Blockade of the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase suppresses tumorigenesis in MMTV/Neu + MMTV/TGF-alpha bigenic mice
- PMID: 10931950
- PMCID: PMC16912
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.160564197
Blockade of the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase suppresses tumorigenesis in MMTV/Neu + MMTV/TGF-alpha bigenic mice
Abstract
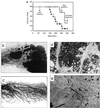
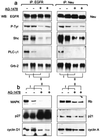
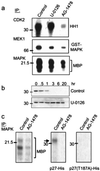
Overexpression of ErbB-2/Neu has been causally associated with mammary epithelial transformation. Here we report that blockade of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) kinase with AG-1478 markedly delays breast tumor formation in mouse mammary tumor virus (MMTV)/Neu + MMTV/transforming growth factor alpha bigenic mice. This delay was associated with inhibition of EGFR and Neu signaling, reduction of cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (Cdk2) and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) activities and cyclin D1, and an increase in the levels of the Cdk inhibitor p27(Kip1). In addition, BrdUrd incorporation into tumor cell nuclei was prevented with no signs of tumor cell apoptosis. These observations prompted us to investigate the stability of p27. Recombinant p27 was degraded rapidly in vitro by untreated but not by AG-1478-treated tumor lysates. Proteasome depletion of the tumor lysates, addition of the specific MEK1/2 inhibitor U-0126, or a T187A mutation in recombinant p27 all prevented p27 degradation. Cdk2 and MAPK precipitates from untreated tumor lysates phosphorylated recombinant wild-type p27 but not the T187A mutant in vitro. Cdk2 and MAPK precipitates from AG-1478-treated tumors were unable to phosphorylate p27 in vitro. These data suggest that increased signaling by ErbB receptors up-regulates MAPK activity, which, in turn, phosphorylates and destabilizes p27, thus contributing to dysregulated cell cycle progression.
Figures

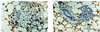

Similar articles
-
ErbB2/neu kinase modulates cellular p27(Kip1) and cyclin D1 through multiple signaling pathways.Cancer Res. 2001 Sep 1;61(17):6583-91. Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11522658
-
ErbB2/Neu-induced, cyclin D1-dependent transformation is accelerated in p27-haploinsufficient mammary epithelial cells but impaired in p27-null cells.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Apr;22(7):2204-19. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.7.2204-2219.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11884607 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation-dependent degradation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27.EMBO J. 1997 Sep 1;16(17):5334-44. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.17.5334. EMBO J. 1997. PMID: 9311993 Free PMC article.
-
Role of p27 in prostate carcinogenesis.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1998-1999;17(4):337-44. doi: 10.1023/a:1006133620914. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1998. PMID: 10453277 Review.
-
Role of the CDK inhibitor p27 (Kip1) in mammary development and carcinogenesis: insights from knockout mice.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2004 Jan;9(1):55-66. doi: 10.1023/B:JOMG.0000023588.55733.84. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2004. PMID: 15082918 Review.
Cited by
-
The AHR represses nucleotide excision repair and apoptosis and contributes to UV-induced skin carcinogenesis.Cell Death Differ. 2018 Nov;25(10):1823-1836. doi: 10.1038/s41418-018-0160-1. Epub 2018 Jul 16. Cell Death Differ. 2018. PMID: 30013037 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine phosphorylation and signaling controlled by a nuclear receptor coactivator, amplified in breast cancer 1.Cancer Res. 2007 Aug 1;67(15):7256-65. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-1013. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17671194 Free PMC article.
-
Oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010 Oct;2(10):a003236. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a003236. Epub 2010 Aug 18. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010. PMID: 20719876 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systematic identification of CDC34 that functions to stabilize EGFR and promote lung carcinogenesis.EBioMedicine. 2020 Mar;53:102689. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102689. Epub 2020 Feb 27. EBioMedicine. 2020. PMID: 32114396 Free PMC article.
-
Prevention of ER-negative breast cancer.Recent Results Cancer Res. 2009;181:121-34. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-69297-3_13. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19213564 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ullrich A, Coussens L, Hayflick J S, Dull T J, Gray A, Tam A W, Lee J, Yarden Y, Libermann T A, et al. Nature (London) 1984;309:418–425. - PubMed
-
- Bargmann C I, Hung M C, Weinberg R A. Nature (London) 1986;319:226–230. - PubMed
-
- Plowman G D, Green J M, Culouscou J M, Carlton G W, Rothwell V M, Buckley S. Nature (London) 1993;366:473–475. - PubMed
-
- Riese D J, Stern D F. BioEssays. 1998;20:41–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

