. 2023 May 25;186(11):2288-2312. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.04.025. Cell. 2023. PMID: 37236155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular pathogenesis of infections caused by Legionella pneumophila.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2010 Apr;23(2):274-98. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00052-09. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2010. PMID: 20375353 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epithelial NAIPs protect against colonic tumorigenesis.J Exp Med. 2015 Mar 9;212(3):369-83. doi: 10.1084/jem.20140474. Epub 2015 Mar 2. J Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 25732303 Free PMC article.
-
The inflammasome in host defense.Sensors (Basel). 2010;10(1):97-111. doi: 10.3390/s100100097. Epub 2009 Dec 28. Sensors (Basel). 2010. PMID: 22315529 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain containing-like receptor family, caspase recruitment domain (CARD) containing 4 (NLRC4) regulates intrapulmonary replication of aerosolized Legionella pneumophila.BMC Infect Dis. 2013 Aug 10;13:371. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-13-371. BMC Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 23937571 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beckers M C, Yoshida S, Morgan K, Skamene E, Gros P. Natural resistance to infection with Legionella pneumophila: chromosomal localization of the Lgn1 susceptibility gene. Mamm Genome. 1995;6:540–545. - PubMed
-
- Bergin A, Kim G, Price D L, Sisodia S S, Lee M K, Rabin B A. Identification and characterization of a mouse homologue of the spinal muscular atrophy–determining gene, survival motor neuron. Gene. 1997;204:47–53. - PubMed
-
- Burglen L, Lefebvre S, Clermont O, Burlet P, Viollet L, Cruaud C, Munnich A, Melki J. Structure and organization of the human survival motor neurone (SMN) gene. Genomics. 1996;32:479–482. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
