NAIP interacts with hippocalcin and protects neurons against calcium-induced cell death through caspase-3-dependent and -independent pathways
- PMID: 10899114
- PMCID: PMC313967
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/19.14.3597
NAIP interacts with hippocalcin and protects neurons against calcium-induced cell death through caspase-3-dependent and -independent pathways
Abstract
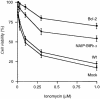
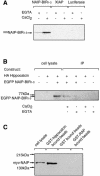
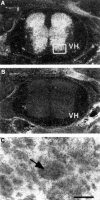
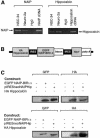
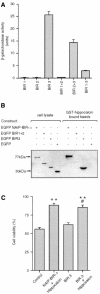
Inhibitor-of-apoptosis proteins (IAPs), including neuronal apoptosis inhibitory protein (NAIP), inhibit cell death. Other IAPs inhibit key caspase proteases which effect cell death, but the mechanism by which NAIP acts is unknown. Here we report that NAIP, through its third baculovirus inhibitory repeat domain (BIR3), binds the neuron-restricted calcium-binding protein, hippocalcin, in an interaction promoted by calcium. In neuronal cell lines NSC-34 and Neuro-2a, over-expression of the BIR domains of NAIP (NAIP-BIR1-3) counteracted the calcium-induced cell death induced by ionomycin and thapsigargin. This protective capacity was significantly enhanced when NAIP-BIR1-3 was co-expressed with hippocalcin. Over-expression of the BIR3 domain or hippocalcin alone did not substantially enhance cell survival, but co-expression greatly increased their protective effects. These data suggest synergy between NAIP and hippocalcin in facilitating neuronal survival against calcium-induced death stimuli mediated through the BIR3 domain. Analysis of caspase activity after thapsigargin treatment revealed that caspase-3 is activated in NSC-34, but not Neuro-2a, cells. Thus NAIP, in conjunction with hippocalcin, can protect neurons against calcium-induced cell death in caspase-3-activated and non-activated pathways.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Neuronal apoptosis inhibitory protein: Structural requirements for hippocalcin binding and effects on survival of NGF-dependent sympathetic neurons.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002 Nov 4;1600(1-2):138-47. doi: 10.1016/s1570-9639(02)00454-5. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002. PMID: 12445469
-
The neuronal apoptosis inhibitory protein is a direct inhibitor of caspases 3 and 7.J Neurosci. 2002 Mar 15;22(6):2035-43. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-06-02035.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 11896143 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocalcin protects against caspase-12-induced and age-dependent neuronal degeneration.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2005 Jan;28(1):85-95. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2004.08.015. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 15607944
-
Neuroprotection by the inhibition of apoptosis.Brain Pathol. 2000 Apr;10(2):283-92. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2000.tb00262.x. Brain Pathol. 2000. PMID: 10764048 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Involvement of caspase on apoptosis in ischemia-induced neuronal cell death: usefulness of caspase inhibitors for stroke therapy].Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 1999 Feb;113(2):97-111. doi: 10.1254/fpj.113.97. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 1999. PMID: 10205784 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Over-expression of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein modulates multiple aspects of neuronal Ca2+ signaling.Neurochem Res. 2013 Apr;38(4):847-56. doi: 10.1007/s11064-013-0989-0. Epub 2013 Feb 10. Neurochem Res. 2013. PMID: 23397285
-
Epigallocatechin gallate improves neuronal damage in animal model of ischemic stroke and glutamate-exposed neurons via modulation of hippocalcin expression.PLoS One. 2024 Mar 1;19(3):e0299042. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0299042. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38427657 Free PMC article.
-
Adenovirus E3-6.7K maintains calcium homeostasis and prevents apoptosis and arachidonic acid release.J Virol. 2002 Feb;76(4):1578-87. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.4.1578-1587.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 11799152 Free PMC article.
-
IAP suppression of apoptosis involves distinct mechanisms: the TAK1/JNK1 signaling cascade and caspase inhibition.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Mar;22(6):1754-66. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.6.1754-1766.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11865055 Free PMC article.
-
The visinin-like proteins VILIP-1 and VILIP-3 in Alzheimer's disease-old wine in new bottles.Front Mol Neurosci. 2012 Feb 23;5:20. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2012.00020. eCollection 2012 Jan 19. Front Mol Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22375104 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams J.M. and Cory,S. (1998) The Bcl-2 protein family: arbiters of cell survival. Science, 281, 1322–1326. - PubMed
-
- Adamus G., Machnicki,M., Elerding,H., Sugden,B., Blocker,Y.S. and Fox,D.A. (1998) Antibodies to recoverin induce apoptosis of photoreceptor and bipolar cells in vivo. J. Autoimmun., 11, 523–533. - PubMed
-
- Ambrosini G., Adida,C. and Altieri,D.C. (1997) A novel anti-apoptosis gene, survivin, expressed in cancer and lymphoma. Nature Med., 3, 917–921. - PubMed
-
- Aspenstrom P. and Olson,M.F. (1995) Yeast two-hybrid system to detect protein–protein interactions with Rho GTPases. Methods Enzymol., 256, 228–241. - PubMed
-
- Berridge M.J., Bootman,M.D. and Lipp,P. (1998) Calcium—a life and death signal. Nature, 395, 645–648. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

