Tat modifies the activity of CDK9 to phosphorylate serine 5 of the RNA polymerase II carboxyl-terminal domain during human immunodeficiency virus type 1 transcription
- PMID: 10866664
- PMCID: PMC85957
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.20.14.5077-5086.2000
Tat modifies the activity of CDK9 to phosphorylate serine 5 of the RNA polymerase II carboxyl-terminal domain during human immunodeficiency virus type 1 transcription
Abstract
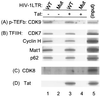
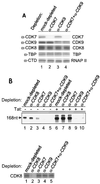
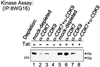
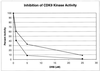
Tat stimulates human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) transcriptional elongation by recruitment of carboxyl-terminal domain (CTD) kinases to the HIV-1 promoter. Using an immobilized DNA template assay, we have analyzed the effect of Tat on kinase activity during the initiation and elongation phases of HIV-1 transcription. Our results demonstrate that cyclin-dependent kinase 7 (CDK7) (TFIIH) and CDK9 (P-TEFb) both associate with the HIV-1 preinitiation complex. Hyperphosphorylation of the RNA polymerase II (RNAP II) CTD in the HIV-1 preinitiation complex, in the absence of Tat, takes place at CTD serine 2 and serine 5. Analysis of preinitiation complexes formed in immunodepleted extracts suggests that CDK9 phosphorylates serine 2, while CDK7 phosphorylates serine 5. Remarkably, in the presence of Tat, the substrate specificity of CDK9 is altered, such that the kinase phosphorylates both serine 2 and serine 5. Tat-induced CTD phosphorylation by CDK9 is strongly inhibited by low concentrations of 5, 6-dichloro-1-beta-D-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole, an inhibitor of transcription elongation by RNAP II. Analysis of stalled transcription elongation complexes demonstrates that CDK7 is released from the transcription complex between positions +14 and +36, prior to the synthesis of transactivation response (TAR) RNA. In contrast, CDK9 stays associated with the complex through +79. Analysis of CTD phosphorylation indicates a biphasic modification pattern, one in the preinitiation complex and the other between +36 and +79. The second phase of CTD phosphorylation is Tat-dependent and TAR-dependent. These studies suggest that the ability of Tat to increase transcriptional elongation may be due to its ability to modify the substrate specificity of the CDK9 complex.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Direct evidence that HIV-1 Tat stimulates RNA polymerase II carboxyl-terminal domain hyperphosphorylation during transcriptional elongation.J Mol Biol. 1999 Jul 30;290(5):929-41. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1999.2933. J Mol Biol. 1999. PMID: 10438593
-
HIV-1 Tat-associated RNA polymerase C-terminal domain kinase, CDK2, phosphorylates CDK7 and stimulates Tat-mediated transcription.Biochem J. 2002 Jun 15;364(Pt 3):649-57. doi: 10.1042/BJ20011191. Biochem J. 2002. PMID: 12049628 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of the RNA polymerase II carboxyl-terminal domain by CDK9 is directly responsible for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Tat-activated transcriptional elongation.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Jul;22(13):4622-37. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.13.4622-4637.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12052871 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory functions of Cdk9 and of cyclin T1 in HIV tat transactivation pathway gene expression.J Cell Biochem. 1999 Dec 1;75(3):357-68. J Cell Biochem. 1999. PMID: 10536359 Review.
-
Tackling Tat.J Mol Biol. 1999 Oct 22;293(2):235-54. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1999.3060. J Mol Biol. 1999. PMID: 10550206 Review.
Cited by
-
Mutual information analysis reveals coevolving residues in Tat that compensate for two distinct functions in HIV-1 gene expression.J Biol Chem. 2012 Mar 9;287(11):7945-55. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.302653. Epub 2012 Jan 17. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22253435 Free PMC article.
-
Recruitment of P-TEFb (Cdk9-Pch1) to chromatin by the cap-methyl transferase Pcm1 in fission yeast.EMBO J. 2007 Mar 21;26(6):1552-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601627. Epub 2007 Mar 1. EMBO J. 2007. PMID: 17332744 Free PMC article.
-
Herpes simplex virus immediate-early protein ICP22 triggers loss of serine 2-phosphorylated RNA polymerase II.J Virol. 2007 May;81(10):5091-101. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00184-07. Epub 2007 Mar 7. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17344289 Free PMC article.
-
High-resolution localization of Drosophila Spt5 and Spt6 at heat shock genes in vivo: roles in promoter proximal pausing and transcription elongation.Genes Dev. 2000 Oct 15;14(20):2635-49. doi: 10.1101/gad.844200. Genes Dev. 2000. PMID: 11040217 Free PMC article.
-
Acetylated Tat regulates human immunodeficiency virus type 1 splicing through its interaction with the splicing regulator p32.J Virol. 2006 Apr;80(7):3189-204. doi: 10.1128/JVI.80.7.3189-3204.2006. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16537587 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
