Limited overlapping roles of P15(INK4b) and P18(INK4c) cell cycle inhibitors in proliferation and tumorigenesis
- PMID: 10880462
- PMCID: PMC313938
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/19.13.3496
Limited overlapping roles of P15(INK4b) and P18(INK4c) cell cycle inhibitors in proliferation and tumorigenesis
Abstract
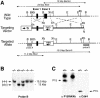
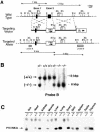
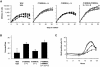
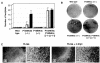
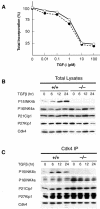
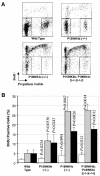
Entry of quiescent cells into the cell cycle is driven by the cyclin D-dependent kinases Cdk4 and Cdk6. These kinases are negatively regulated by the INK4 cell cycle inhibitors. We report the generation of mice defective in P15(INK4b) and P18(INK4c). Ablation of these genes, either alone or in combination, does not abrogate cell contact inhibition or senescence of mouse embryo fibroblasts in culture. However, loss of P15(INK4b), but not of P18(INK4c), confers proliferative advantage to these cells and makes them more sensitive to transformation by H-ras oncogenes. In vivo, ablation of P15(INK4b) and P18(INK4c) genes results in lymphoproliferative disorders and tumor formation. Mice lacking P18(INK4c) have deregulated epithelial cell growth leading to the formation of cysts, mostly in the cortical region of the kidneys and the mammary epithelium. Loss of both P15(INK4b) and P18(INK4c) does not result in significantly distinct phenotypic manifestations except for the appearance of cysts in additional tissues. These results indicate that P15(INK4b) and P18(IKN4c) are tumor suppressor proteins that act in different cellular lineages and/or pathways with limited compensatory roles.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tumor suppressor INK4: comparisons of conformational properties between p16(INK4A) and p18(INK4C).J Mol Biol. 1999 Nov 19;294(1):201-11. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1999.3231. J Mol Biol. 1999. PMID: 10556039
-
Suppression of tumorigenesis and induction of p15(ink4b) by Smad4/DPC4 in human pancreatic cancer cells.Clin Cancer Res. 2002 Nov;8(11):3628-38. Clin Cancer Res. 2002. PMID: 12429655
-
Consistent inactivation of p19(Arf) but not p15(Ink4b) in murine myeloid cells transformed in vivo by deregulated c-Myc.Oncogene. 2003 Mar 20;22(11):1600-10. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206268. Oncogene. 2003. PMID: 12642863
-
INK4 proteins, a family of mammalian CDK inhibitors with novel biological functions.IUBMB Life. 2007 Jul;59(7):419-26. doi: 10.1080/15216540701488358. IUBMB Life. 2007. PMID: 17654117 Review.
-
Role of the cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6 inhibitor gene family p15, p16, p18 and p19 in leukemia and lymphoma.Leuk Lymphoma. 1996 Nov;23(5-6):505-20. doi: 10.3109/10428199609054859. Leuk Lymphoma. 1996. PMID: 9031081 Review.
Cited by
-
Triptolide and its prodrug Minnelide target high-risk MYC-amplified medulloblastoma in preclinical models.J Clin Invest. 2024 Jun 17;134(15):e171136. doi: 10.1172/JCI171136. J Clin Invest. 2024. PMID: 38885332 Free PMC article.
-
CIP/KIP and INK4 families as hostages of oncogenic signaling.Cell Div. 2024 Apr 1;19(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s13008-024-00115-z. Cell Div. 2024. PMID: 38561743 Free PMC article. Review.
-
METTL3 promotes cellular senescence of colorectal cancer via modulation of CDKN2B transcription and mRNA stability.Oncogene. 2024 Mar;43(13):976-991. doi: 10.1038/s41388-024-02956-y. Epub 2024 Feb 15. Oncogene. 2024. PMID: 38361047
-
CRISPR/dCas9 DNA methylation editing is heritable during human hematopoiesis and shapes immune progeny.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Aug 22;120(34):e2300224120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2300224120. Epub 2023 Aug 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 37579157 Free PMC article.
-
Cell cycle regulators and bone: development and regeneration.Cell Biosci. 2023 Feb 21;13(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s13578-023-00988-7. Cell Biosci. 2023. PMID: 36810262 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Blain S.W., Montalvo,E. and Massagué,J. (1997) Differential interaction of the cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) inhibitor p27Kip1 with cyclin A–Cdk2 and cyclin D2–Cdk4. J. Biol. Chem., 272, 25863–25872. - PubMed
-
- Deng C., Zhang,P., Harper,J.W., Elledge,S.J. and Leder,P. (1995) Mice lacking p21CIP1/WAF1 undergo normal development, but are defective in G1 checkpoint control. Cell, 82, 675–684. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

