Unlabeled helper oligonucleotides increase the in situ accessibility to 16S rRNA of fluorescently labeled oligonucleotide probes
- PMID: 10919826
- PMCID: PMC92190
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.66.8.3603-3607.2000
Unlabeled helper oligonucleotides increase the in situ accessibility to 16S rRNA of fluorescently labeled oligonucleotide probes
Abstract
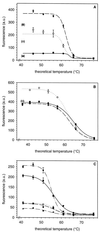
Target site inaccessibility represents a significant problem for fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) of 16S rRNA with oligonucleotide probes. Here, unlabeled oligonucleotides (helpers) that bind adjacent to the probe target site were evaluated for their potential to increase weak probe hybridization signals in Escherichia coli DSM 30083(T). The use of helpers enhanced the fluorescence signal of all six probes examined at least fourfold. In one case, the signal of probe Eco474 was increased 25-fold with the use of a single helper probe, H440-2. In another case, four unlabeled helpers raised the FISH signal of a formerly weak probe, Eco585, to the level of the brightest monolabeled oligonucleotide probes available for E. coli. The temperature of dissociation and the mismatch discrimination of probes were not significantly influenced by the addition of helpers. Therefore, using helpers should not cause labeling of additional nontarget organisms at a defined stringency of hybridization. However, the helper action is based on sequence-specific binding, and there is thus a potential for narrowing the target group which must be considered when designing helpers. We conclude that helpers can open inaccessible rRNA regions for FISH with oligonucleotide probes and will thereby further improve the applicability of this technique for in situ identification of microorganisms.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In situ accessibility of Escherichia coli 23S rRNA to fluorescently labeled oligonucleotide probes.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2001 Feb;67(2):961-8. doi: 10.1128/AEM.67.2.961-968.2001. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11157269 Free PMC article.
-
Enumeration of bacteria from the Clostridium leptum subgroup in human faecal microbiota using Clep1156 16S rRNA probe in combination with helper and competitor oligonucleotides.Syst Appl Microbiol. 2005 Jul;28(5):454-64. doi: 10.1016/j.syapm.2005.02.010. Syst Appl Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16094872
-
Flow cytometric analysis of the in situ accessibility of Escherichia coli 16S rRNA for fluorescently labeled oligonucleotide probes.Appl Environ Microbiol. 1998 Dec;64(12):4973-82. doi: 10.1128/AEM.64.12.4973-4982.1998. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1998. PMID: 9835591 Free PMC article.
-
Oligonucleotide probes for RNA-targeted fluorescence in situ hybridization.Adv Clin Chem. 2007;43:79-115. Adv Clin Chem. 2007. PMID: 17249381 Review.
-
Single Copy Oligonucleotide Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization Probe Design Platforms: Development, Application and Evaluation.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 1;22(13):7124. doi: 10.3390/ijms22137124. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34281175 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Making target sites in large structured RNAs accessible to RNA-cleaving DNAzymes through hybridization with synthetic DNA oligonucleotides.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Oct 14;52(18):11177-11187. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae778. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 39248110 Free PMC article.
-
Ligand cross-feeding resolves bacterial vitamin B12 auxotrophies.Nature. 2024 May;629(8013):886-892. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07396-y. Epub 2024 May 8. Nature. 2024. PMID: 38720071
-
The Improvement of Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization Technique Based on Explorations of Symbionts in Cicadas.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 31;24(21):15838. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115838. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958818 Free PMC article.
-
A ubiquitous gammaproteobacterial clade dominates expression of sulfur oxidation genes across the mesopelagic ocean.Nat Microbiol. 2023 Jun;8(6):1137-1148. doi: 10.1038/s41564-023-01374-2. Epub 2023 Apr 24. Nat Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37095175
-
A Study on Symbiotic Systems of Cicadas Provides New Insights into Distribution of Microbial Symbionts and Improves Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization Technique.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 26;24(3):2434. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032434. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768757 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ban N, Nissen P, Hansen J, Capel M, Moore P B, Steitz T A. Placement of protein and RNA structures into a 5 A-resolution map of the 50S ribosomal subunit. Nature. 1999;400:841–847. - PubMed
-
- Brosius J, Dull T J, Sleeter D D, Noller H F. Gene organization and primary structure of a ribosomal RNA operon from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1981;148:107–127. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

