Sensitivity of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 to the fusion inhibitor T-20 is modulated by coreceptor specificity defined by the V3 loop of gp120
- PMID: 10954535
- PMCID: PMC116346
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.74.18.8358-8367.2000
Sensitivity of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 to the fusion inhibitor T-20 is modulated by coreceptor specificity defined by the V3 loop of gp120
Abstract
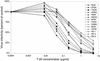
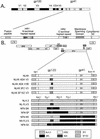
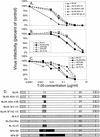
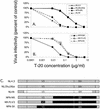
T-20 is a synthetic peptide that potently inhibits replication of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 by interfering with the transition of the transmembrane protein, gp41, to a fusion active state following interactions of the surface glycoprotein, gp120, with CD4 and coreceptor molecules displayed on the target cell surface. Although T-20 is postulated to interact with an N-terminal heptad repeat within gp41 in a trans-dominant manner, we show here that sensitivity to T-20 is strongly influenced by coreceptor specificity. When 14 T-20-naive primary isolates were analyzed for sensitivity to T-20, the mean 50% inhibitory concentration (IC(50)) for isolates that utilize CCR5 for entry (R5 viruses) was 0.8 log(10) higher than the mean IC(50) for CXCR4 (X4) isolates (P = 0. 0055). Using NL4.3-based envelope chimeras that contain combinations of envelope sequences derived from R5 and X4 viruses, we found that determinants of coreceptor specificity contained within the gp120 V3 loop modulate this sensitivity to T-20. The IC(50) for all chimeric envelope viruses containing R5 V3 sequences was 0.6 to 0.8 log(10) higher than that for viruses containing X4 V3 sequences. In addition, we confirmed that the N-terminal heptad repeat of gp41 determines the baseline sensitivity to T-20 and that the IC(50) for viruses containing GIV at amino acid residues 36 to 38 was 1.0 log(10) lower than the IC(50) for viruses containing a G-to-D substitution. The results of this study show that gp120-coreceptor interactions and the gp41 N-terminal heptad repeat independently contribute to sensitivity to T-20. These results have important implications for the therapeutic uses of T-20 as well as for unraveling the complex mechanisms of virus fusion and entry.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sensitivity of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 to fusion inhibitors targeted to the gp41 first heptad repeat involves distinct regions of gp41 and is consistently modulated by gp120 interactions with the coreceptor.J Virol. 2001 Sep;75(18):8605-14. doi: 10.1128/jvi.75.18.8605-8614.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11507206 Free PMC article.
-
CD4-induced T-20 binding to human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120 blocks interaction with the CXCR4 coreceptor.J Virol. 2004 May;78(10):5448-57. doi: 10.1128/jvi.78.10.5448-5457.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15113923 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations That Increase the Stability of the Postfusion gp41 Conformation of the HIV-1 Envelope Glycoprotein Are Selected by both an X4 and R5 HIV-1 Virus To Escape Fusion Inhibitors Corresponding to Heptad Repeat 1 of gp41, but the gp120 Adaptive Mutations Differ between the Two Viruses.J Virol. 2019 May 15;93(11):e00142-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00142-19. Print 2019 Jun 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30894471 Free PMC article.
-
HIV entry inhibitors: mechanisms of action and resistance pathways.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2006 Apr;57(4):619-27. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkl027. Epub 2006 Feb 7. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2006. PMID: 16464888 Review.
-
Progress in targeting HIV-1 entry.Drug Discov Today. 2005 Aug 15;10(16):1085-94. doi: 10.1016/S1359-6446(05)03550-6. Drug Discov Today. 2005. PMID: 16182193 Review.
Cited by
-
Drug-eluting fibers for HIV-1 inhibition and contraception.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e49792. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049792. Epub 2012 Nov 28. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23209601 Free PMC article.
-
The Low-Cost Compound Lignosulfonic Acid (LA) Exhibits Broad-Spectrum Anti-HIV and Anti-HSV Activity and Has Potential for Microbicidal Applications.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 1;10(7):e0131219. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0131219. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26132818 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Exposure to PC-1005 and Cervicovaginal Lavage Fluid from Women Vaginally Administered PC-1005 Inhibits HIV-1 and HSV-2 Infection in Human Cervical Mucosa.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Aug 22;60(9):5459-66. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00392-16. Print 2016 Sep. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016. PMID: 27381393 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Novel inhibitors of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus entry that act by three distinct mechanisms.J Virol. 2013 Jul;87(14):8017-28. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00998-13. Epub 2013 May 15. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23678171 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial glutaminase release contributes to glutamate-mediated neurotoxicity during human immunodeficiency virus-1 infection.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2012 Sep;7(3):619-28. doi: 10.1007/s11481-012-9364-1. Epub 2012 Apr 18. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22527635 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berger E A, Murphy P M, Farber J M. Chemokine receptors as HIV-1 coreceptors: roles in viral entry, tropism, and disease. Annu Rev Immunol. 1999;17:657–700. - PubMed
-
- Bullough P A, Hughson F M, Skehel J J, Wiley D C. Structure of influenza haemagglutinin at the pH of membrane fusion. Nature. 1994;371:37–43. - PubMed
-
- Carr C K. A spring-loaded mechanism for the conformational change of influenza hemagglutinin. Cell. 1993;73:823–832. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

