In vivo induction of a high-avidity, high-frequency cytotoxic T-lymphocyte response is associated with antiviral protective immunity
- PMID: 10846055
- PMCID: PMC112070
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.74.13.5769-5775.2000
In vivo induction of a high-avidity, high-frequency cytotoxic T-lymphocyte response is associated with antiviral protective immunity
Abstract
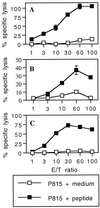
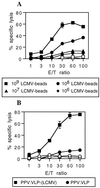
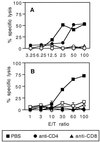
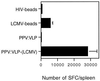
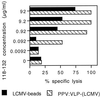
Many approaches are currently being developed to deliver exogenous antigen into the major histocompatibility complex class I-restricted antigen pathway, leading to in vivo priming of CD8(+) cytotoxic T cells. One attractive possibility consists of targeting the antigen to phagocytic or macropinocytic antigen-presenting cells. In this study, we demonstrate that strong CD8(+) class I-restricted cytotoxic responses are induced upon intraperitoneal immunization of mice with different peptides, characterized as CD8(+) T-cell epitopes, bound to 1-microm synthetic latex microspheres and injected in the absence of adjuvant. The cytotoxic response induced against a lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) peptide linked to these microspheres was compared to the cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL) response obtained upon immunization with the nonreplicative porcine parvovirus-like particles (PPV:VLP) carrying the same peptide (PPV:VLP-LCMV) previously described (C. Sedlik, M. F. Saron, J. Sarraseca, I. Casal, and C. Leclerc, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94:7503-7508, 1997). We show that the induction of specific CTL activity by peptides bound to microspheres requires CD4(+) T-cell help in contrast to the CTL response obtained with the peptide delivered by viral pseudoparticles. Furthermore, PPV:VLP are 100-fold more efficient than microspheres in generating a strong CTL response characterized by a high frequency of specific T cells of high avidity. Moreover, PPV:VLP-LCMV are able to protect mice against a lethal LCMV challenge whereas microspheres carrying the LCMV epitope fail to confer such protection. This study demonstrates the crucial involvement of the frequency and avidity of CTLs in conferring antiviral protective immunity and highlights the importance of considering these parameters when developing new vaccine strategies.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A protective cytotoxic T cell response to a subdominant epitope is influenced by the stability of the MHC class I/peptide complex and the overall spectrum of viral peptides generated within infected cells.Eur J Immunol. 1998 Oct;28(10):3301-11. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-4141(199810)28:10<3301::AID-IMMU3301>3.0.CO;2-Q. Eur J Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9808199
-
Molecularly engineered vaccine which expresses an immunodominant T-cell epitope induces cytotoxic T lymphocytes that confer protection from lethal virus infection.J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4311-6. doi: 10.1128/JVI.63.10.4311-4316.1989. J Virol. 1989. PMID: 2476571 Free PMC article.
-
Virus-specific, CD8+ major histocompatibility complex class I-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocytes in lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus-infected beta2-microglobulin-deficient mice.J Virol. 1997 Nov;71(11):8392-6. doi: 10.1128/JVI.71.11.8392-8396.1997. J Virol. 1997. PMID: 9343195 Free PMC article.
-
Dengue fever virus and Japanese encephalitis virus synthetic peptides, with motifs to fit HLA class I haplotypes prevalent in human populations in endemic regions, can be used for application to skin Langerhans cells to prime antiviral CD8+ cytotoxic T cells (CTLs)--a novel approach to the protection of humans.Virus Genes. 1994 Sep;9(1):33-45. doi: 10.1007/BF01703433. Virus Genes. 1994. PMID: 7871759 Review.
-
Hierarchies of antigen-specific cytotoxic T-cell responses.Immunol Rev. 1998 Aug;164:29-36. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1998.tb01205.x. Immunol Rev. 1998. PMID: 9795761 Review.
Cited by
-
High avidity cytotoxic T lymphocytes can be selected into the memory pool but they are exquisitely sensitive to functional impairment.PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e41112. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041112. Epub 2012 Jul 19. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22829916 Free PMC article.
-
Altered function in CD8+ T cells following paramyxovirus infection of the respiratory tract.J Virol. 2005 Mar;79(6):3339-49. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.6.3339-3349.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15731228 Free PMC article.
-
Epitope-specific TCRbeta repertoire diversity imparts no functional advantage on the CD8+ T cell response to cognate viral peptides.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Feb 12;105(6):2034-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0711682102. Epub 2008 Jan 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18238896 Free PMC article.
-
Citrullinated Epitopes Identified on Tumour MHC Class II by Peptide Elution Stimulate Both Regulatory and Th1 Responses and Require Careful Selection for Optimal Anti-Tumour Responses.Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 9;12:764462. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.764462. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34858415 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional correlates of enhanced antiviral immunity generated by heteroclitic CD8 T cell epitopes.J Immunol. 2014 Jun 1;192(11):5245-56. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1400111. Epub 2014 May 2. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24795457 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abraham R, Singh N, Mukhopadhyay A, Basu S K, Bal V, Rath S. Modulation of immunogenicity and antigenicity of proteins by maleylation to target scavenger receptors on macrophages. J Immunol. 1995;154:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Bennett S R, Carbone F R, Karamalis F, Flavell R A, Miller J F, Heath W R. Help for cytotoxic-T-cell responses is mediated by CD40 signalling. Nature. 1998;393:478–480. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

